Published on May 11, 2021
Study finds natural sunlight may rapidly inactivate SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces and be used as an effective disinfectant
 Past research has shown that the survival of several viruses, including the influenza and SARS-CoV-1 virus, is dependent on factors such as temperature, humidity, sunlight, and the matrix in which the virus is suspended (such as saliva). In our last post, we discussed a review by Gorman and Weller suggesting that UV exposure may reduce viability of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, its rates of infection and replication, as well as disease severity, and that these effects are due to different wavelengths of light from sunshine. Their paper describes the anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, and cardiometabolic benefits offered by UV light within the body specifically, due in part to the release of vitamin D upon exposure to UVB and nitric oxide upon exposure to UVA.
Past research has shown that the survival of several viruses, including the influenza and SARS-CoV-1 virus, is dependent on factors such as temperature, humidity, sunlight, and the matrix in which the virus is suspended (such as saliva). In our last post, we discussed a review by Gorman and Weller suggesting that UV exposure may reduce viability of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, its rates of infection and replication, as well as disease severity, and that these effects are due to different wavelengths of light from sunshine. Their paper describes the anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, and cardiometabolic benefits offered by UV light within the body specifically, due in part to the release of vitamin D upon exposure to UVB and nitric oxide upon exposure to UVA.
Another study by Cherrie et al. investigated the association between UVA exposure and death due to COVID-19 in particular areas of the United States, England and Italy, and found a predicted decrease in average risk of death by one-third to one-half from the lowest level of UVA to the highest level in each country.
Could Sunshine Deactivate Viruses and Help Stop Transmission?
The above mentioned posts focused mostly on the correlation between sunshine and/or UV exposure and COVID-19 disease outcomes among those who were already infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Could sunshine help prevent the spread of viral infection before infection happens?
A study by Schuit et al. (2019) showed the impact of simulated sunlight on aerosol transmission of the influenza virus, demonstrating an inverse relationship between simulated sunlight intensity and transmission of the influenza virus over long distances, regardless of humidity. This experimental study demonstrated nearly 100% viral decay after only 8 minutes of exposure to simulated sunlight, with a decay rate (of influenza virus) 13-times higher for sunlight compared to darkness.
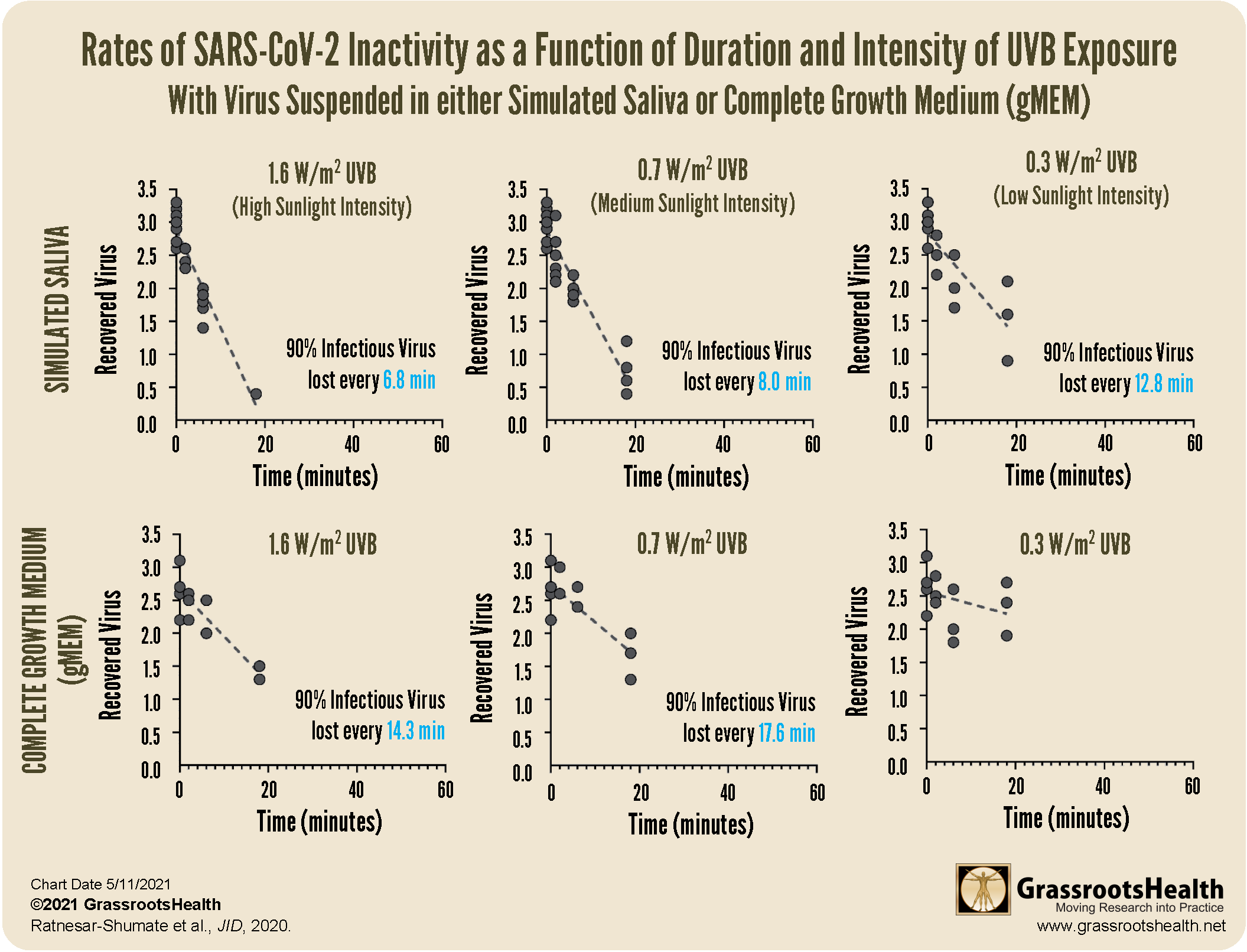
Another study by Ratnesar-Shumate et al., examined the effect of simulated sunlight on the activity of SARS-CoV-2 virus in either a simulated saliva or complete growth medium (gMEM). The researchers built a custom solar simulator that produced light in the ultraviolet (UV) range of 280-400 nm to best match natural sunlight, a range that contains both UVA and UVB wavelengths. Light intensity was controlled and adjusted to three different levels to imitate different times of day and year, with a UVB irradiance of 1.6 W/m2 (high sunlight intensity), 0.7 W/m2 (medium sunlight intensity), and 0.3 W/m2 (low sunlight intensity).
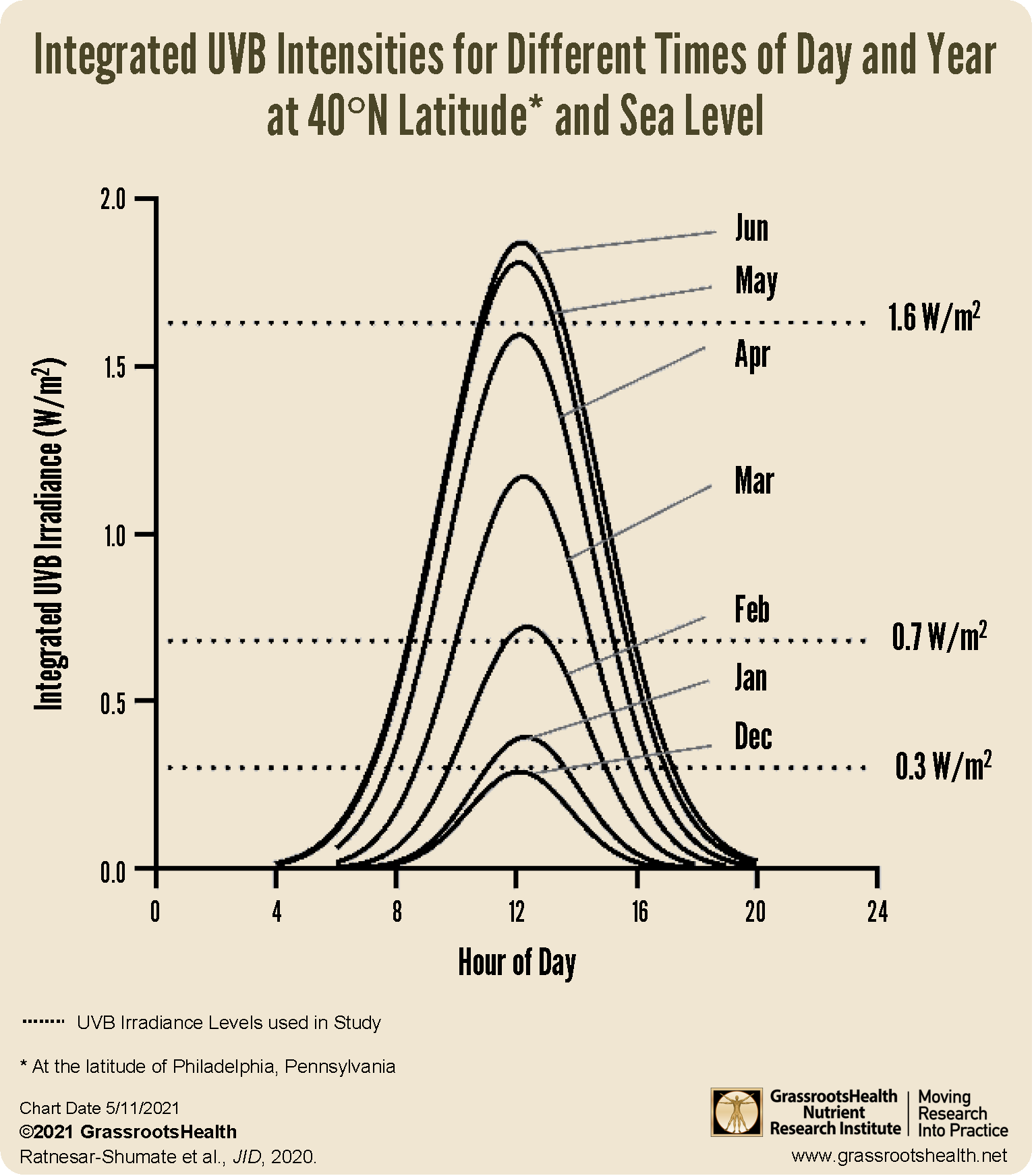
The chart below illustrates the estimated varying levels of UVB available throughout the day, depending on the month, at a location 40 degrees N latitude (the level of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania). The horizontal dotted lines represent the three levels of intensity simulated in this study.
Temperature and relative humidity were controlled for and monitored continuously. The virus was added to either a simulated saliva solution or gMEM cell culture before being placed on a stainless steel surface, and allowed to dry for 30 minutes. The drying period led to a small decrease in the viral concentration when suspended in gMEM, which did not occur with the simulated saliva solution. Both were then exposed to the simulated sunlight for durations ranging from 2 to 18 minutes. The initial concentration of SARS-CoV-2 was 1:10, and viral concentrations were measured after each duration of exposure.
Simulated Sunlight had a Significant Effect on SARS-CoV-2 Viral Activity
Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 is charted as a function of UVB irradiance in the charts below. The rate of inactivation at any level of UVB irradiance was significantly faster when compared to the rate of inactivation in darkness (P<0.0001) – in fact, darkness had no significant effect on viral activity over the duration times studied, at a max of 60 minutes.
Overall, the study found that the inactivation rate of the virus was significantly associated with the amount of UVB irradiance and the suspension matrix. Compared to the lowest intensity UVB, the inactivation rate of the virus was much faster at the medium and high UVB levels. Based on analysis, ninety percent of the infectious virus would have been lost every 6.8, 8.0, and 12.8 minutes for high, medium, and low levels of UVB irradiance when in saliva, and 14.3 and 17.6 minutes for high and medium UVB irradiance when in the gMEM matrix. The viral inactivation rate was greater in the simulated saliva compared to the gMEM at all levels of UVB irradiance.
More Than UVB at Play?
A correspondence by Luzzatto-Fegiz et al. addresses several hypotheses on the mechanisms of sunlight on viral inactivation, and mentions that more must be at play than UVB exposure alone. As demonstrated by Cherrie et al, UVA exposure was shown to decrease the mortality rate of COVID-19 in a dose-dependent manner, and the review by Gorman and Weller mentioned the possibility of other wavelengths of sunlight also playing a role. These observations indicate that sunlight from a broader range of latitudes and daytimes may also help to deactivate the virus and reduce its spread.
Overall, these studies provide evidence that sunlight may not only help reduce the risk of severe viral infections, but it may also be an effective disinfectant for SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses.
Are You Relying on Sunshine for Your Vitamin D? Make Sure You Are Getting Enough
With almost 90% of the general population having vitamin D levels below the recommended 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L), it is obvious that most people need more vitamin D. While most of us cannot achieve a vitamin D level of 40-60 ng/ml from sun alone, either due to our lifestyle, where we live, or other circumstances, we can certainly reach those levels with the right amount of supplementation.
Below is a guide for how much you might need, and who may need more. Your levels can be tested safely at home – order your home test kit today.
By joining the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to our study, but you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it. Do you know what your status of vitamin D, omega-3s, and other essential nutrients is? Could your levels be improved? Test now to find out!
 We now have a NEW GIFTING SERVICE that allows you to quickly send ‘Gift Cards’ to friends, family and coworkers who you consider might need immediate access to testing, and to Claim the Joy of Your Health TODAY. Give the gift today!
We now have a NEW GIFTING SERVICE that allows you to quickly send ‘Gift Cards’ to friends, family and coworkers who you consider might need immediate access to testing, and to Claim the Joy of Your Health TODAY. Give the gift today!
What does the Research Say about Vitamin D & COVID-19?
It’s TIME to start saving lives! If you can help PREVENT the majority of the death, it’s time! What’s it costing you/us not to take action NOW?
There is much published research that supports a clear link between vitamin D and COVID-19 showing that higher vitamin D levels are related to:
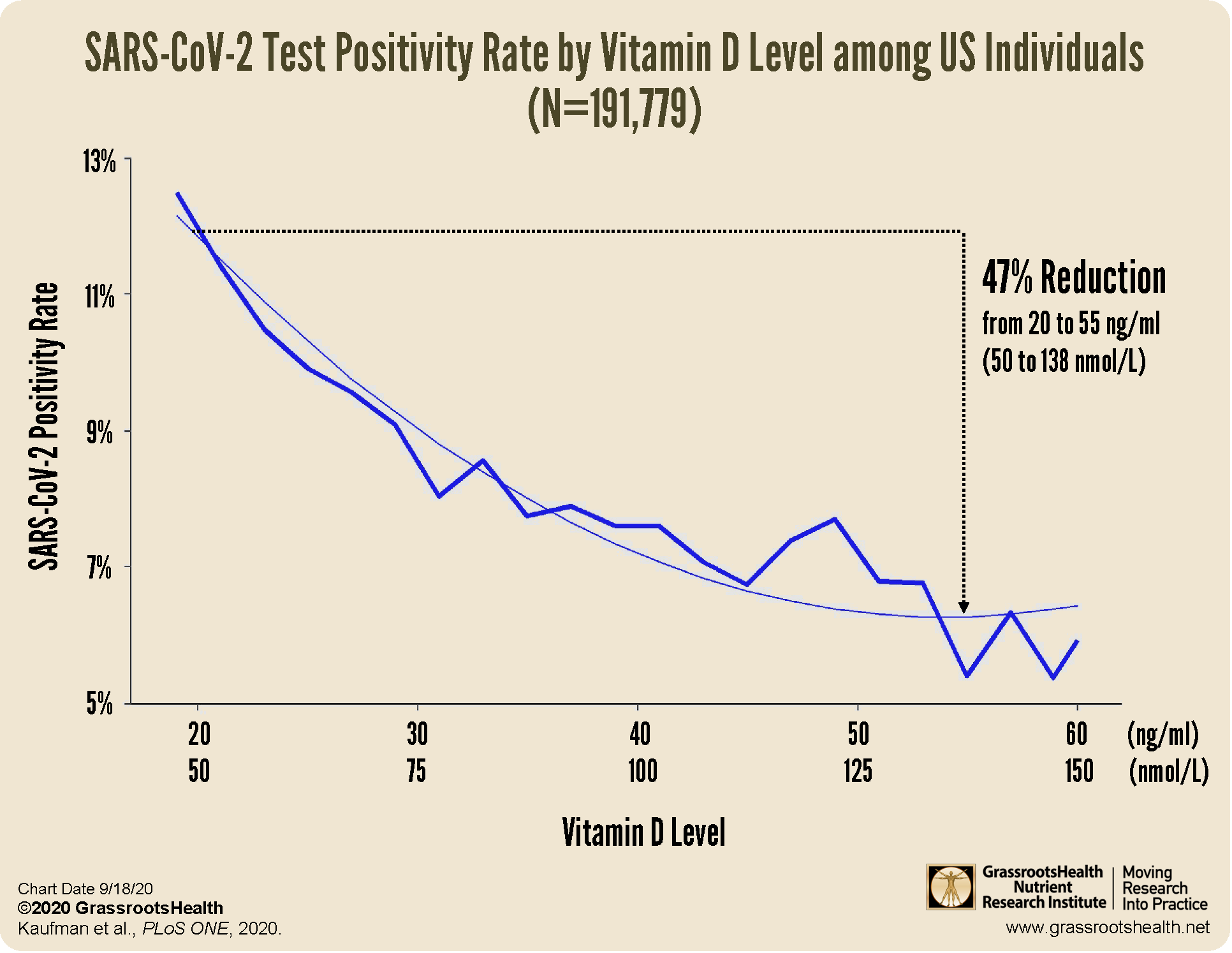
a decreased risk of testing positive for COVID-19
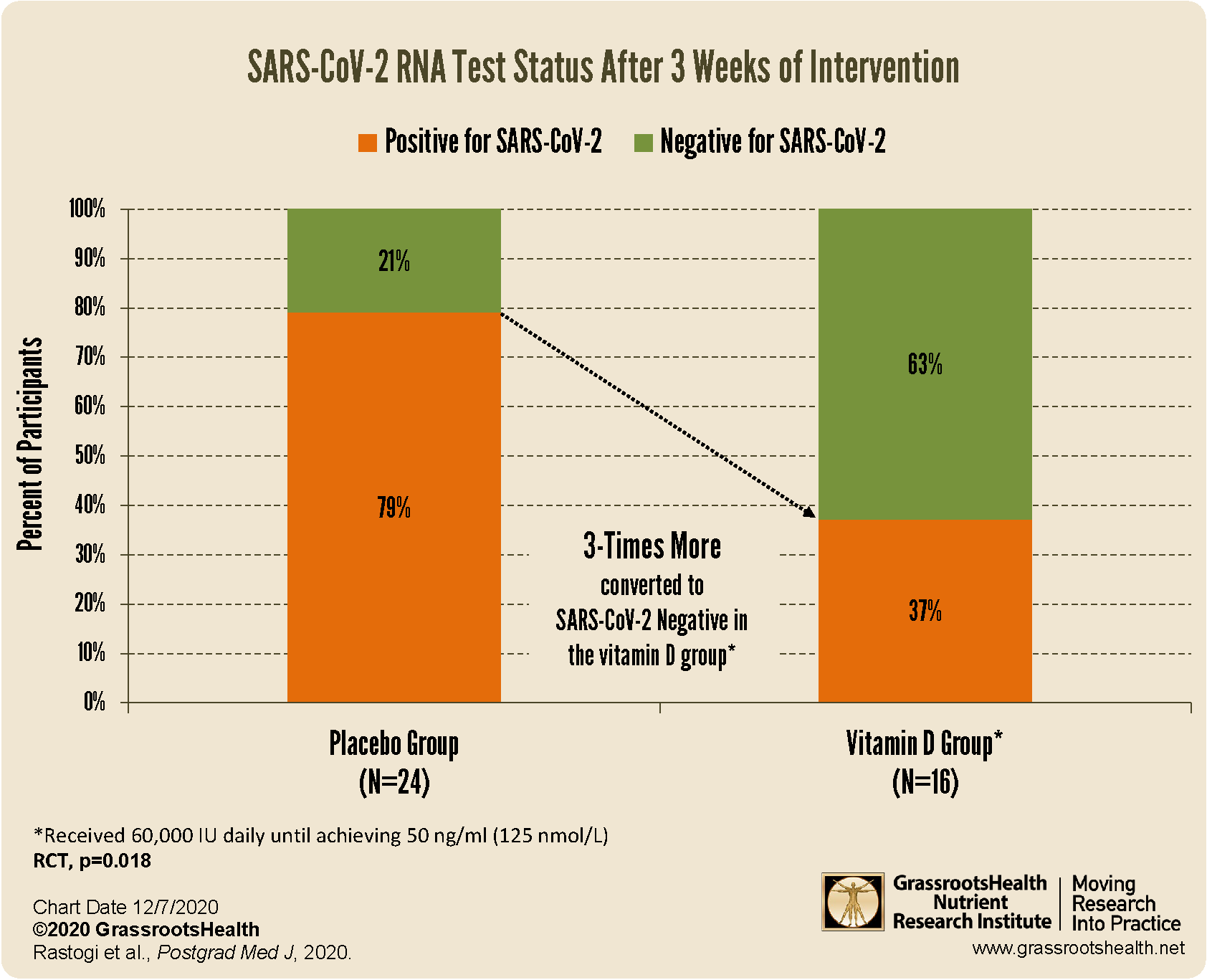 increased viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance
increased viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance
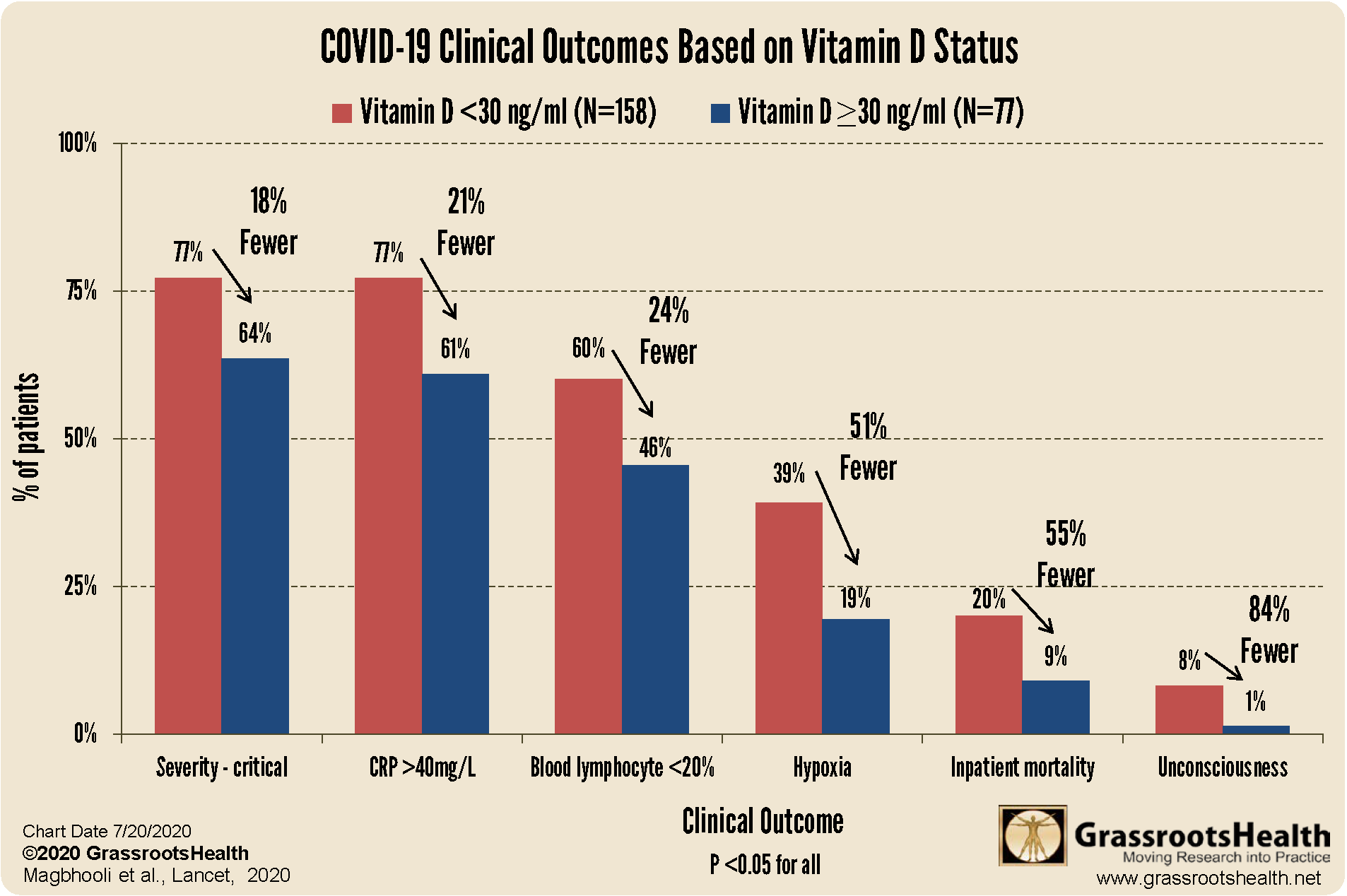
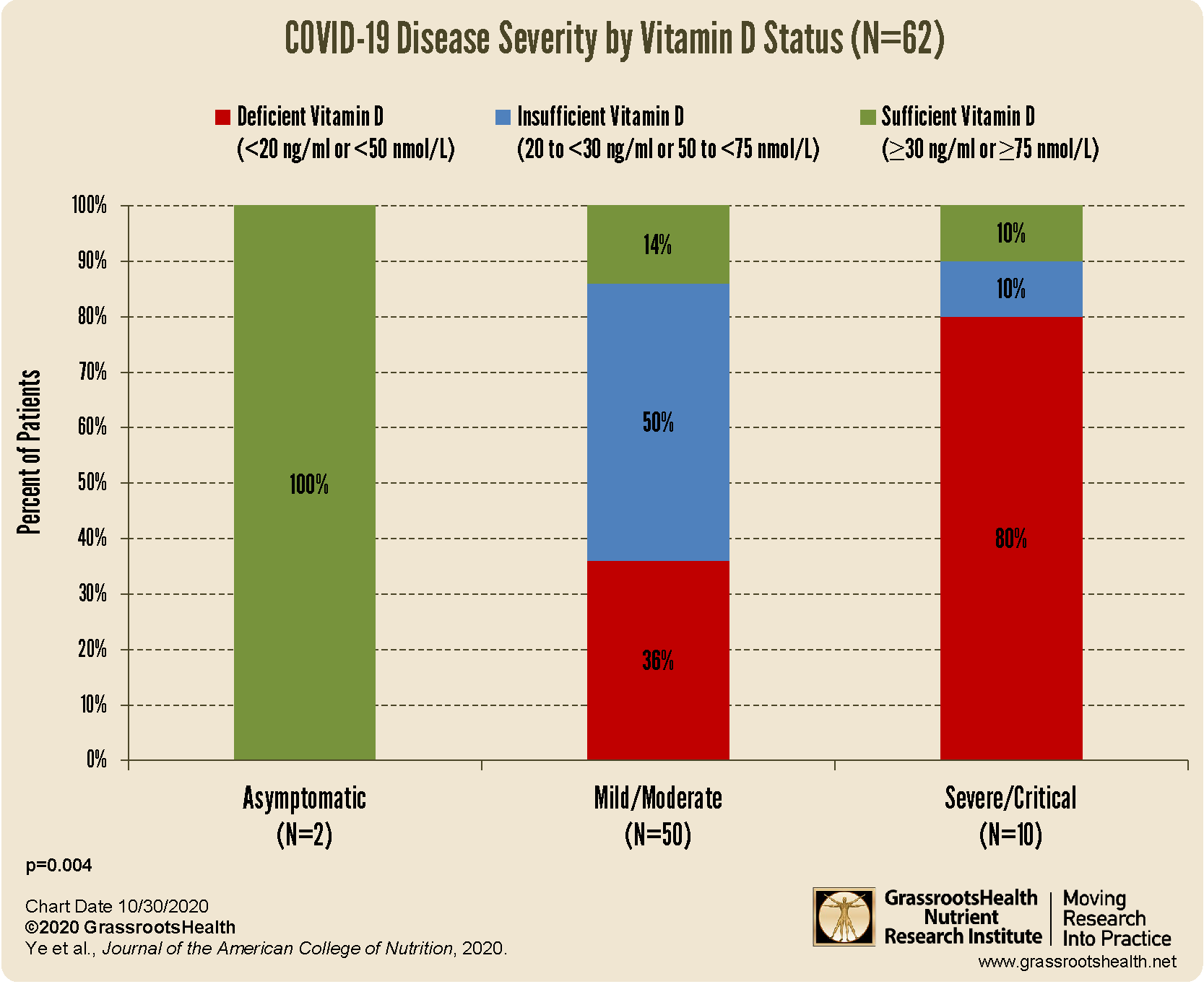
better clinical outcomes among patients with COVID-19
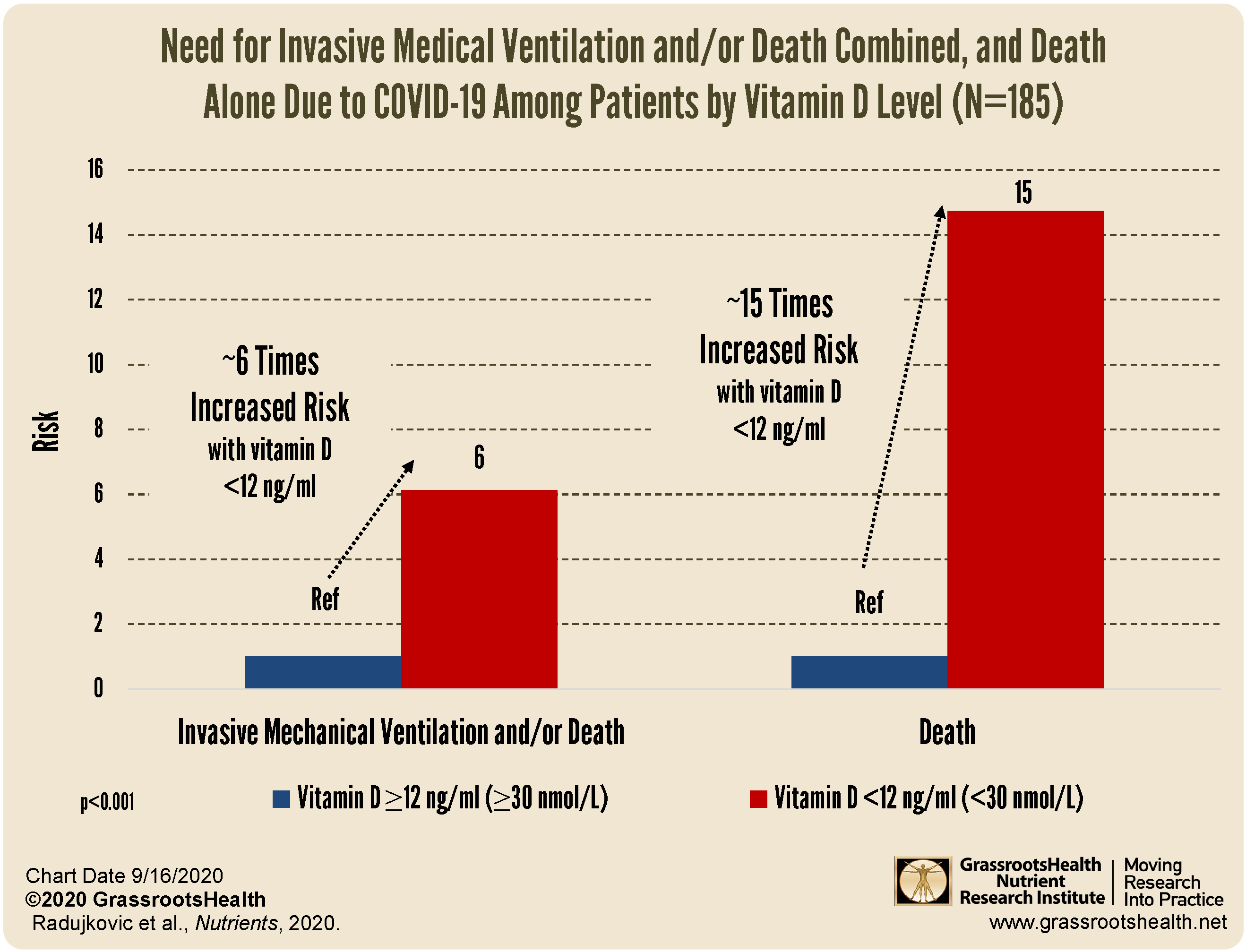
decreased risk of death due to COVID-19
Be sure to educate yourself on the benefits and importance of vitamin D for immune health, and take steps to ensure you and your loved ones are getting enough.
You can review all of the COVID-19 and immune health information we have shared on this page.