Published on May 21, 2020
In a previous post, we analyzed data from the GrassrootsHealth cohort to show that participants who did not supplement with vitamin D could reach the recommended level of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L) with the regular use of indoor tanning. What are the sources of indoor UV that people could use when the sunshine is not available or practical? With vitamin D as a focus, the following represents the summary of effectiveness of artificial lights to help the body take the same wave lengths we get from the sun, to generate the same beneficial effects in the body. Note that alternative sources need the same kind of usage guidelines as does the sun to be most effective and safe – give your skin time to acclimate and be mindful not to burn.
Different Types of Indoor UV Give Different Results
When considering using a source of artificial UV light, it is important to be aware of the type of UV, its safety, and the physiological effects it may produce, especially in terms of vitamin D.
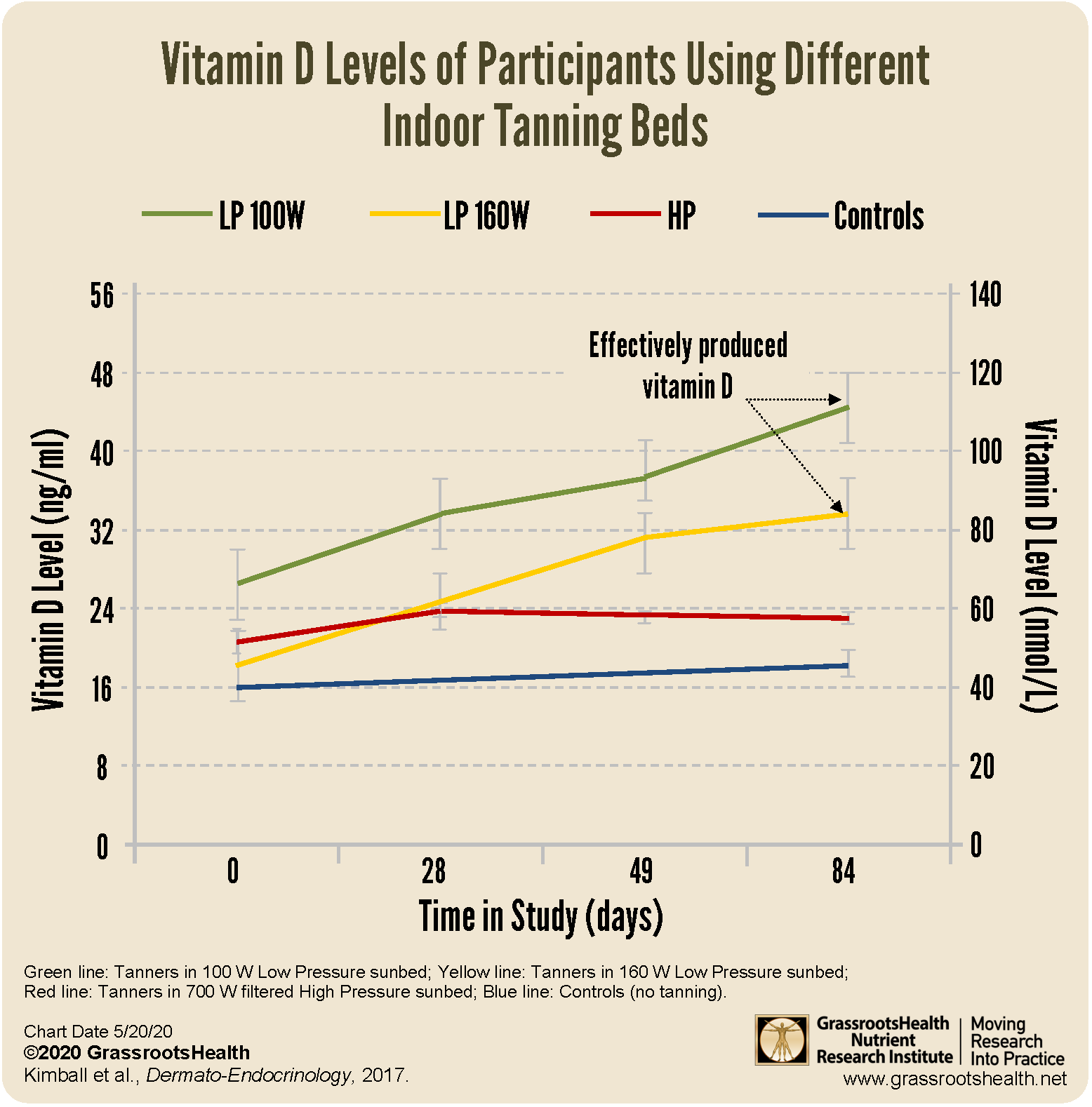
A study by Kimball et al. (2017) on sunbeds and vitamin D in Canada found that individuals following standard sunbed tanning protocols in a typical tanning salon can achieve physiological levels of vitamin D when the sunbed emits UVB light in the range equivalent to outdoor summer sunshine, which most sunbed lamps do. More than 75% of all four study groups were considered vitamin D deficient (<30 ng/mL, or <75 nmol/L) at the start of the study, in the wintertime. As shown in the chart above, vitamin D levels increased by an average of 17 ng/ml (42 nmol/L) in participants using sunbeds that used 100W and 160W fluorescent bulbs with 2.2% and 4.2% UVB. Vitamin D levels continued to increase after a base tan was achieved, all the way to the end of the 12-week study, with no adverse events or skin burns reported. This study supports the use of artificially derived UVB light to raise serum vitamin D levels when the UV index of the sun is low, especially in the winter months of northern countries.
A practical use of sunbeds for increasing vitamin D levels
During the winter months at latitudes above ∼35°, there is minimal, if any, vitamin D3 production in the skin. This leads many individuals to rely on supplementation to maintain their target vitamin D levels. However, for some individuals supplementation may not always be the most effective way to get vitamin D, especially for individuals with digestive conditions or on certain medications that may inhibit absorption.
 Another study to address using indoor UV sources to produce vitamin D was run by Dr. Michael Holick. Using The Fitzpatrick classification of skin phototype to classify skin type, Dr. Holick found that healthy adults with skin type 2 (fair, burns easily) and skin type 3 (darker white skin, tans after initial burn) experienced dramatic improvement in vitamin D status after exposure to UVB radiation in a commercial tanning bed. Exposure to one minimal erythemal dose (MED) of UVB, the amount of UV radiation that will produce minimal redness or sunburn, is roughly equivalent to ingesting between 10,000 and 25,000 IU of vitamin D2. Fifteen healthy adult study participants were exposed to 0.75 MED three times a week. After 1 week, vitamin D levels had risen by 50% and continued to rise over 5 weeks to approximately 150%. After 5 weeks, vitamin D levels plateaued and were sustained until week 7.
Another study to address using indoor UV sources to produce vitamin D was run by Dr. Michael Holick. Using The Fitzpatrick classification of skin phototype to classify skin type, Dr. Holick found that healthy adults with skin type 2 (fair, burns easily) and skin type 3 (darker white skin, tans after initial burn) experienced dramatic improvement in vitamin D status after exposure to UVB radiation in a commercial tanning bed. Exposure to one minimal erythemal dose (MED) of UVB, the amount of UV radiation that will produce minimal redness or sunburn, is roughly equivalent to ingesting between 10,000 and 25,000 IU of vitamin D2. Fifteen healthy adult study participants were exposed to 0.75 MED three times a week. After 1 week, vitamin D levels had risen by 50% and continued to rise over 5 weeks to approximately 150%. After 5 weeks, vitamin D levels plateaued and were sustained until week 7.
Dr. Holick concludes that exposure to lamps that produce UVB radiation are an excellent source for producing vitamin D3 in the skin. This can be especially effective in patients with fat malabsorption syndromes or other digestive issues or health conditions that may prevent them from getting the amount of vitamin D they need from supplements alone.
Guidelines for safe use of sunbeds from Health Canada
If considering using indoor tanning options, such as sunbeds, do your research and be sure to follow safety guidelines, such as those set by Health Canada.
- Look for, read, and follow the warning and technical labels on the equipment. Labels tell you the recommended time you should be exposed each session (the time will vary, in part, depending on your skin type).
- Talk to the salon operator about your skin’s sensitivity and your ability to tan.
- Do not go over the recommended time in a tanning session for your skin type.
- Do not use tanning lamps more often than is prescribed for your particular skin type.
- Always wear the safety eyewear that is recommended for the type of lamp you are using.
- Allow at least 48 hours between each tanning session. This will give your skin a chance to repair some of the damage from the UV rays and may slow down the aging effects caused by the exposure.
- Report any side effects (like sunburn or itchiness) to the salon operator. In cases of severe sunburn, see your health care provider.
Are there other indoor UV options available?
Indoor sun and UVB lamps and bulbs are also available and effective at helping to boost vitamin D production in the skin. Be mindful that some of these lamps may only offer UVB and no UVA exposure, so vitamin D may be produced with exposure, but not nitric oxide, and the full benefits of sunshine may not be achieved.
Practicing safe sun exposure is a natural way to increase your vitamin D levels. As reviewed above, studies have shown that you can also reach recommended vitamin D levels (>40 ng/mL) using sunbeds containing UVB and following time exposure guidelines for your skin type without adverse events.
The need to make up for our sunshine deficit, beyond vitamin D deficiency, is certainly there! Which option will you choose?
Do You Have Enough Vitamin D to Support a Healthy Immune System?
We’re in a time of great crisis that could be greatly affected by making sure you and everyone you know has a serum level of at least 40 ng/ml. Help us help you.
Do you know what your vitamin D level is? Be sure to test today to find out, and take steps to keep it within a target of 40-60 ng/ml or 100-150 nmol/L! Give your immune system the nutrients it needs to support a healthy you and protect yourself from unnecessary diseases.
GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute is preparing to do a Community RCT with the use of our myData-myAnswers nutrient health system that over 15,000 people are already using for their health. We will demonstrate how one can use the Nutrient Research Model established by Dr. Robert Heaney to establish the effect of vitamin D serum levels of at least 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L) on risk reduction with different ethnicities in the population. Please let us know if you’re interested in helping sponsor this project.
Through GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute, you can also test your essential elements magnesium, copper, zinc and selenium, toxins such as lead, mercury and cadmium, as well as your omega-3 levels, inflammation levels and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level. Find out your levels today! Log on to the test selection page (click the link below) to get your tests and see for yourself if your levels can be improved.
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
Click Here to Access the Test Page
How can I track my nutrient intake and levels over time?
To help you track your supplement use and nutrient levels, GrassrootsHealth has created the Personal Health Nutrient Decision System called
For each specific supplement, you can track what days you take it, how much, and many other details. This will help you know your true supplemental intake and what patterns of use work for you to reach and maintain optimum nutrient levels. Check it out today!