Published on May 28, 2019
The GrassrootsHealth panel of expert scientists’ recommended range of vitamin D levels for general health is 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L). This is based on overwhelming evidence about the association between vitamin D and many diseases including bone diseases (rickets, osteomalacia, and osteoporosis), multiple sclerosis, diabetes, cancer, and many others. This optimal range is comparable to levels occurring naturally among groups of people with consistent sun exposure.
Vitamin D status among groups with high sun exposure
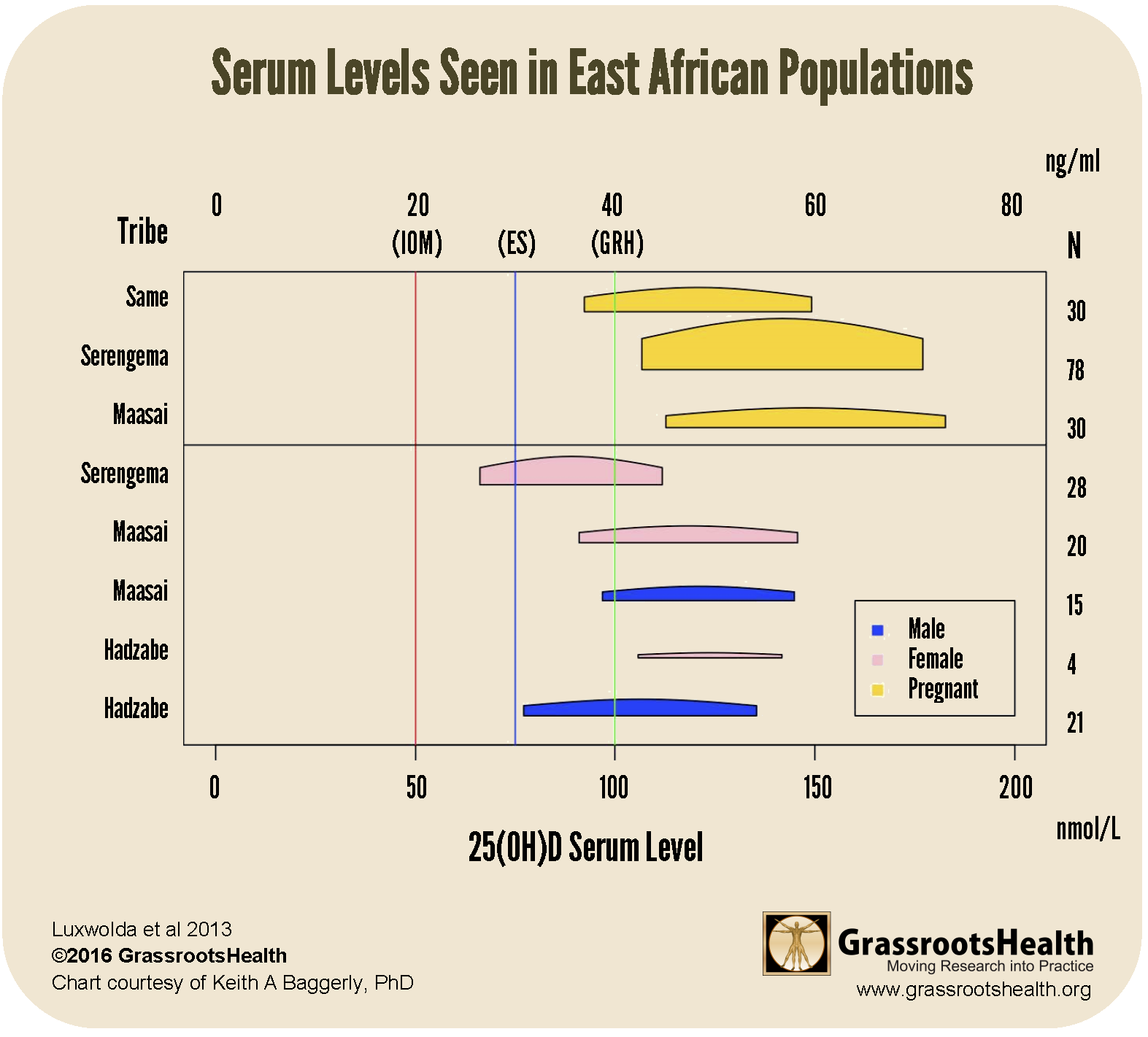
Based on evidence that humans originated in East Africa, Martine Luxwolda and Remko Kuipers, two Dutch researchers, assessed the vitamin D levels among 60 traditionally living Africans to determine the optimal vitamin D status from an evolutionary perspective. They found that the average vitamin D level from members of two ethnic groups was 46 ng/ml (115 nmol/L) and that 72% had levels of 40 ng/ml or higher. In a second study, these researchers assessed vitamin D levels among 449 traditionally living Africans from five ethnic groups. Similar to their first study, they found that the average vitamin D level was 43 ng/ml (107 nmol/L) in non-pregnant adults and 56 ng/ml (139 nmol/L) in pregnant women as shown in the chart below.
Click here for more information about these studies.
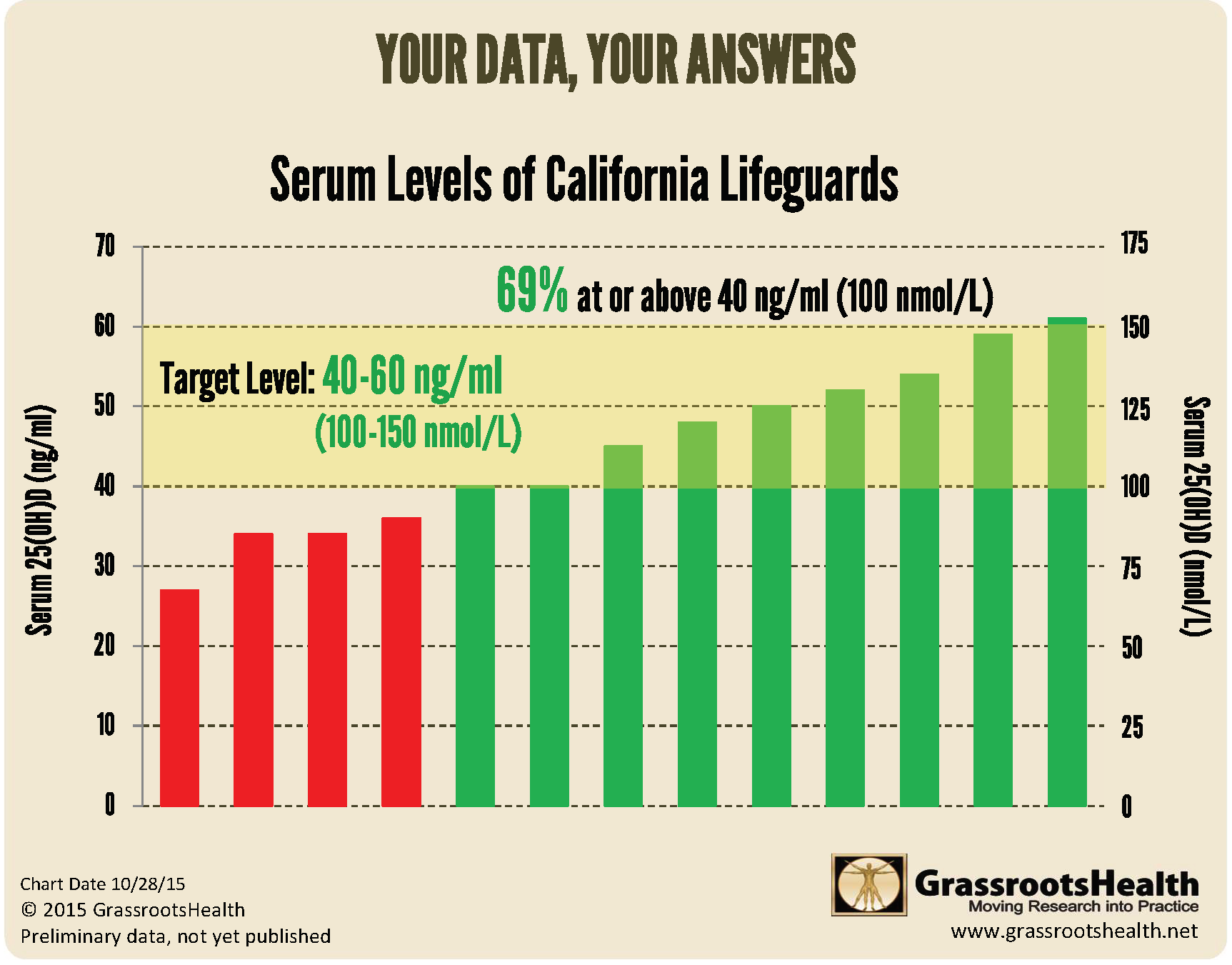
Additionally, GrassrootsHealth tested the vitamin D levels among a group of San Diego beach lifeguards at summer’s end. The average vitamin D level was 45 ng/ml, and as shown in the chart below, the majority of the lifeguards (69%) had vitamin D levels at or above 40 ng/ml. Since none of the lifeguards reported taking vitamin D supplements, observed vitamin D levels are primarily from sun exposure.
These studies show that vitamin D levels in the range of 40-60 ng/ml can be achieved with sun exposure. However, it takes more than just 10-15 minutes per day for most people. Results from a study published in 2018 showed that Caucasians living in the UK needed nine minutes of mid-day sun with arms and legs exposed each day from March to September to maintain a vitamin D level at or above 10 ng/ml (25 nmol/L) year-round, which is significantly below the optimal range for health. While some individuals can reach 40 ng/ml though sun exposure alone, many may not be able to due to factors such as skin type, burning threshold, latitude, cloud cover, and time availability. Even if the sun can’t be your only source of vitamin D, it can still be an important contributor to vitamin D status. A study published in 2019 found that sunshine is a significant determinant of vitamin D level even among those taking 2000 IU/day of supplemental vitamin D.
Could artificial UV light be used to increase vitamin D levels?
Indoor tanning could be used to increase vitamin D levels, especially when sunlight is inadequate due to season or cloud cover. Results from a study published in 2017 showed that vitamin D levels increased by an average of 17 ng/ml (42 nmol/L) after 12 weeks of sunbed use with no adverse effects. Participants in this study used professional indoor tanning beds irradiating adequate UVB (100 W and 160 W low pressure fluorescent lamps) 2-3 times per week at a sub-erythema dose, which is less time than it takes for the skin to turn pink. While a 2019 review article suggested there is a causal relationship between sunbed use and melanoma, a different review paper from 2018 found that such conclusions are not supported by current scientific knowledge. The researchers state that the overall data quality is poor and there is a high degree of bias, such as excluding individuals with high past UV exposure from controls (those without melanoma) but not from cases (those with melanoma) and the lack of adjustment for important risk factors such as smoking, alcohol use, and diet. Additionally, they point out that analyses showing no increase in melanoma risk with sunbed use or sub-erythema UV exposure are ignored. To maximize the benefits of UVB and UVA exposure from indoor tanning while minimizing potential risks with overexposure, studies have shown that it is important to use a sunbed in a professional setting and be mindful of the total dose (irradiance and duration), not dose rate (irradiance) alone so burning does not occur.
Are you using sun exposure as a source of vitamin D?
Is sun exposure helping to improve your vitamin D level? Make sure you know your vitamin D level, and see if you are in the target range of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L). Find out your levels today! Log on to the shop (click the link below) to get your tests and see for yourself if your levels can be improved. Use coupon code SunMonth to receive 15% off during Sunshine Month only!
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
How can I track my sun exposure and my vitamin D levels?
To help you track your sun exposure and vitamin D levels, GrassrootsHealth has created an online tracking system called myData-myAnswers. You can also track your dietary intake and supplement use to see how both sun exposure and vitamin D from food and supplements impact your vitamin D levels and your health. Check it out today!