Newly published findings from a Randomized Clinical Trial show that high doses of oral vitamin D reduced disease activity among patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Key Points
- A newly published study found positive benefits when evaluating the efficacy of high-dose cholecalciferol as monotherapy in reducing disease activity in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) typical forMS
- Participants were randomized to receive either 100,000 IU of oral cholecalciferol (n=163) or placebo (n=153) every 2 weeks for 24 months; the primary outcome was disease activity, defined as relapse occurrence and/or MRI evidence of new or contrast-enhancing lesions
- The study concluded that oral high-dose cholecalciferol reduced disease activity in clinically isolated syndrome and in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.

March 19, 2025, Practical Neurology – High-dose vitamin D (cholecalciferol) monotherapy significantly reduced disease activity in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) and early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) according to results of the D-Lay MS clinical trial (NCT01817166) published in JAMA. Conducted across 36 centers in France from 2013 to 2020, this study provides compelling evidence supporting vitamin D as a therapeutic option for CIS and early-stage RRMS.
The study enrolled 316 participants with untreated CIS aged 18 to 55 years, who were within 90 days of symptom onset and had serum vitamin D levels less than 100 nmol/L (40 ng/ml) and MRI findings consistent with multiple sclerosis. Following the 2017 update of the McDonald criteria, 247 of the participants met the diagnostic requirements for RRMS. Participants were randomized to receive either 100,000 IU of oral cholecalciferol (n=163) or placebo (n=153) every 2 weeks for 24 months. The primary outcome was disease activity, defined as relapse occurrence and/or MRI evidence of new or contrast-enhancing lesions.
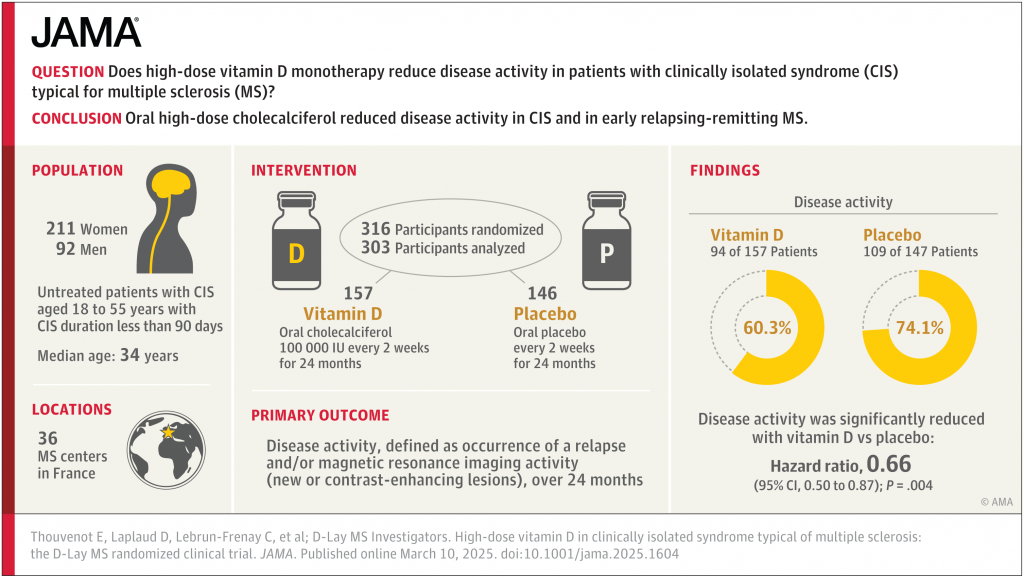
Results showed a significantly reduced incidence of disease activity among patients receiving vitamin D compared to placebo (60.3% vs. 74.1%; hazard ratio [HR], .66; P=.004), and median time to disease activity was notably longer in the vitamin D group (432 days vs. 224 days; P=.003). MRI outcomes also favored vitamin D treatment, with fewer new lesions (46.2% vs. 59.2%; HR, .61; P=.003) and fewer contrast-enhancing lesions (18.6% vs. 34%; HR, .47; P=.001). However, clinical secondary outcomes such as relapse rate and disability progression showed no significant differences between groups. Post-hoc analysis showed similar results for the RRMS group.
The findings suggest that high-dose vitamin D supplementation may be effective in reducing early inflammatory activity in people with CIS who are at high risk of developing MS, as well as in people with early-stage RRMS.
Given its favorable safety profile and low cost, vitamin D could represent an accessible therapeutic approach, particularly beneficial for patients with severe vitamin D deficiency or limited access to conventional disease-modifying therapies. Further research into its role as an adjunctive therapy is warranted.
Measure Your Vitamin D Level Today
Create your custom home blood spot kit to help determine if you are getting enough of the following nutrients shown to benefit overall health, along with other measures, including:
 Vitamin D
Vitamin D- Omega-3 Index plus Omega-3:Omega-6 and AA:EPA Ratios
- Magnesium (plus Zinc, Copper, Selenium, Lead, Cadmium & Mercury)
- hsCRP
- HbA1c
- Type 1 Diabetes Autoantibodies
- TSH
Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of omega-3s, vitamin D and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.

 Vitamin D
Vitamin D