Published on September 5, 2024
How does your blood sugar level contribute to inflammation and chronic illness, and what can you do about it?
Key Points
- Today, we are featuring a video by Dr. Mobeen Syed on one of the ways excess sugar in the blood can speed up the aging process and lead to inflammation and the development of chronic disease, as well as other featured posts that discuss what can be done to help improve blood sugar levels and decrease the risk of metabolic and inflammatory diseases
- As explained in the video, glycation is the process of non-enzymatic glucose attachment to various cells, tissues, and enzymes, which reduces or compromises cell function and leads to an inflammatory state and also results in aging; diabetes, stiffness, joint pains, chronic inflammation, etc. are accelerated by the end products of glycation
- Higher levels of HbA1c can indicate blood sugar imbalance, pre-diabetes or metabolic disorder, which is often a combination of increasing insulin resistance and inflammation; considering this measurement can give additional clues as to how diet, and therefore your blood sugar level, may be affecting your levels of inflammation
Measure Your Vitamin D, Inflammation, and Blood Sugar Levels
Many who follow GrassrootsHealth know about the link between inflammation and chronic disease, but what role does your blood sugar level play in this dynamic? Those of you who have ordered our Inflammation Panel Test Kit know that one of the measurements included is the Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), which is a measure of blood sugar health. Higher levels of HbA1c can indicate blood sugar imbalance, pre-diabetes or metabolic disorder, which is often a combination of increasing insulin resistance and inflammation. Considering this measurement can give additional clues as to how diet, and therefore your blood sugar level, may be affecting your levels of inflammation.
Today, we are featuring the video below by Dr. Mobeen Syed on one of the ways excess sugar in the blood can speed up the aging process and lead to inflammation and the development of chronic disease. Following the video are several other blogs that discuss what can be done to help improve blood sugar levels and decrease the risk of metabolic and inflammatory diseases.
Watch the Video: Glycation and Aging
About the Video
Glycation is the process of non-enzymatic glucose attachment to various cells, tissues, and enzymes. This process reduces or compromises cell function and leads to an inflammatory state which also results in aging. Diabetes, stiffness, joint pains, chronic inflammation, etc. are accelerated by the end products of glycation. These end products are called Advanced Glycation End-products or AGE products, which can build up inside and around our cells and can be consumed directly from some of the foods we eat. (As we age, we accumulate more AGE products.) In this video, Dr. Mobeen Syed reviews this mechanism and how to prevent or slow the process.
What Else Can Help Manage Blood Sugar and Inflammation Levels?
Learn more from the related posts below!
Lower HbA1c Levels Found Among T1D Adults Taking More Vitamin D
 Key Points
Key Points
- Measuring the percentage of HbA1c in the blood provides information about the average blood glucose levels over the prior few months; this test can be used by a health care professional, along with other tests and a physical exam, to help diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes and for diabetes management
- A new study published in 2024 by Ahola et al. found that vitamin D supplementation of at least 1200 IU per day was associated with better glycemic control among type 1 diabetics compared to those supplementing with less or no vitamin D
- A 2019 study among adolescents diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) found an inverse, linear correlation between the HbA1c values and vitamin D levels (as vitamin D levels increased, HbA1c levels decreased) for those with T1D
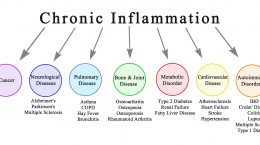
How to Detect Silent Inflammation, an Early Warning of Un-Diagnosed Diseases
 Key Points
Key Points
- When unresolved, the following initial injuries can lead to chronic, low-level inflammation: microbial invasions, physical injuries (internal and external), diet-induced, oxidative stress-induced, surgery-induced, drug-induced (cancer drugs in particular), and sensor-induced (physical, emotional, environmental)
- Inflammation can go unnoticed and be very damaging long term; sometimes an individual will experience symptoms such as pain or fatigue due to inflammation, but often there will be no symptoms until disease occurs
- Several tests, such as those included in the Inflammation Panel, can help an individual identify the amount of inflammation hiding within their body
Analysis by Vitamin D Level: A 76% Decreased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Among those with Prediabetes
 Key Points
Key Points
- 25% of those with diabetes and 90% of those with prediabetes are unaware of their diagnosis; diabetes itself is the leading cause of kidney failure, non-traumatic lower limb amputations, and new cases of blindness among adults and is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States
- A meta-analysis on vitamin D and type 2 diabetes found a 76% reduced risk of diabetes among individuals with prediabetes who maintained a vitamin D blood level of at least 50 ng/ml (125 nmol/L) compared to those with a vitamin D level of 20-29 ng/ml (50 to 74 nmol/L)
- A blood test for HbA1c can help determine one’s risk for diabetes and pre-diabetes
Measure Your Levels of Vitamin D, HbA1c and Inflammation
 Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D, omega-3s, magnesium, and other nutrient levels can help improve your inflammation levels and your health now and for your future. Choose which to measure, such as your vitamin D, omega-3s, and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D, omega-3s, magnesium, and other nutrient levels can help improve your inflammation levels and your health now and for your future. Choose which to measure, such as your vitamin D, omega-3s, and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of vitamin D (see below) and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.