Published on April 5, 2024
Research is now showing evidence that both DHA and EPA have unique benefits to our health
Key Points
- Much of what you hear about the health effects of omega-3 fatty acids is as a whole combination of omega-3s versus the individual omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA; however, some of the latest research has begun to focus on differentiating the effects of each, with evidence mounting on their unique benefits and their interactions with other nutrients
- EPA may have stronger benefit for mood disorders, especially depression and anxiety, other protective effects in the brain, and a strong protective effect against melanoma
- DHA is especially essential for newborn health and development during pregnancy and lactation, benefits learning and behavior in children with ADHD, and seems to have a greater influence on brain health and Alzheimer’s disease
Get 15% Off Test Kits Measuring Your Omega-3 Index with Code OMEGA3S
 Healthy omega-3 levels, defined as an Omega-3 Index of at least 8%, have been associated with heart health, a longer life, brain health, breast cancer, reduced inflammation, and even an improved immune response to viral infection. Much of what you hear about the health effects of omega-3 fatty acids is as a whole combination of omega-3s versus the individual omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA. However, some of the latest research has begun to focus on differentiating the effects of each, with evidence mounting on their unique benefits and their interactions with other nutrients.
Healthy omega-3 levels, defined as an Omega-3 Index of at least 8%, have been associated with heart health, a longer life, brain health, breast cancer, reduced inflammation, and even an improved immune response to viral infection. Much of what you hear about the health effects of omega-3 fatty acids is as a whole combination of omega-3s versus the individual omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA. However, some of the latest research has begun to focus on differentiating the effects of each, with evidence mounting on their unique benefits and their interactions with other nutrients.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
EPA is a 20-carbon fatty acid whose main function is to produce chemicals called eicosanoids, which help reduce inflammation. Findings from research indicate strengths of EPA may include the following.
EPA may have stronger benefit for mood disorders, especially depression and anxiety
- mental emotional wellness, especially depression, may be beneficially affected to a greater extent with EPA, although some effect has also been seen with DHA
- a meta-analysis by Sublette et al (2011) found the greatest improvements in anxiety and depression were associated with EPA/DHA combinations with at least 60% EPA, where there was at least 200-2200 mg more EPA than DHA
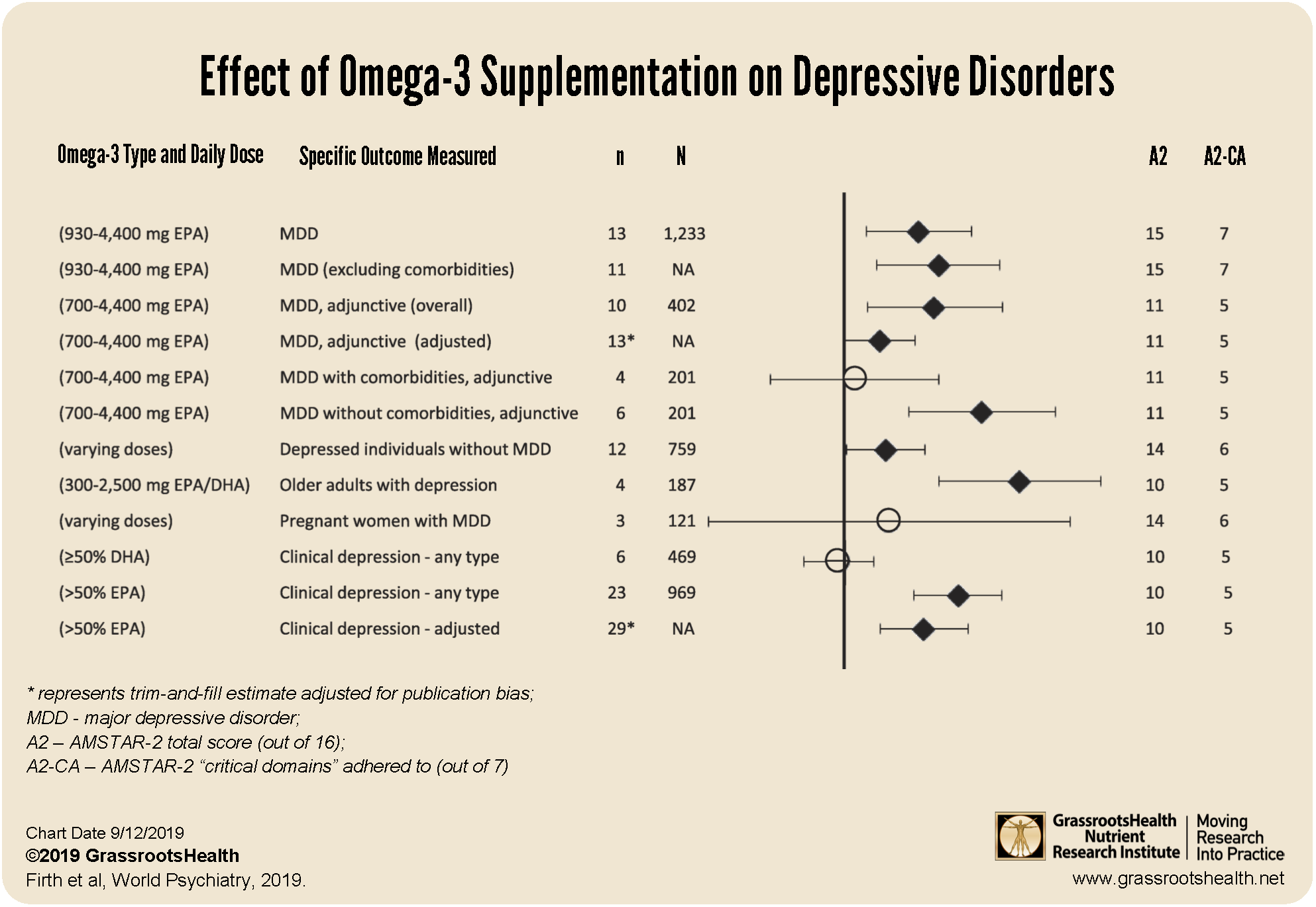
- The world’s largest review (called a meta-synthesis) of nutrient supplements and mental disorders published by Firth et al. examined 33 meta analyses of randomized controlled trials on dietary supplements and mental health. The analysis included data from 10,951 individuals with diagnoses such as depression, stress and anxiety, bipolar, personality disorder, schizophrenia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The strongest evidence from this review showed that supplementation with omega-3s (with an average dose of 1422 mg/day of EPA) reduced symptoms of major depressive disorder, which produced benefits beyond those of taking antidepressants alone. As seen in the forest plot below, the strongest effect (in the studies with the black diamonds further on the right) was seen with omega-3 supplements that contained at least 50% EPA.
EPA has some protective effects in the brain
- higher EPA levels in the blood have been associated with less grey matter atrophy (shrinking of the brain) and delayed cognitive decline, and lower risk of dementia and depressive symptoms
- supplementation with EPA has shown positive effects on reversing age-related impairment in spatial learning and long-term potentiation
EPA may have a strong protective effect against melanoma
- omega-3 fatty acids may help protect against skin cancer as shown by a recent study that found daily supplementation with 5 grams EPA-rich omega-3 fish oils (70% EPA, 10% DHA) decreased immunosuppression induced by sun exposure in skin cells when exposed to UVR
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
DHA is a 22-carbon fatty acid which makes up about 8% of brain weight and is extremely important for normal brain growth and development during pregnancy and infancy. DHA is a major structural component of the retina of the eye, making it essential to eye health as well. Research has shown a strong connection especially between omega-3s and the risk of macular degeneration. Findings from research indicate additional strengths of DHA may include the following.
DHA is essential for newborn health and development during pregnancy and lactation
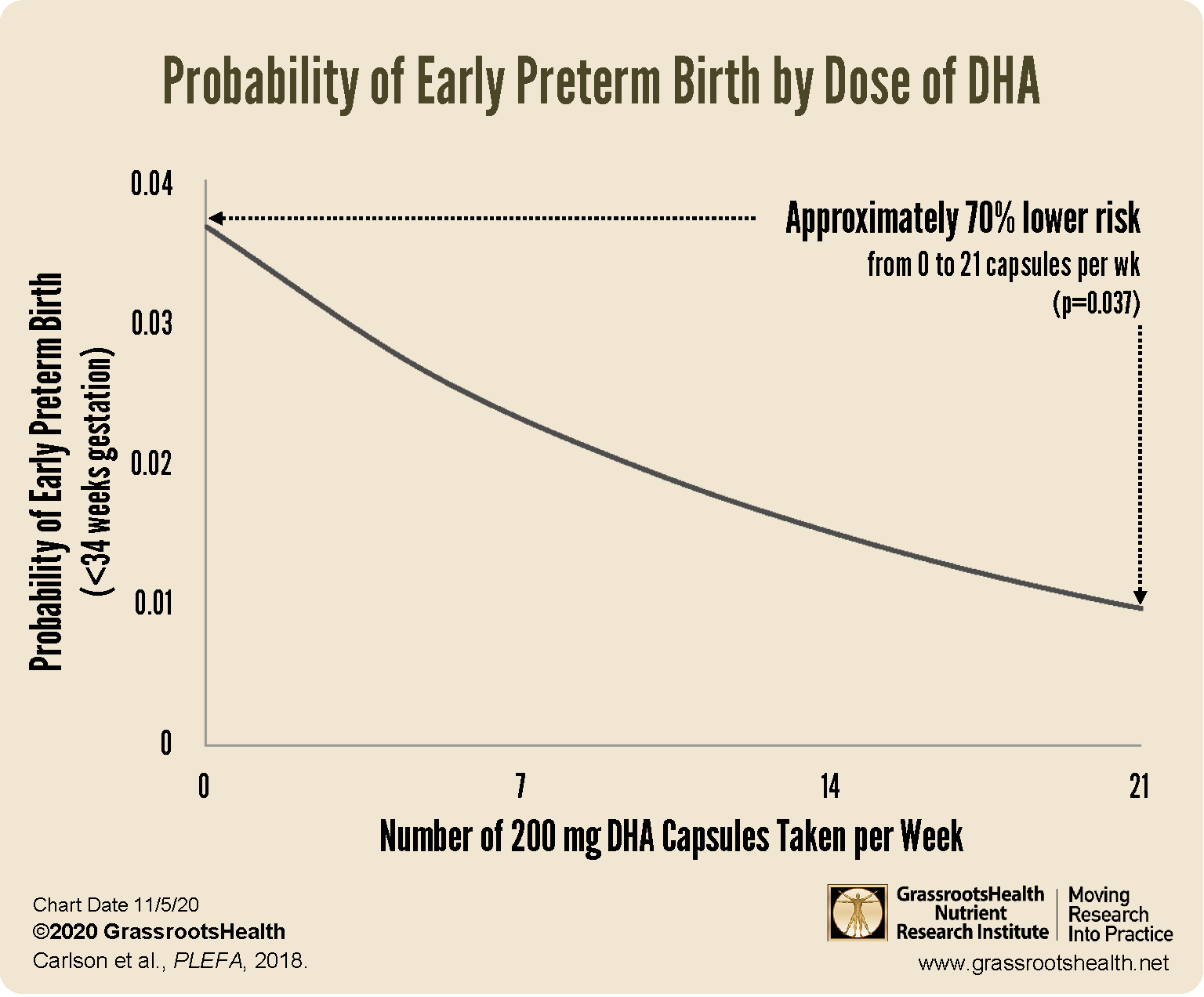
- DHA supplementation during pregnancy has been shown to decrease the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight babies. One study showed an approximate decrease of 70% for early preterm birth, 85% for very low birth weight, and 60% for low birth weight among women taking DHA supplements.
- Research suggests that DHA supplementation during pregnancy and breast feeding may result in an improved immune response of the infant. Granot et al. investigated whether DHA supplementation during pregnancy and lactation affected immune cell numbers and function in babies breastfed up to 4 months of age. The study found that the number of T cell subsets (discussed in a previous post) were affected by DHA supplements. Women who were supplemented with 400 mg DHA per day from the first trimester until up to 4 months after birth had babies who experienced lower levels of inflammation and higher numbers of immune cells known for fighting off viral infections.
- a study by Tai et al. has linked the intake of DHA during infancy to improved eye sight for the child, higher IQ, better communication and social skills, less behavioral problems, and a decreased risk of developmental delay, ADHD, autism and cerebral palsy
DHA benefits learning in children and may improve symptoms of ADHD
- a study by Rodriguez et al. found that omega-3 supplementation among children and adolescents with ADHD (specifically DHA) led to greater improvements in cognitive and visual-sensory test performance as well as behavioral improvements compared to placebo
DHA seems to have a greater influence on brain health and Alzheimer’s disease
- DHA is the most important omega-3 fatty acid in the brain and within nerve cell membranes. In fact, brain EPA levels are usually 250-300 times lower than DHA levels.
- DHA has a greater effect on cell signaling, promotes synaptogenesis (forming of new connections in the brain and nervous system), and in that way, may help protect brain health and cognition in older age and prevent Alzheimer’s disease
- DHA has been shown to improve memory, learning, verbal fluency, and depression scores among those with mild cognitive impairment (EPA was only related to improved depression scores)
EPA, DHA, and Inflammation
Omega-3s are known to counteract chronic inflammation. As mentioned above, a main function of EPA is to produce chemicals called eicosanoids, which help reduce inflammation. DHA is also the precursor to several important resolvins (hormones that turn off inflammation). Both EPA and DHA show protective effects against inflammation in the brain specifically, with DHA showing a more pronounced effect on inhibiting brain inflammation overall. Another study on general inflammation found that over 3 months, individuals receiving DHA specifically had significantly lower levels of several blood markers of inflammation (including CRP and IL-6) compared to those receiving a placebo.
Cardiovascular Health, EPA and DHA
There have been many studies on the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for cardiovascular health and the prevention of ischemic events. The VITAL trial, which focused on cancer and cardiovascular health, found several significant benefits among those assigned to omega-3s (1000 mg/day) vs. placebo. A meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials that used supplementation of EPA and DHA found a preventive effect of supplementation on cardiovascular disease (CVD), with a stronger effect associated with higher doses, especially for CVD events and heart attack.
One study found that among those with high triglyceride levels who were on statins and at risk of major ischemic events, taking 4g per day of a slightly modified, purified form of the essential fatty acid EPA significantly lowered the risk of ischemic events, including cardiovascular death. Another review, however, concluded that higher omega-3s may be related to an increased risk of atrial fibrillation. Upon a more detailed inspection, only those studies using high ethyl ester products consisting of only EPA (and no DHA) or a highly oxidative form of free fatty acid DHA and EPA products (which can increase inflammation) produced this effect, indicating the importance of both EPA and DHA and a need to maintain some sort of balance between the two.
How Much EPA and DHA Do You Need?
 Whether deciding to get more EPA or DHA for your particular health benefits, it is still important to make sure the combined intake is helping to achieve and maintain an Omega-3 Index of at least 8%. An analysis of GrassrootsHealth data found that approximately 1,300 mg/day of EPA+DHA was needed for 50% of the population and 1,900 mg/day was needed for 90% of the population to achieve and Omega-3 Index of 8%. It is important to point out that, similar to the large variability seen with vitamin D dose response to intake, these intake amounts are averages and there is a large amount of variability in the omega-3 status for different people with the same intake amount. For example, our initial analysis showed that the range of response with 1000 mg of EPA+DHA per day was 5.7% to 10.2%. Therefore, we recommend that individuals measure their Omega-3 Index and determine a personalized dose.
Whether deciding to get more EPA or DHA for your particular health benefits, it is still important to make sure the combined intake is helping to achieve and maintain an Omega-3 Index of at least 8%. An analysis of GrassrootsHealth data found that approximately 1,300 mg/day of EPA+DHA was needed for 50% of the population and 1,900 mg/day was needed for 90% of the population to achieve and Omega-3 Index of 8%. It is important to point out that, similar to the large variability seen with vitamin D dose response to intake, these intake amounts are averages and there is a large amount of variability in the omega-3 status for different people with the same intake amount. For example, our initial analysis showed that the range of response with 1000 mg of EPA+DHA per day was 5.7% to 10.2%. Therefore, we recommend that individuals measure their Omega-3 Index and determine a personalized dose.
Once results are received, consider your next steps for adjusting the Omega-3 Index, such as how to choose between the different types of omega-3 sources, how to evaluate and choose an omega-3 supplement, and how to achieve a desired Omega-3 Index using an estimated dose of EPA and DHA as determined by our Omega-3 calculator. Taking simple dietary steps to increase consumption of foods rich in EPA and DHA can also help increase your Omega-3 Index.
Choose What to Measure While Participating as a Citizen Scientist!
Becoming a participant of GrassrootsHealth means that anyone is joining thousands of people in collaborating on nutrient research – we call it “citizen science.” Citizen science welcomes everyone’s participation in the discovery and sharing of scientific knowledge. As a citizen scientist, you’ll help everyone gain a better understanding of the role of nutrients in health and disease, and use the results to help inform public health officials to create change. Additionally, you can use your results to make informed decisions about nutrients that affect your health.
What Are Your Levels?
 Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of vitamin D (see below) and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.