Published on April 8, 2025
It’s National Cancer Control Month – Research clearly shows cancer control benefits associated with vitamin D, diets that balance pro and anti-inflammatory fatty acids, and exercise.
Key Points
- Research has shown that taking steps to reducing and managing inflammation, including increasing vitamin D, omega-3s, and exercising, can help decrease cancer risk and improve outcomes
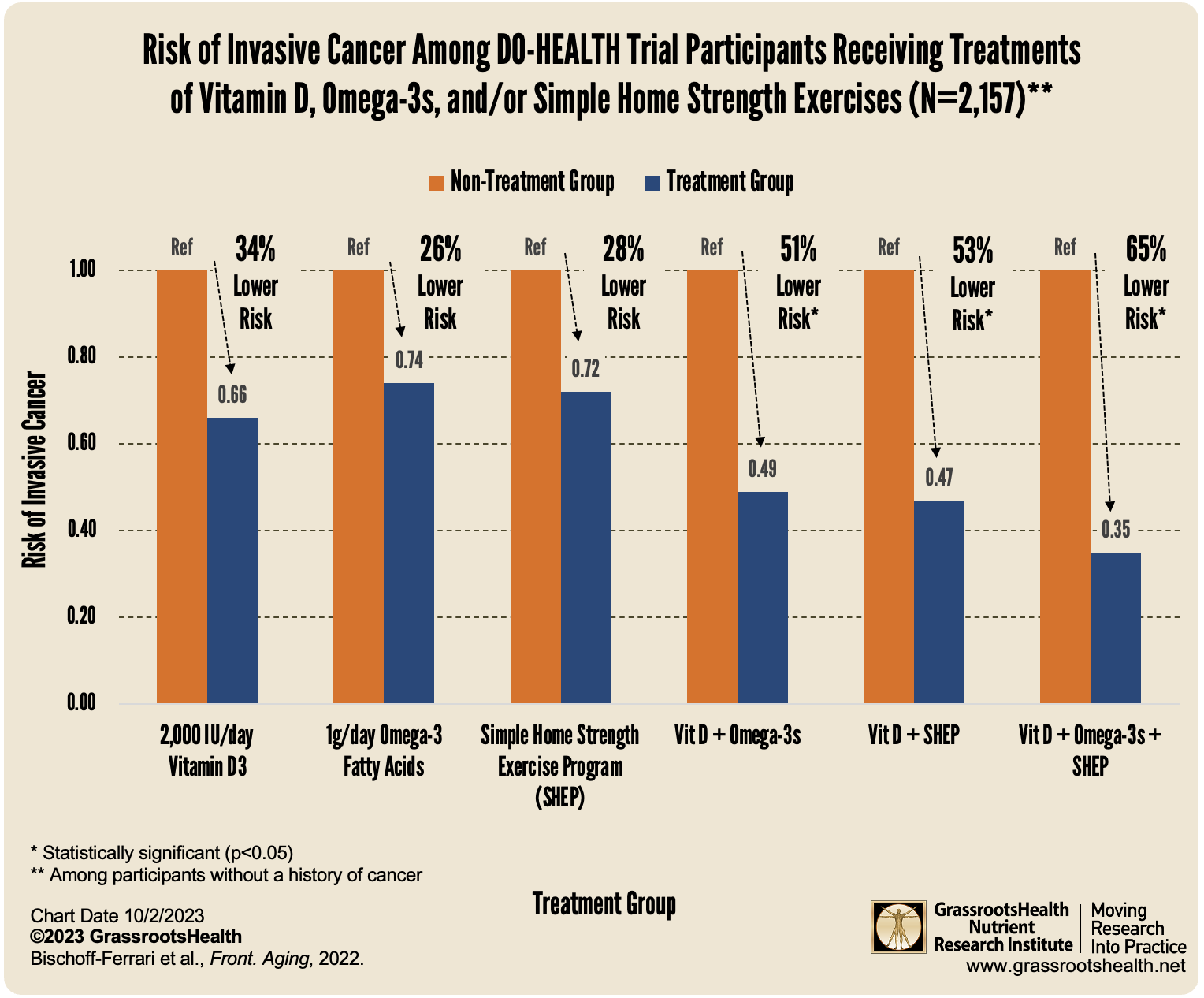
- The DO-HEALTH trial found that supplementation with vitamin D resulted in a decreased cancer risk, and was more effective when combined with omega-3 supplements, exercise, or both; all 3 resulted in a 65% decreased risk of invasive cancer
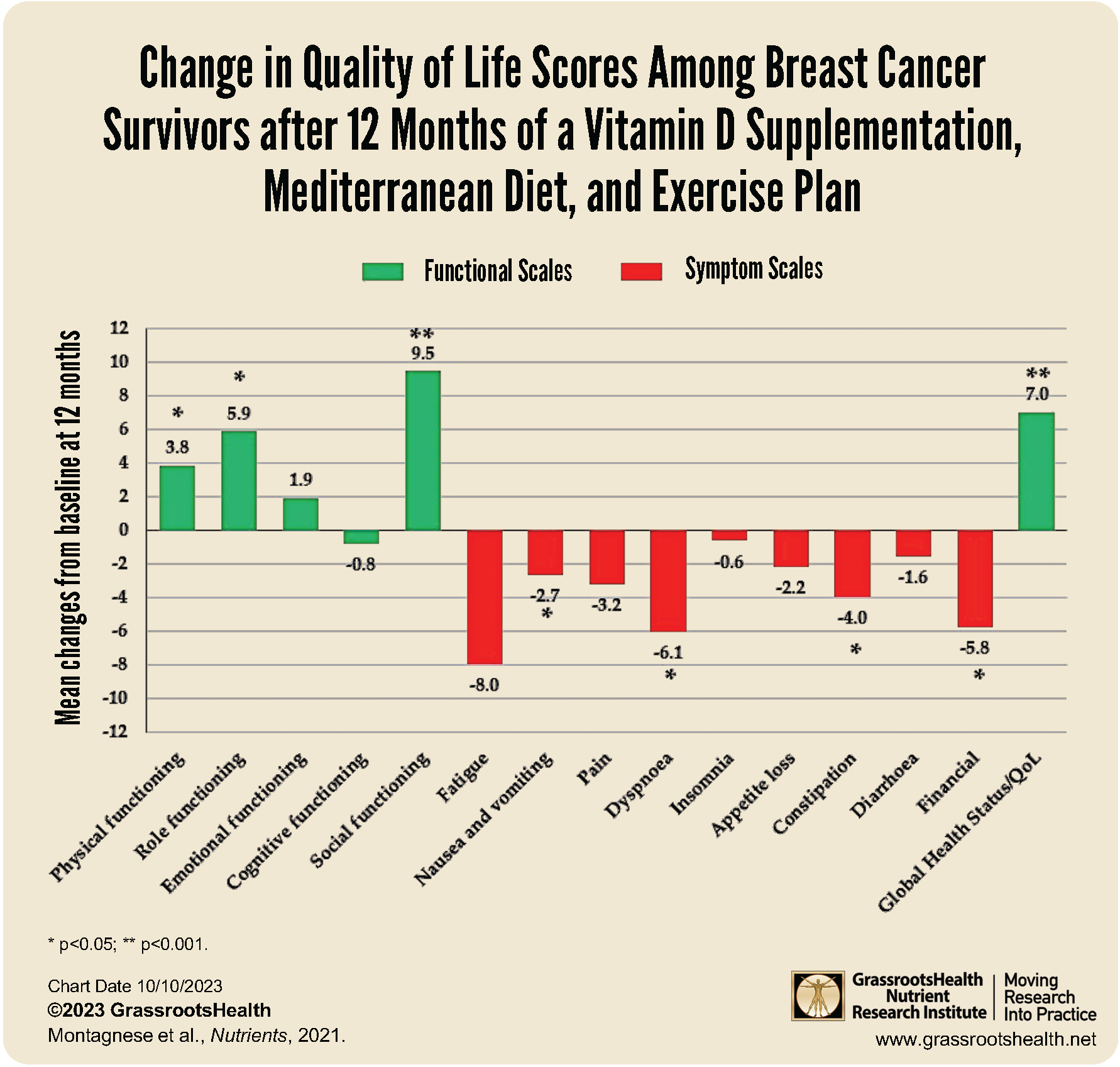
- Another study found that breast cancer survivors who implemented a vitamin D, Med Diet, and exercise plan experienced increases in global health status, physical health status, social and role functioning, body image, future perspective, and well-being; they also experienced reductions in fatigue, digestive issues, systematic side effects from therapy, and breast symptoms
 April is National Cancer Control Month, dedicated to awareness about cancer prevention and treatment options. At GrassrootsHealth, we believe that these awareness months are a great opportunity to share research about what can be done to safely and effectively help lower your risk of cancer, reduce recurrence, and improve outcomes in case of diagnosis.
April is National Cancer Control Month, dedicated to awareness about cancer prevention and treatment options. At GrassrootsHealth, we believe that these awareness months are a great opportunity to share research about what can be done to safely and effectively help lower your risk of cancer, reduce recurrence, and improve outcomes in case of diagnosis.
Two studies reviewed below illustrate the importance of 3 key components to reducing cancer risk and improving outcomes specifically among breast cancer survivors:
- Vitamin D: We have previously reviewed research showing that 80% of breast cancer could potentially be prevented just by achieving a vitamin D level of at least 60 ng/ml (150 nmol/L). Vitamin D can help even after a breast cancer diagnosis… in fact, one study found that when looking at the direct relationship between vitamin D level and breast cancer fatality, the vitamin D level accounted for 97% of the variance (meaning it made almost all the difference)
- Diets that Increase Omega-3s, Decrease Omega-6s: Having higher levels of anti-inflammatory omega-3s can counteract the pro-inflammatory influence of omega-6s and their production of inflammatory signals, therefore reducing inflammation. It is also thought that increasing omega-3s in the cell membrane may help disrupt the signals that lead to cancer development (called an oncogenic protein). Creating this balance can be done through diet (such as the Mediterranean Diet) and supplementation.
- Exercise! Increasing physical activity is recommended to help prevent and improve outcomes for nearly all chronic diseases, including cancer. It has been shown to improve the quality of life, extend cancer survival, and reduce treatment-related side effects.
Each of the above contributes to lower inflammation and improved immune function – which are essential to fighting cancer. Additional nutrients of importance are magnesium, selenium, vitamin C, and others. To measure your current immune and inflammation status, you can order the Immune Boost Panel Test Kit to see what levels could be improved to help support your immune system and response.
Order the Immune Boost Panel Test Kit Here
SHARE THE RESEARCH!
Vitamin D Supplementation Resulted in Lower Risk of Invasive Cancer, with Additional Benefits from Omega-3s and Exercise
The DO-HEALTH trial, conducted by Bischoff-Ferrari et al., enrolled 2,157 healthy and active adults, 70 years of age or older. This randomized controlled trial aimed to test the effects of the individual or combined treatments of 2000 IU/day of supplemental vitamin D3, 1g/day of supplemental omega-3 fatty acids, and/or a simple home strength exercise program (SHEP). Average time of follow up was around 3 years, during which 81 cases of invasive cancer were diagnosed and verified.
Based on an analysis adjusted for several variables including BMI, compared to participants in the non-treatment groups, the risk of invasive cancer diagnosis for participants without a history of cancer was decreased by
- 34% among those receiving only vitamin D (p=.09)
- 26% among those receiving only omega-3 fatty acids (p=.214)
- 28% among those given the home strength exercise program (SHEP) (p=.18)
- 51% among those given both vitamin D and omega-3 supplements (p=.04)
- 53% among those given both vitamin D and SHEP (p=.03)
- 47% among those given both omega-3s and SHEP (p=.07)
- 65% among those given all 3 treatments (p=.01)
This study shows that, while the dose of vitamin D supplementation was below what would get the majority of the population to the recommended 40-60 ng/ml range, supplementation still resulted in a decreased cancer risk, and was more effective when combined with omega-3 supplements, exercise, or both.
Study Shows Increasing Vitamin D, Exercising, and Eating an Anti-Inflammatory Diet also Improves Life for Breast Cancer Survivors
Many cancer survivors report a reduced quality of life, including decreased physical functioning and increased pain, which in turn has been shown to negatively affect treatment compliance and disease outcome. Montagnese et al. evaluated the quality of life among 227 breast cancer survivors (average age of 52 years, 96% postmenopausal) who had participated a 12-month lifestyle modification program that included the Mediterranean diet, exercise, and vitamin D supplementation. The Mediterranean Diet has been shown to lower inflammation levels and help reduce cancer. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and foods high in omega-3 fatty acids are central to the Mediterranean diet.
At the end of the 12 months, 87% of participants maintained high adherence to the Mediterranean diet, 37% remained physically active (measured as greater than 7500 steps per day), and 70% of participants reached a vitamin D level of at least 30 ng/ml (75 nmol/L). After participating in the program, participants experienced increases in global health status, physical health status, social and role functioning, body image, future perspective, and well-being. They also experienced reductions in fatigue, digestive issues, systematic side effects from therapy, and breast symptoms.
The authors found that changes in breast symptoms were inversely related to vitamin D levels (p=0.002).
Multiple Studies Show Lower Rates of Metastatic Cancer and Cancer Death with Vitamin D
One study by Treteli et al. included 658 Norwegian patients diagnosed between 1984 and 2004 with either breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer or lymphoma. Vitamin D levels were determined within 90 days of diagnosis, and subjects were followed until 2008. Researchers monitored for death. The analysis divided patients into four vitamin D groupings of roughly equal size and plotted survival over time for each of the different groups.
The study found that the highest survival rate was achieved by the group with the highest vitamin D level, over 33 ng/ml (81 nmol/L). Approximately 22% more survived among the group with the highest vitamin D levels compared to those with the lowest.
The VITAL trial was another more recent, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted in multiple centers around the United States. It included 25,871 participants who were free of cancer and cardiovascular disease diagnoses at baseline. Participants were either male, ages 50 years and older, or female, ages 55 years and older. Participants were given 2000 IU vitamin D per day and 1 gram of marine omega-3 fatty acids per day, or placebo. The average vitamin D level at baseline among all participants was about 30 ng/ml (75 nmol/L).
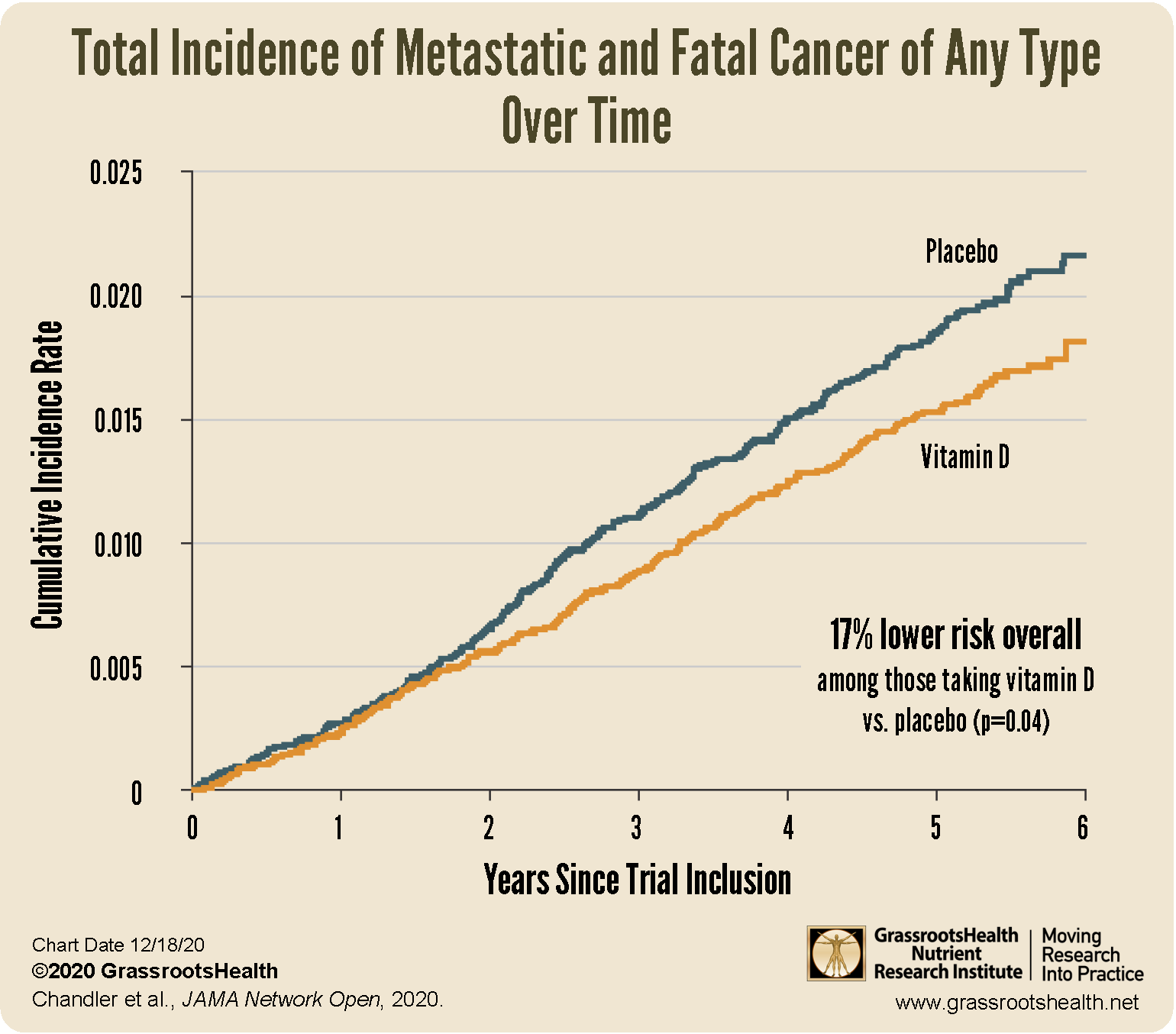
A secondary analysis of the VITAL randomized clinical trial data by Chandler et al. was completed to determine the effect of daily 2,000 IU vitamin D supplementation on the development of advanced, metastatic cancer and cancer death with BMI (grouped as below 25, 25 to under 30, and above 30) included to see if it modified the effects of supplementation.
A total of 1,617 participants were diagnosed with invasive cancer, with an average follow up time of 5.3 years. Supplementation with vitamin D did reduce the incidence of metastatic or fatal cancer in the overall cohort. Of those diagnosed, 226 (1.7%) had been receiving vitamin D and 274 (2.1%) had been receiving a placebo. Overall, there was a 17% reduced risk of metastatic or fatal cancer among the vitamin D group versus the placebo group (p=0.02).
When taking BMI into consideration the reduction in cancer was more pronounced. A significant reduction of metastatic or fatal cancer was seen among those with a normal BMI, with a decreased risk of 38% among those taking vitamin D compared to placebo (p=0.004); the findings were non-significant among those who were overweight or obese. In other words, the greatest risk reduction was seen among those with the lowest BMI.
How Vitamin D Fights Cancer
The active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, controls multiple pathways associated with the life cycle of the cell including those involved with reproduction, maturation and programmed death. Calcitriol regulates the production of a number of signals and growth factors at the genetic level. As detailed in the table included in this blog, some of the signals turned on by vitamin D stimulate growth, development, maturation and programmed cell death while other signals inhibit inflammation, prevent blood vessels from being made that can feed cancer cells, and stop the spread of the cancer to other parts of the body.
More on Vitamin D’s Anti-Cancer Effects Here
Take Action Today and Measure Your Levels!
Based on the findings presented above and those of many other studies, measuring your levels of vitamin D, magnesium, selenium, and omega-3s may help determine if more of these nutrients might be needed to provide the greatest risk reduction for breast cancer and improve outcomes in the case of a breast cancer diagnosis.
The Immune Boost Panel Test Kit includes each of these measurements:
- Vitamin D
- Omega-3 Index
- Magnesium PLUS Elements
- hsCRP as a marker of inflammation
Get the Inflammation Panel Here
Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for the future. Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of vitamin D (see below) and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.