Published on March 14, 2019
 In the United States, diabetes affects more than 30 million people, with type 2 diabetes accounting for 90-95% of cases. Additionally, more than a third of US adults (84 million) have prediabetes. Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure, non-traumatic lower limb amputations, and new cases of blindness among adults and is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. Many people with diabetes don’t even know they have it (25% of those with diabetes and 90% of those with prediabetes)!
In the United States, diabetes affects more than 30 million people, with type 2 diabetes accounting for 90-95% of cases. Additionally, more than a third of US adults (84 million) have prediabetes. Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure, non-traumatic lower limb amputations, and new cases of blindness among adults and is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. Many people with diabetes don’t even know they have it (25% of those with diabetes and 90% of those with prediabetes)!
 What causes Type 2 diabetes?
What causes Type 2 diabetes?
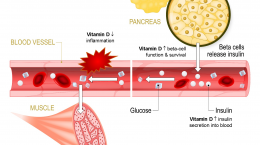
The main cause of type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance, which is when the body doesn’t use insulin as well as it should. Less commonly, type 2 diabetes can be caused by the body not producing enough insulin. In either case, too much glucose builds up in the blood.
Who is most at risk for prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes?
There are many genetic and lifestyle factors that can increase an individual’s risk for diabetes. These include being overweight, aged 45 years or older, lack of exercise, poor diet, having a close relative with type 2 diabetes, or having previously had gestational diabetes. Additionally, individuals who are African American, Hispanic, American Indian / Alaska Native, or Pacific Islander have a higher risk.
What are the symptoms of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes include being very thirsty, urinating often, blurry vision, feeling tired, numbness or tingling in the hands or feet, and having more infections than usual. However, symptoms often develop slowly without being noticed and sometimes there are no observable symptoms at all.
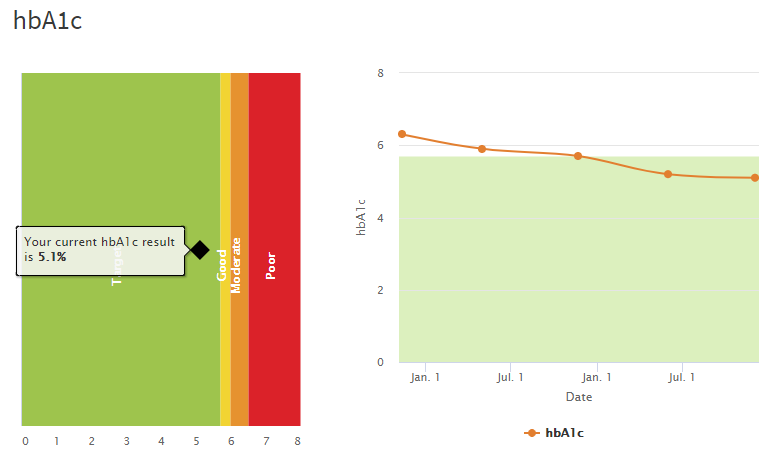
What is Hemoglobin A1c?
Hemoglobin A1c, or HbA1c, is the compound formed in the blood when a hemoglobin molecule in a red blood cell binds with a glucose molecule; the resulting molecule is also known as glycated hemoglobin. The more glucose that enters the bloodstream, the higher the amount of hemoglobin A1c. Measuring the percentage of hemoglobin A1c in the blood provides information about the average blood glucose levels over the prior few months. Generally levels below 5.7% are considered normal, 5.7% to 6.4% are considered prediabetic, and levels of 6.5% or higher are considered diabetic. This test can be used by a healthcare professional, along with other tests and a physical exam, to help diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes and for diabetes management.

How can I find out my Hemoglobin A1c levels?
GrassrootsHealth offers a Hemoglobin A1c dried blood spot test. Knowing your Hemoglobin A1c levels can enable you to focus your health efforts on lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, which can help prevent or even reverse prediabetes. Additionally, studies have shown that increasing vitamin D and omega-3 levels can lower Hemoglobin A1c levels. Be sure to consult your physician if you think you are at risk for diabetes and for specific recommendations for your health. Find out your levels today!
How can I track my Hemoglobin A1c levels?
To help you track your Hemoglobin A1c levels, GrassrootsHealth has created an online tracking system called myData-myAnswers. You can also track your vitamin D and omega-3 levels as well as your diet, weight and exercise to see how they impact your Hemoglobin A1c levels. Check it out today!

 What causes Type 2 diabetes?
What causes Type 2 diabetes?