Published on March 29, 2021
A recent review describes the bi-directional links between diabetes and COVID-19, and the role vitamin D may play
 Increased COVID-19 disease severity has been linked to several independent risk factors, including vitamin D deficiency, obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Diabetes specifically affects more than 400 million people around the world, and leads to complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, kidney damage, and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a life-threatening situation. In the past, diabetes has also been associated with a greater risk of infection during the SARS-CoV-1 epidemic, H1N1 pandemic, and the MERS-CoV epidemic.
Increased COVID-19 disease severity has been linked to several independent risk factors, including vitamin D deficiency, obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Diabetes specifically affects more than 400 million people around the world, and leads to complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, kidney damage, and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a life-threatening situation. In the past, diabetes has also been associated with a greater risk of infection during the SARS-CoV-1 epidemic, H1N1 pandemic, and the MERS-CoV epidemic.
It is interesting to note that the countries with the highest prevalence of diabetes (India, United States, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Mexico and Brazil) are listed in the top 8% of countries contributing to death due to COVID-19. What might be causing this strong disease relationship, and what is the role of vitamin D?
Could COVID-19 Infection Lead to Diabetes?
More recent studies are revealing the possibility of a reverse association between diabetes and COVID-19 – meaning new onset diabetes is increasingly being diagnosed among COVID-19 patients who had no previous history of diabetes. Could COVID-19 infection cause a patient to become diabetic, and if so, how? A review by Viswanathan et al. set out to answer this question, as well as identify the possible roles of vitamin D.
How Could Diabetes Increase Susceptibility to COVID-19?
The following describe several pathways that may contribute to increased COVID-19 susceptibility among patients with diabetes.
1. Medications increase ACE-2 expression. Many diabetes patients also suffer from increased blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, which are often treated using medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I), angiotensin-II type I receptor blockers (ARB) and lipid-lowering drugs. These medications, along with those used to treat diabetes, have been shown to increase the expression of ACE2 receptors in the epithelial cells of the lung, intestines, kidneys, and heart, which in turn facilitates entry of the SARS-CoV-2 virus into human cells. In other words, the medications that diabetics are often on can cause a “Drug-induced” increase in ACE2 expression, making it easier for COVID-19 infection to occur.
2. Impaired immunity leads to easier infection. Diabetics have an impaired immune response leading to greater risk of infections due to higher blood sugar and increased oxidative stress. Once infection occurs, this impaired response along with poor blood glucose control allows for the virus to proliferate at a much easier, faster rate than a non-diabetic individual.
3. Furin, a molecule that is increased in diabetics, has been shown to facilitate SARS-CoV-2 entry into human cells as well as viral replication.
Indications that COVID-19 Might Cause Diabetes
DKA is a severe, life-threatening complication of diabetes that is a result of the blood sugar being too high for too long. This condition that is a result of not having enough insulin (the key diagnosing factor for diabetes) is seen in patients infected with COVID-19, even in the absence of pre-diagnosed diabetes. Other indications that COVID-19 infection could possibly cause new-onset diabetes or worsen pre-existing diabetes include the following:
1. Certain respiratory viruses have been identified as a potential trigger and cause of type 1 diabetes. Due to high ACE2 receptor expression, the pancreas cells responsible for the facilitation of blood glucose regulation are highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Severe COVID-19 patients have shown a higher prevalence of autoimmunity that results in pancreatic cell destruction and resulting or worsening diabetes. Several studies have now confirmed the direct damage to pancreatic islet cells caused by COVID-19, leading to diabetes.
2. SARS-CoV-2 causes problems with the blood supply to the pancreas, which may impair insulin secretion.
3. The increase in systemic inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokines can directly result in decreased insulin sensitivity, and worsen insulin resistance, leading to diabetes.
What Role does Vitamin D Play?
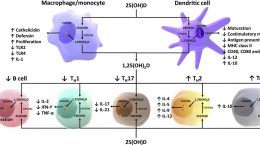
Multiple studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to increased severity and death due to COVID-19; it is known to affect the immune response in several important ways, specifically against viral infections. One of the most important ways vitamin D helps protect against COVID-19 is through its role in modulating inflammation and preventing the cytokine storm, which could also be a reason vitamin D has shown to help prevent diabetes.
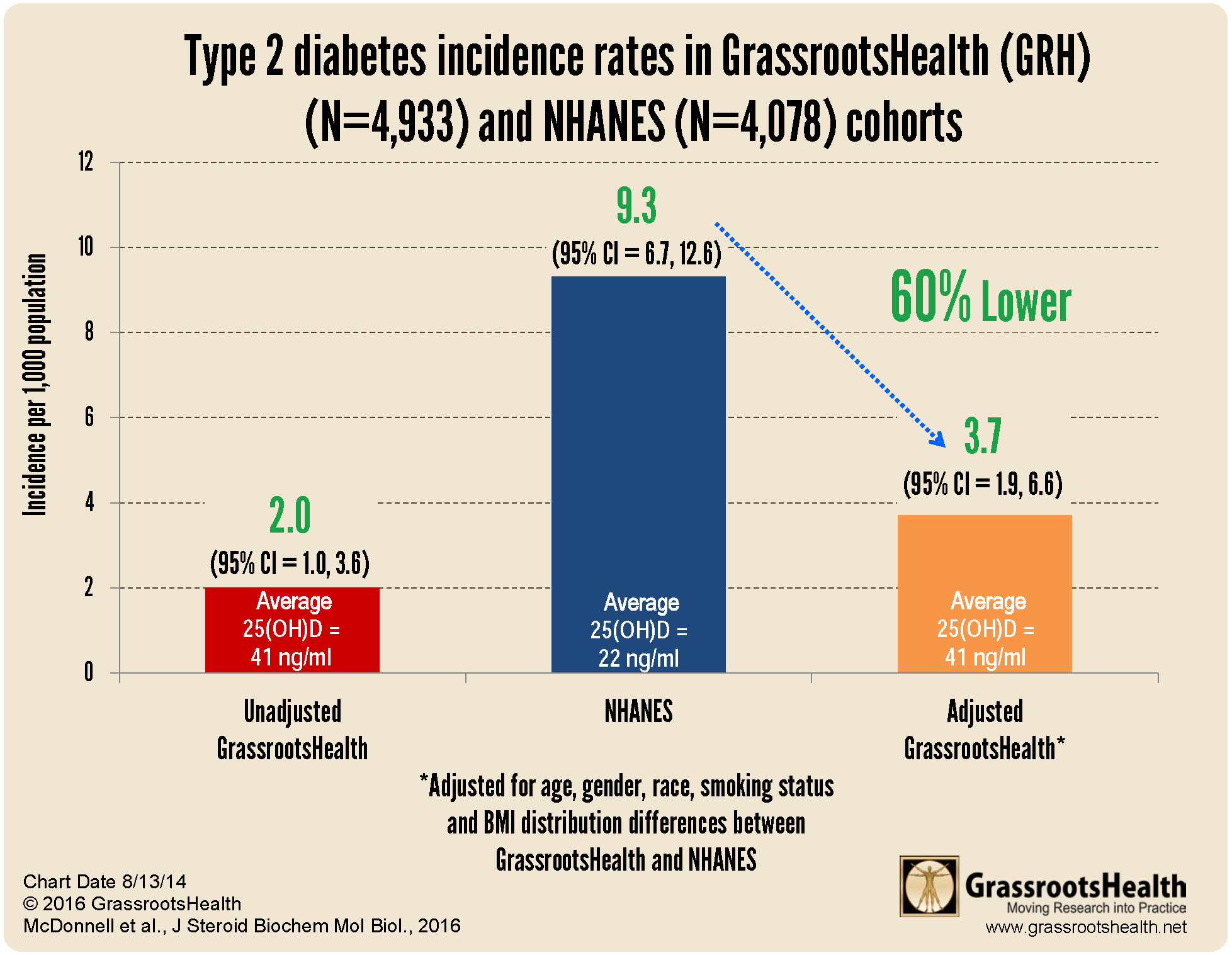
In fact, vitamin D deficiency has also been linked to the increased incidence of type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Vitamin D supplementation has been found to increase beta cell function and insulin sensitivity, as well as reduce insulin resistance by 15% and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes by 40-60% with achieved vitamin D blood levels of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L). Further, GrassrootsHealth published an analysis in 2016 that found that the incidence of type 2 diabetes was 60% lower in the GrassrootsHealth cohort, whose average vitamin D level was 41 ng/ml (103 nmol/L), compared to the U.S. population, whose average level was 22 ng/ml (55 nmol/L).
Vitamin D Influences Insulin Secretion and Response
Vitamin D, as 1,25(OH)2D, plays a regulatory role in insulin secretion as well as the function and survival of the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas (beta-cells). Vitamin D deficiency impairs insulin sensitivity (or promotes insulin resistance) because 1,25(OH)2D activates insulin receptors on cells throughout the body, which in turn affects their sensitivity to insulin. Overall, vitamin D is needed for insulin to be made and it is needed for cells to respond to insulin.
Chronic low-grade inflammation, frequently observed in obese individuals, is involved in the development of insulin resistance by interfering with normal sugar metabolism and disrupting insulin signaling. All forms of vitamin D regulate the inflammatory response and higher blood levels of vitamin D have been associated with lower levels of C reactive protein, a general marker of inflammation in the body.
Should You be Getting More Vitamin D to Help Protect Against Both COVID-19 and Diabetes?
With almost 90% of the general population having vitamin D levels below the recommended 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L), it is obvious that most people need more vitamin D. While most of us cannot achieve a vitamin D level of 40-60 ng/ml from sun alone, either due to our lifestyle, where we live, or other circumstances, we can certainly reach those levels with the right amount of supplementation.
Below is a guide for how much you might need, and who may need more. Your levels can be tested safely at home – order your home test kit today.
By joining the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to our study, but you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it. Do you know what your status of vitamin D, omega-3s, and other essential nutrients is? Could your levels be improved? Test now to find out!
 We now have a NEW GIFTING SERVICE that allows you to quickly send ‘Gift Cards’ to friends, family and coworkers who you consider might need immediate access to testing, and to Claim the Joy of Your Health TODAY. Give the gift today!
We now have a NEW GIFTING SERVICE that allows you to quickly send ‘Gift Cards’ to friends, family and coworkers who you consider might need immediate access to testing, and to Claim the Joy of Your Health TODAY. Give the gift today!
What does the Research Say about Vitamin D & COVID-19?
It’s TIME to start saving lives! If you can help PREVENT the majority of the death, it’s time! What’s it costing you/us not to take action NOW?
There is much published research that supports a clear link between vitamin D and COVID-19 showing that higher vitamin D levels are related to:
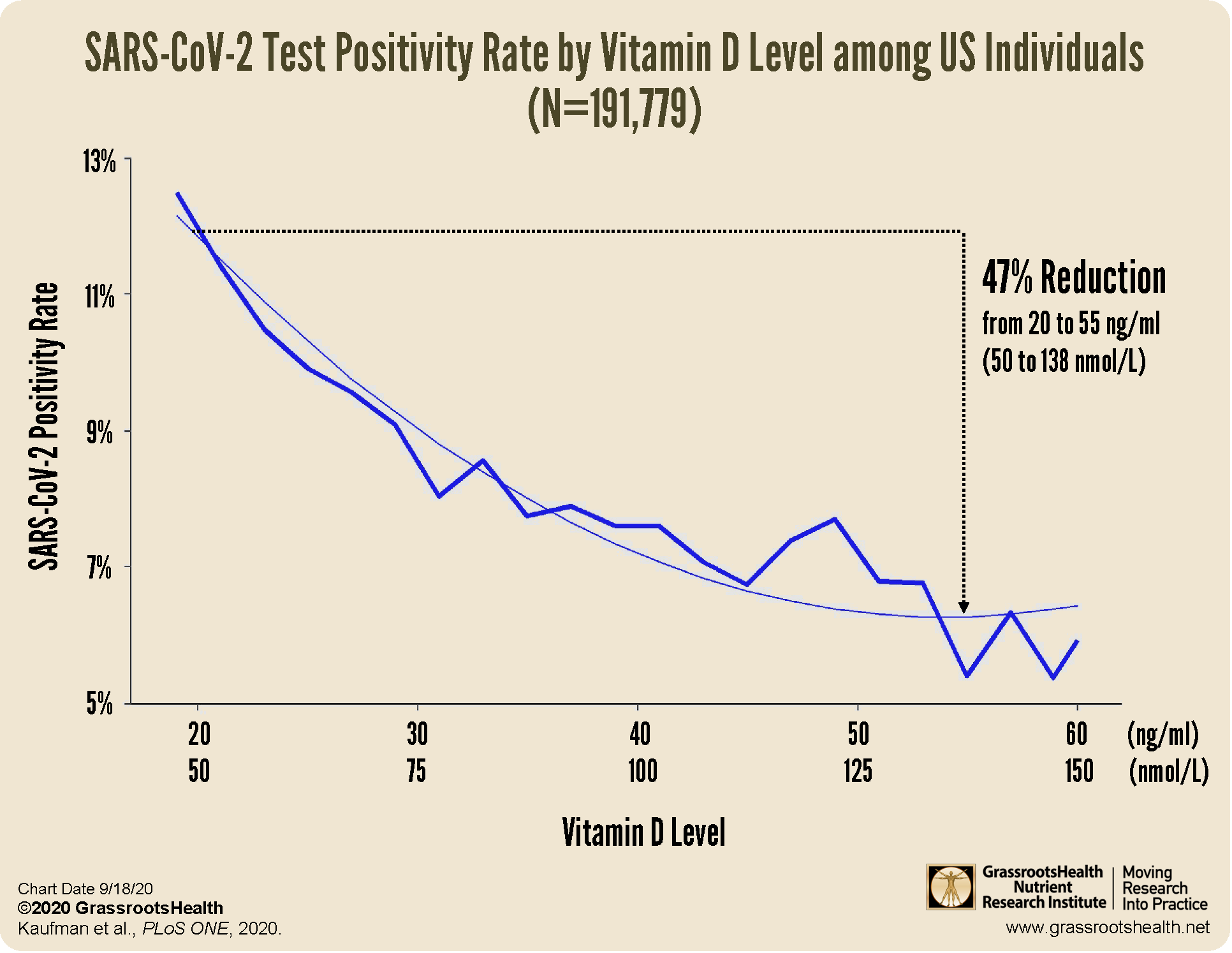
a decreased risk of testing positive for COVID-19
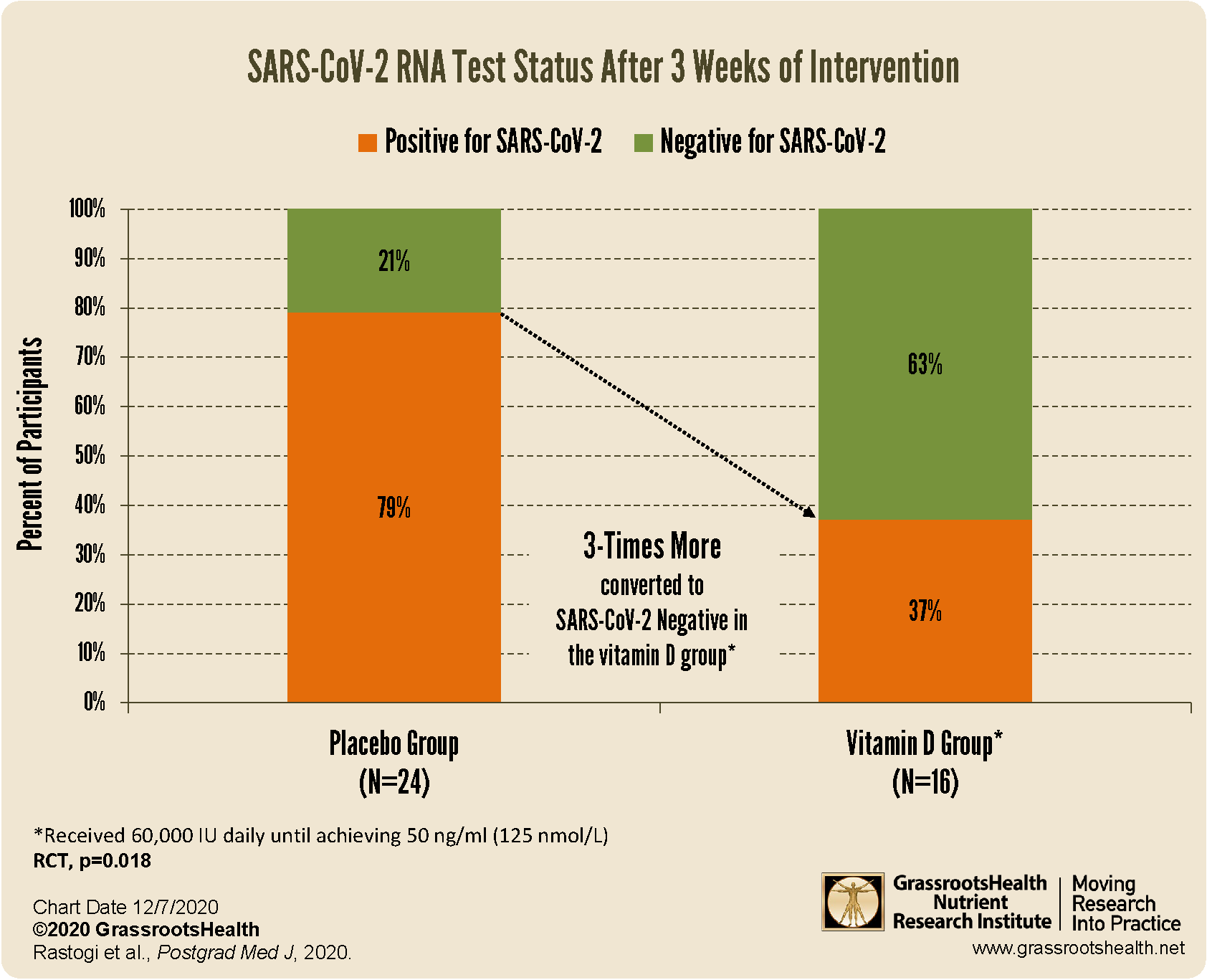 increased viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance
increased viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance
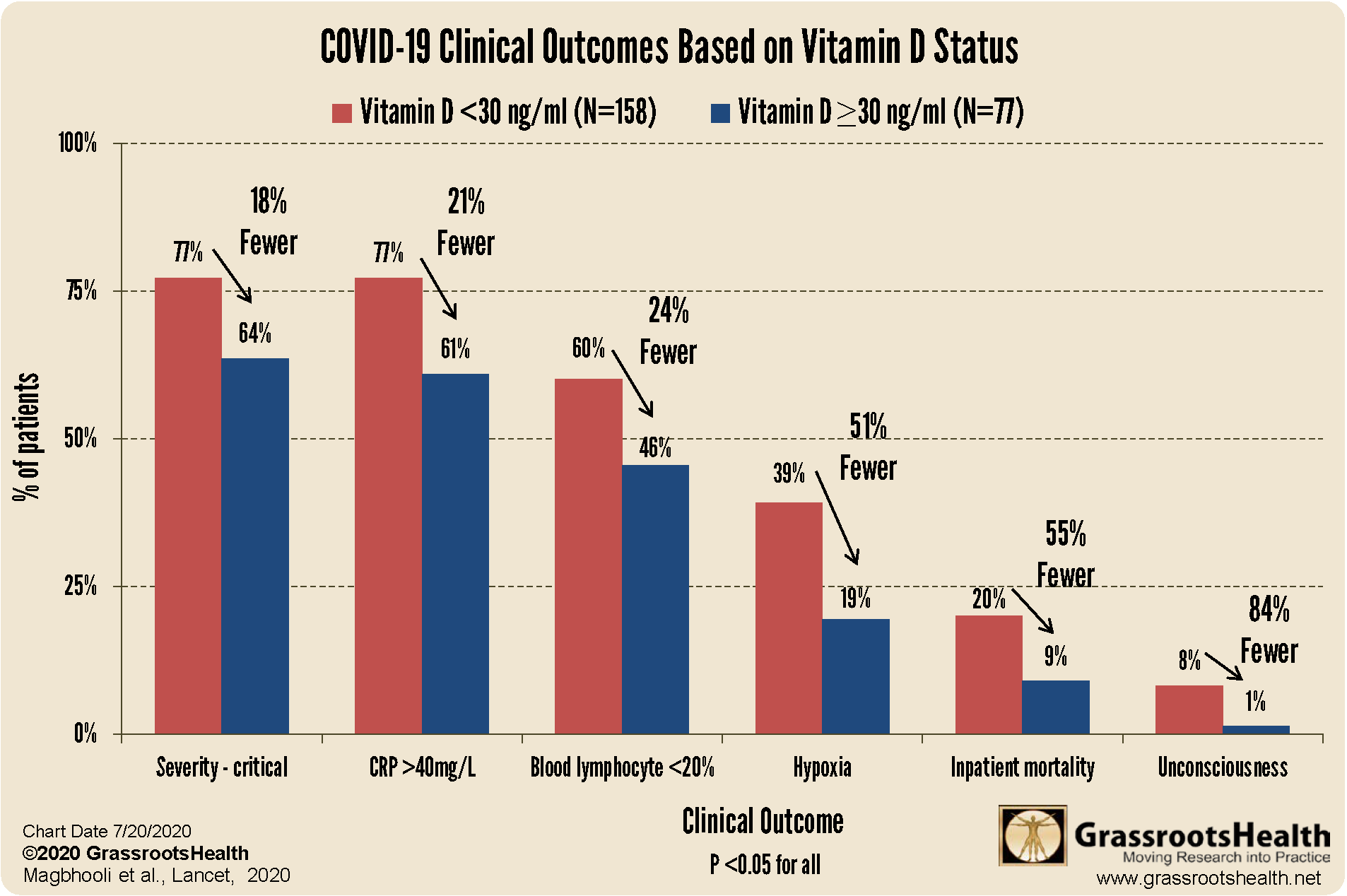
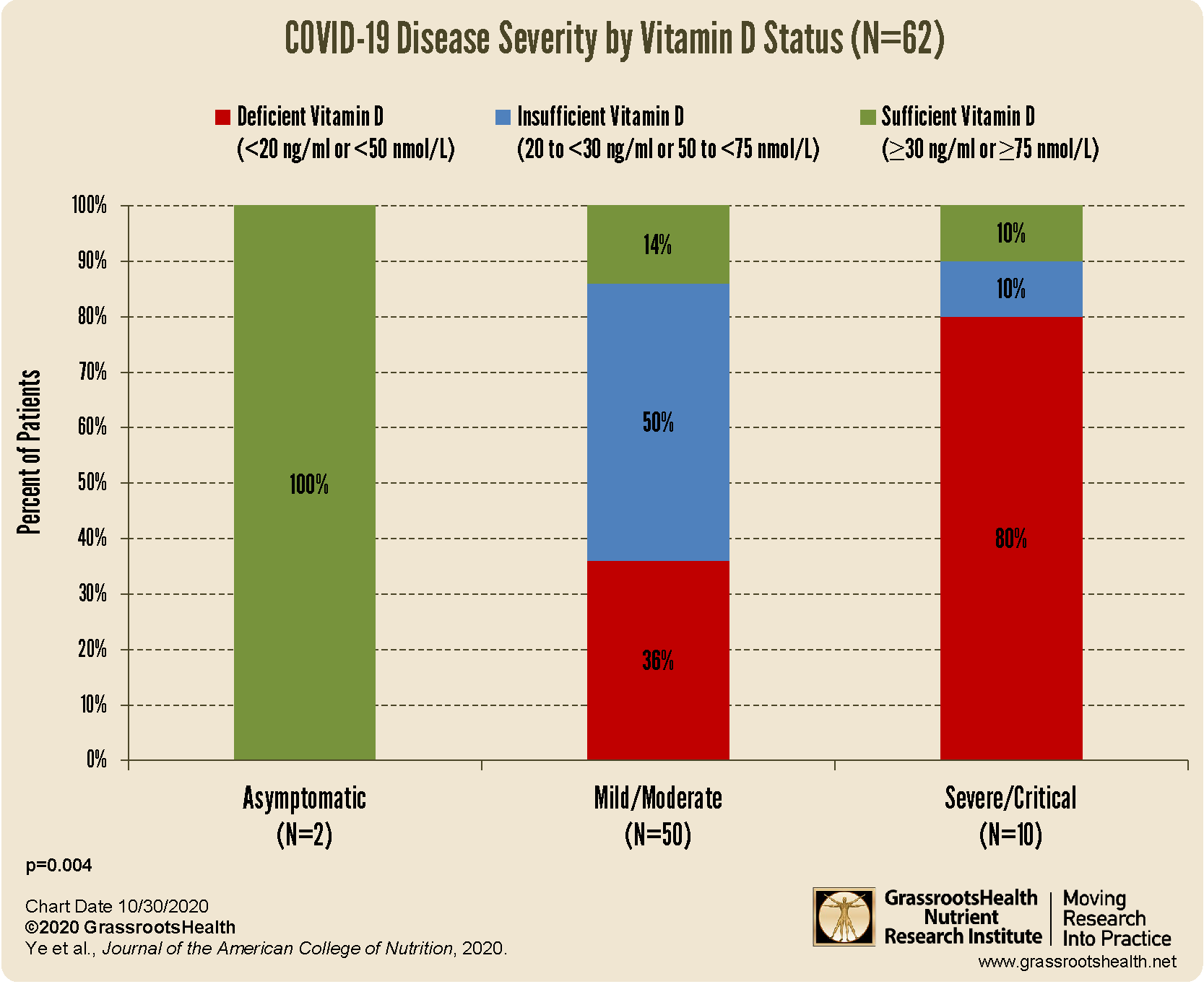
better clinical outcomes among patients with COVID-19
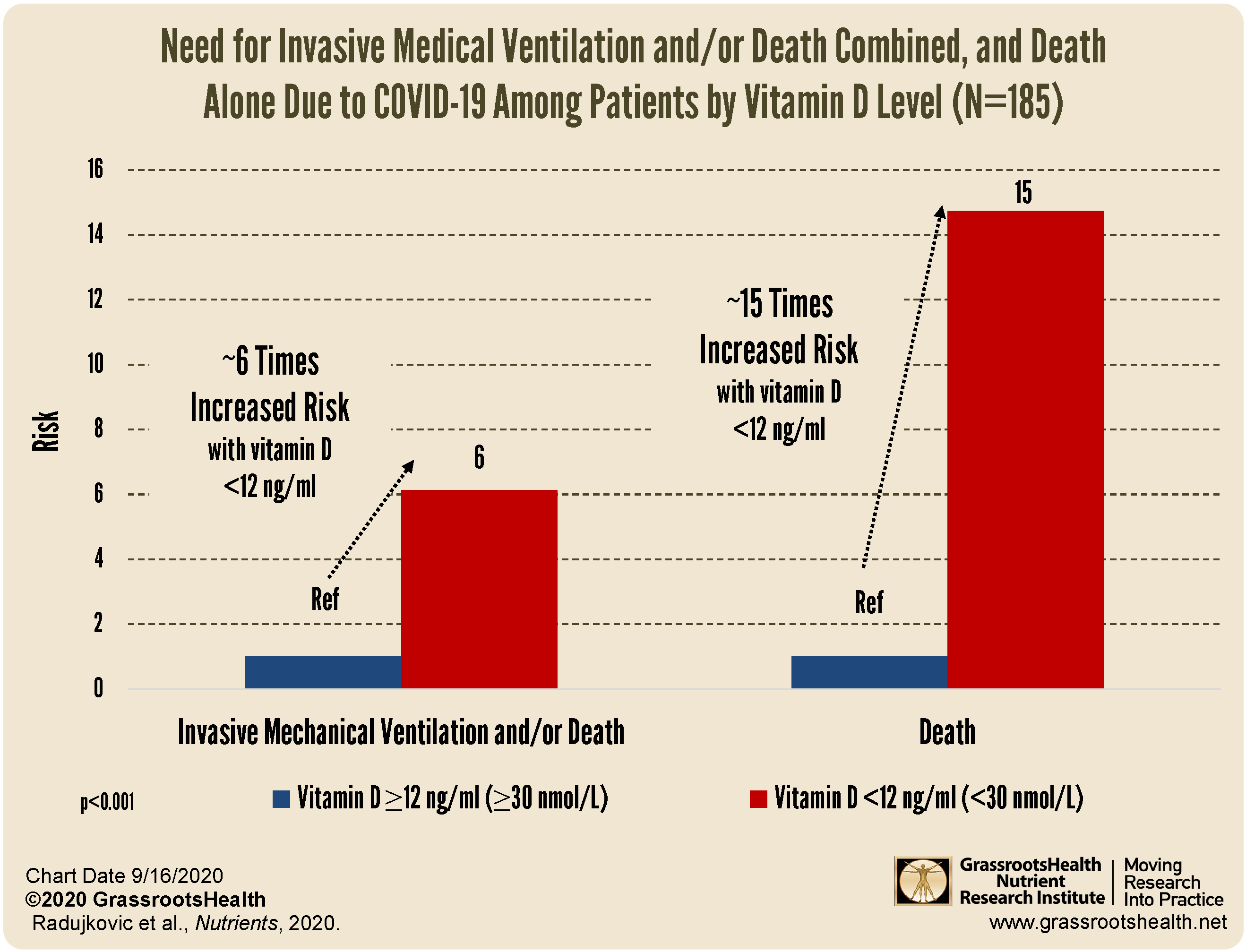
decreased risk of death due to COVID-19
Be sure to educate yourself on the benefits and importance of vitamin D for immune health, and take steps to ensure you and your loved ones are getting enough.
You can review all of the COVID-19 and immune health information we have shared on this page.