Published on August 2, 2021
Our paper on breast cancer and vitamin D has been named as one of the top 10% most cited PLOS ONE papers published in 2018!
 Exciting news!! Our paper, titled Breast cancer risk markedly lower with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations ≥ 60 vs < 20 ng/ml (150 vs 50 nmol/L): Pooled analysis of two randomized trials and a prospective cohort, is among the top 10% of 2018 papers published in PLOS ONE for being cited in other research.
Exciting news!! Our paper, titled Breast cancer risk markedly lower with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations ≥ 60 vs < 20 ng/ml (150 vs 50 nmol/L): Pooled analysis of two randomized trials and a prospective cohort, is among the top 10% of 2018 papers published in PLOS ONE for being cited in other research.
What Did This Paper Look At?
The study pooled and analyzed data from two randomized controlled trials (RCTs), led by Dr. Joan Lappe at Creighton University (2007, N=1129 and 2016, N=2196), combined with data from the GrassrootsHealth Breast Cancer Prevention Study cohort (N=1713). This analysis aimed to investigate the relationship between vitamin D level and breast cancer risk across a broad range of vitamin D concentrations among women aged 55 years or older.
The first RCT was published in 2007 and is summarized in our blog here. This study followed 1,179 healthy, postmenopausal women, aged 55 or older for four years and put them in one of three groups – taking a daily dose of 1,100 IU vitamin D and 1,400-1,500 mg calcium; calcium only; or placebo only. The study found that the vitamin D and calcium group had a 77% reduced risk of cancer as compared to the placebo group.
The second RCT focused solely on cancer. The 2,303 women enrolled in this study received either 2,000 IU/day of vitamin D and 1,500 mg/day of calcium or placebo. This study found a 30% reduction in cancer incidence with the vitamin D + calcium group, as compared to the placebo group. (paper here, blog here)
The third set of women comes from the GrassrootsHealth Breast Cancer Prevention Project. This group of women self-select to be in the study. To match the entry requirements of the RCTs, data from women aged 55 or older with no current cancer and not in treatment for cancer were included. They are asked to conduct an at-home blood test every six months (they prick their finger and drop blood on a special card) and answer a health questionnaire. At the time of this paper, there were 1,713 women enrolled whose data could be included in the analysis.
What were the Findings of this Paper?
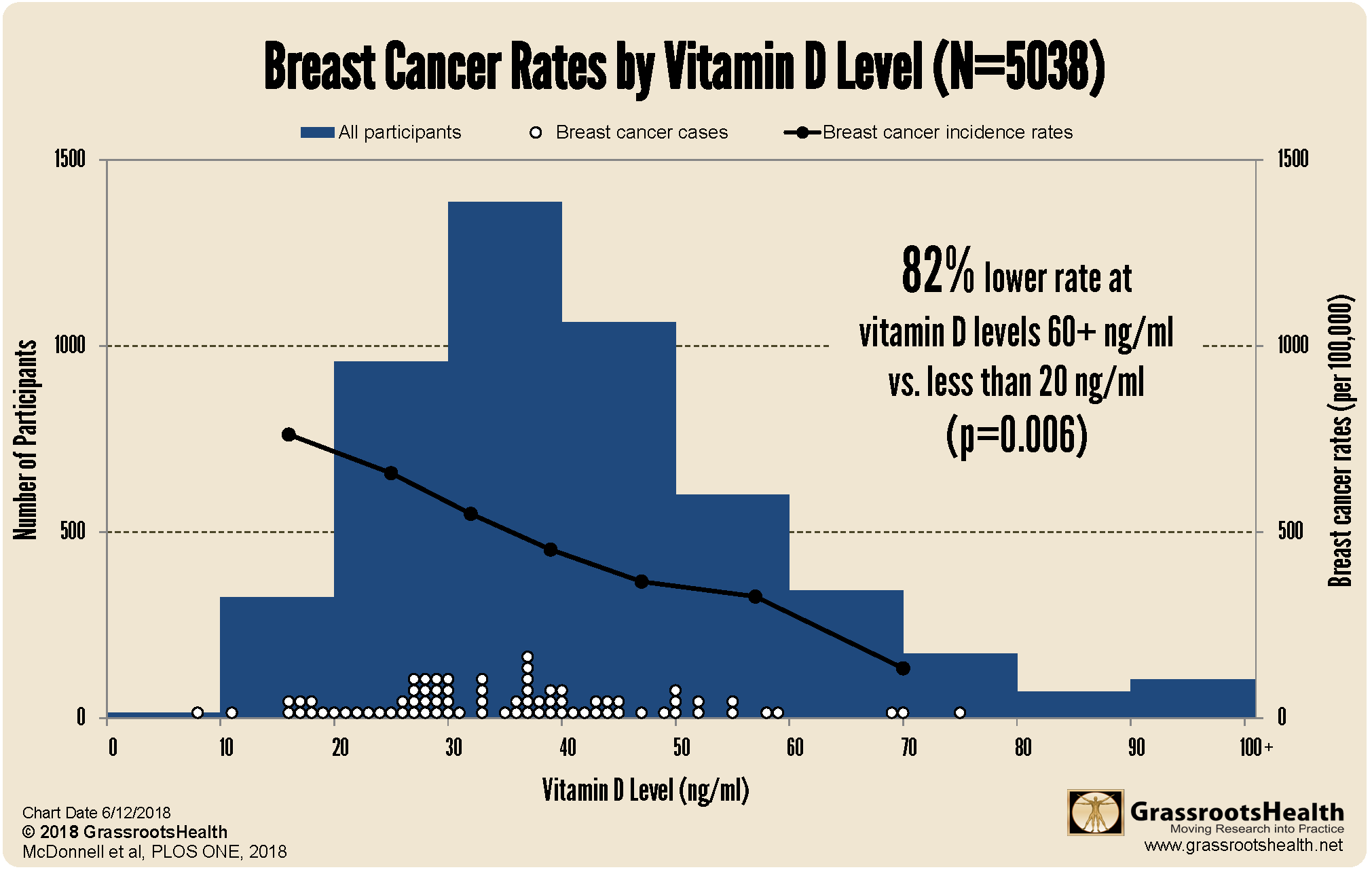
Within the pooled cohort (N=5038), 77 women were diagnosed with breast cancer during the observation periods (median follow-up time: 4.0 years) with an age-adjusted incidence of 512 cases per 100,000 person-years. Comparing incidence rates of breast cancer by vitamin D level showed an 82% lower rate for women with 25(OH)D concentrations of at least 60 ng/ml (150 nmol/L) compared to less than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L; P = 0.006).
As you can see, vitamin D levels have a significant correlation with breast cancer incidence. The horizontal, or x-axis, records increasing vitamin D levels, from 0 to 100 ng/ml (250 nmol/L). Keep in mind that the average vitamin D level for all women in the US is 29 ng/ml, for African Americans, 21 ng/ml.
The vertical axis on the left-hand side shows the number of people in the blue bars that fall into each 10-ng/ml block of vitamin D levels. The white dots represent breast cancer occurrence; note that most of the dots (69%) are below 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L), and very rarely above 60 ng/ml (150 nmol/L).
What Makes this Research Unique?
A big difference in this research is that the analysis assessed breast cancer risk across a broad range of vitamin D levels, including levels higher than 40 ng/ml (most previous studies focused on the lower ranges).
Also, most vitamin D clinical trials are designed and interpreted by assigned treatment dose, not by blood levels of vitamin D. Not all people react the same to a specific dosage nor does this capture vitamin D from the sun, food and personal supplements. Therefore, it is better to report on blood levels achieved, than the dosage given.
Measure Your Level of Vitamin D and Other Important Nutrients
 Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Choose which to measure, such as your vitamin D, omega-3s, and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Choose which to measure, such as your vitamin D, omega-3s, and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of vitamin D (see below) and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.
Help everyone Move Research into Practice with vitamin D and other nutrients! As a special birthday gift to everyone, in honor of the science, we have created a special scholarship fund for anyone to donate to that will go towards helping others participate. Your donation will allow anyone to get help with funding their participation when they need it.
Text-to-give: Text Daction to 44321 to add to our Scholarship Fund.