Published on August 5, 2022
Video Friday: This short, animated video describes what the HbA1c test measures, and what conditions might lead to falsely high or low results
Key Points
- The hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c or A1c) test is a measure of how healthy average blood sugar levels have been in the recent few months, and is a better representation of blood sugar health than a single glucose measurement; it can be a good indicator of glucose intolerance even in the absence of abnormal fasting glucose levels
- A healthy A1c level is less than 5.7%; greater than 6.5% indicates diabetes; between 5.7-6.5% represents prediabetes
- Several factors described can lead to an inaccurate HbA1c result, including several blood disorders, iron deficiency anemia, and liver or kidney disease
The hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c or A1c) test was introduced to GrassrootsHealth participants as part of the Type 1 Diabetes Prevention project, and is a measure of how healthy average blood sugar levels have been in the recent few months. This particular test is a better representation of blood sugar health than a single glucose measurement, since glucose levels vary throughout the day. It can be a good indicator of glucose intolerance even in the absence of abnormal fasting glucose levels, and higher levels of HbA1c are associated with higher levels of inflammation.
Watch today’s quick, informational video to get details about what the A1c test is a measure of, and what conditions might affect the accuracy of the results.
Watch the Video to Learn More
After watching the video, be sure to make note of our added details below!
The A1c Test – What it Measures & What Results Mean
Here is a quick summary of what this video discusses, along with additional information and details from GrassrootsHealth:
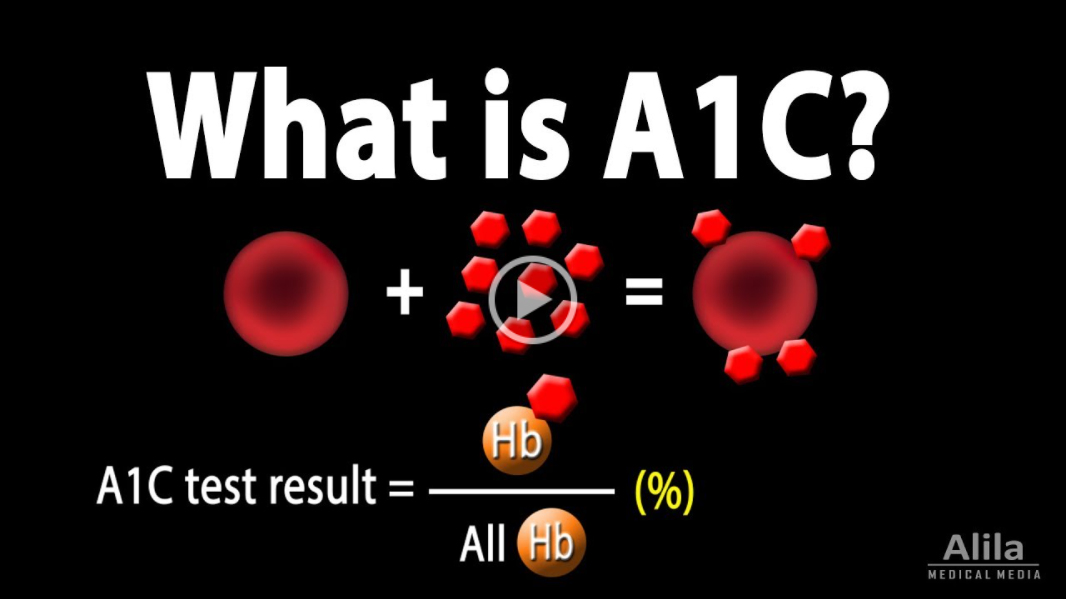
- the A1c (or HbA1c) blood test is used to diagnose and manage diabetes, representing the average blood sugar level over the past 3 months
- HbA1c is the compound formed in the blood when a hemoglobin molecule in a red blood cell binds with a glucose molecule in the blood; the resulting molecule is also known as glycated hemoglobin
- the higher the blood glucose, the more glucose becomes attached to the hemoglobin, resulting in a higher A1c level
- A1c shows the percent of hemoglobin bound to glucose
- once hemoglobin is glycated, it remains that way until the red blood cell is removed from the system
- average lifespan of a red blood cell is 3-4 months, which is why A1c is a representation of blood sugar status over approximately the last 3 months
- a healthy A1c level is less than 5.7%; greater than 6.5% indicates diabetes; between 5.7-6.5% represents prediabetes (see below for special circumstances)
- an estimated average glucose level, eAG, measured in concentration units (mg/dL or mmol/L), can be calculated and reported in addition to the A1C percentage to help link A1C to the numbers from an at home blood sugar measuring device
What Could Cause an Inaccurate A1c Result?
Several factors can affect the accuracy of the A1c test result:
- blood disorders such as sickle cell disease, thalassemia, and hemolytic anemia (in which the lifespan of red blood cells is shorter) can lead to falsely low A1c
- iron deficiency anemia (and other conditions in which the lifespan of the red blood cells is increased) can lead to a falsely high A1c
- individuals from an African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian decent may have certain uncommon forms of hemoglobin which can lead to falsely low or high A1c levels
- certain kidney and liver diseases may also affect the accuracy of the test, as can recent blood loss or transfusion
Measure Your HbA1c from Home
Do you know your HbA1c level? Add it to your custom home test kit today! You can also measure your:
- Vitamin D (always included)
- Magnesium PLUS Other Essential and Toxic Elements
- Omega-3 Index with or without Fatty Acid Ratios
- hsCRP
Did you know that each of the above can be measured at home using a simple blood spot test? As part of our ongoing research project, you can order your home blood spot test kit to get your levels, followed by education and steps to take to help you reach your optimal target levels. Start by enrolling and ordering your kit to measure each of the above important markers, and make sure you are in a healthy range of each!