Join D*actionLower Disease Incidence with Vitamin D levels 40-60 ng/ml
Scientists have found that most of the world is vitamin D deficient.
GrassrootsHealth’s International Panel of Scientists recommend a vitamin D serum level in the range of 40-60 ng/ml for good general health. The average person, however, has a vitamin D serum level around 25 ng/ml. In today’s world it takes effort to get within the recommended range because most people are predominantly inside; use sunscreen when outdoors; rely on multi-vitamins with low dosage; and do not get enough from food.
Why is the RDA too low? Why is milk not enough?
GrassrootsHealth and others have argued that the US RDA is too low due to an error made by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) in their analysis of the scientific data when they adjusted the RDA in 2010.
Petition for Change
Currently there is a petition to encourage the IOM and Health Canada to review the guidelines based on a paper describing the error. When talking to your doctor do not be surprised if they think 20 ng/ml is enough, or if they discourage you from taking over 2000 IU/day of vitamin D supplementation.
 Rickets and Vitamin D
Rickets and Vitamin D
The US began a voluntary fortification program to add vitamin D to milk in the 1930s in an effort to combat rickets. Rickets is a disease caused by a lack of sunlight (vitamin D) which leads to softening and weakening of developing bones in young children. It was prevalent in the early 1900s as people moved from farms to the cities and got less and less sunlight. Children with vitamin D levels less than 20 ng/ml are at risk for rickets. The fortification program worked and rickets virtually disappeared! Despite the fact that a vitamin D level of 20 ng/ml is enough to prevent rickets in children, it is not enough to support overall good health throughout our lifetime.
Why do I need more?
To understand why the amount necessary to prevent rickets is not enough for overall good health, it is helpful to understand more about vitamin D and how it affects your body. Vitamin D is actually a hormone that affects over 3000 cell processes within your body. Without enough vitamin D circulating regularly in your blood, your body simply does not function as it was intended (ridding the body of intruders, fighting disease, repairing cells).
D-Lightful Vitamin D: Bone and Muscle Health and Prevention of Autoimmune and Chronic Diseases
Michael F. Holick, PhD, MD
This 1-hour presentation is a great introduction to how vitamin D affects your body’s systems.
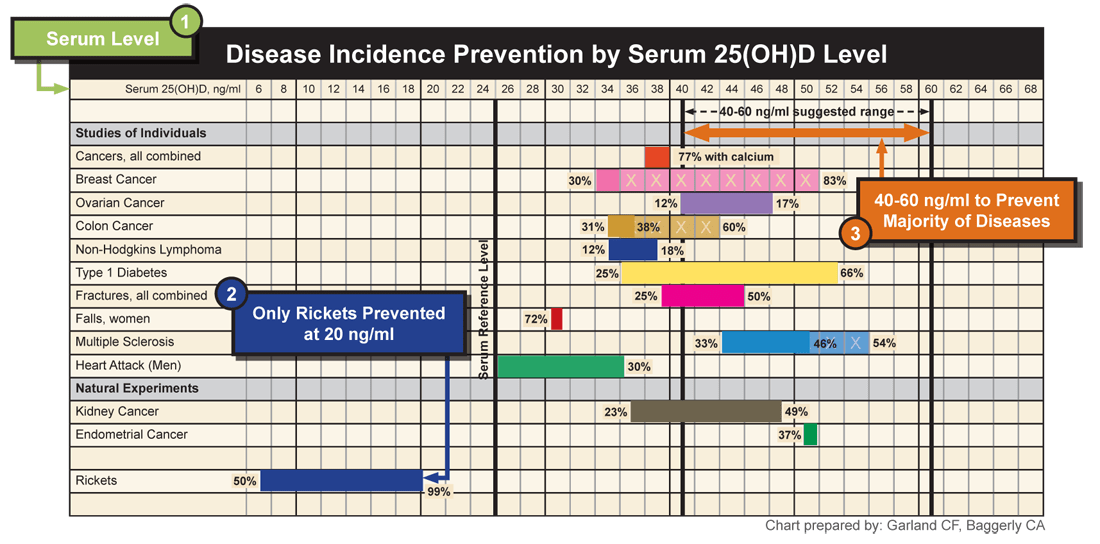
Around the 1960s scientists started doing studies on vitamin D and disease prevention. While these studies are not as prolific as the studies on bone health, there are many that have found that vitamin D serum levels well above 20 ng/ml, in the range of 40-60 ng/ml, are necessary to prevent a number of diseases and cancers. Some of these studies have been randomized control trials (RCTs) and others have been epidemiological studies (looking at trends to determine cause and effect).
GrassrootsHealth put together these chart to show how Vitamin D can Prevent Disease.
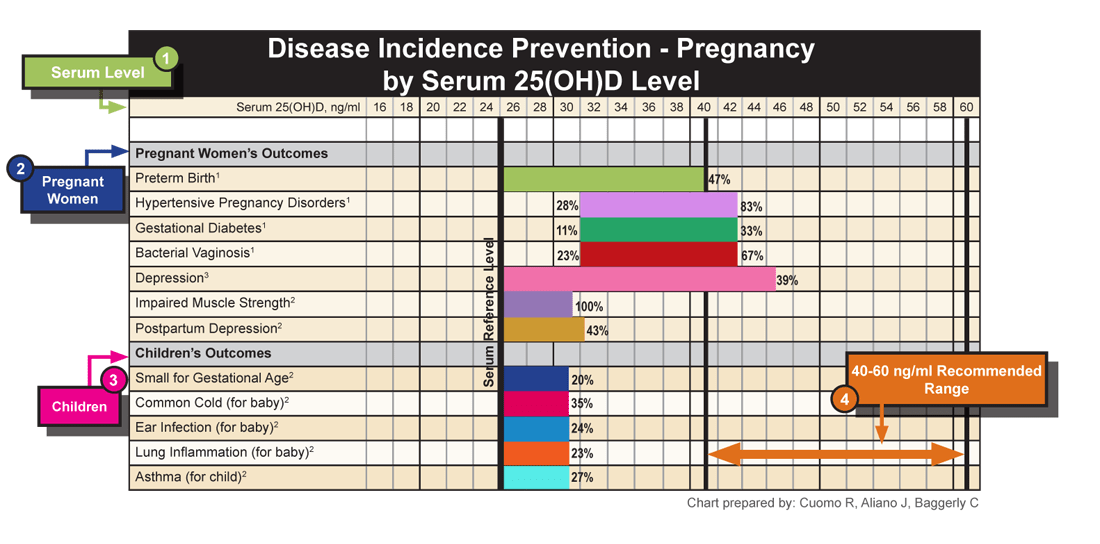
In the past ten years, there has been some research that showed how beneficial vitamin D supplementation is with pregnant women. Please see above Disease Incidence Prevention Chart for Pregnancy.
I have a specific condition, can vitamin D help me?
GrassrootsHealth, working with 48 leading vitamin D scientists, has amassed many videos (from conferences, webinars and interviews) that can explain in more detail how vitamin D can prevent a certain disease. Please consult this list for the video that might be pertinent to you or your family.
Cancer
Possible 75% less cancer deaths with vitamin D
Results of Prostate Cancer/Vitamin D trial
Vitamin D and sunlight for cancer prevention
Cancer risk factors
Vitamin D and breast cancer
Alzheimer’s
Vitamin D and Alzeimer’s Prevention
Pregnancy
Meeting the vitamin D needs of pregnant women
Vitamin D requirements for breast feeding mothers
Vitamin D and pregnancy
Diabetes
Prevention of type 1 diabetes with vitamin D and sunshine
Diabetes and vitamin D
Colds and Flus
Vitamin D and the Immune System
Upper Respiratory Infections 1
Upper Respiratory Infections 2
Cystic Fibrosis
Vitamin D and Cystic Fibrosis
Autism
Vitamin D and Autism
OK, I’m convinced. Now what do I do?
 The first thing to do is test your vitamin D level.
The first thing to do is test your vitamin D level.
You may check with your doctor for a test or join D*action. With D*action you will be asked to pay for the test and complete an online questionnaire to enroll in our study. Then you will receive a card and instructions in the mail. You will prick your finger and put blood on this card and return it to us. A couple of weeks later you will receive a link via email to view your vitamin D serum level.
Stay on track.
We recommend you test your blood level every 6 months, especially when you are new – as you will most likely be changing your habits and/or diet to achieve a higher serum level. Doing this through D*action will help provide us with more data and help fund vitamin D research and education.


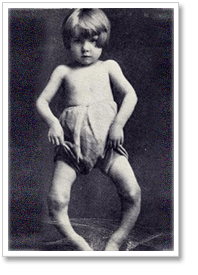 Rickets and Vitamin D
Rickets and Vitamin D