Published on February 23, 2024
A new study among adults with Type 1 Diabetes shows those taking more vitamin D had better glycemic control
Key Points
- Measuring the percentage of HbA1c in the blood provides information about the average blood glucose levels over the prior few months; this test can be used by a health care professional, along with other tests and a physical exam, to help diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes and for diabetes management
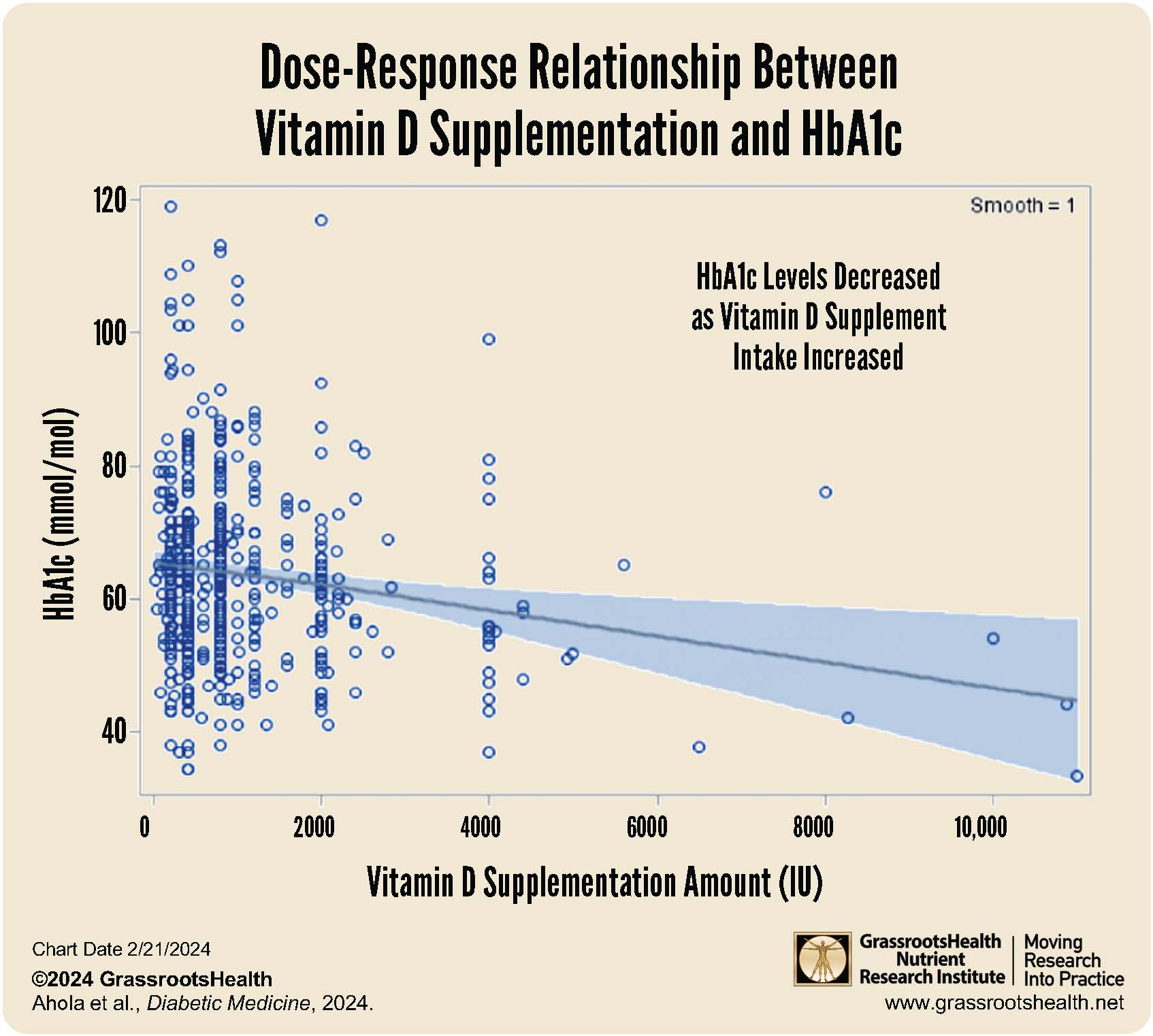
- A brand-new study published in 2024 by Ahola et al. found that vitamin D supplementation of at least 1200 IU per day was associated with better glycemic control among type 1 diabetics compared to those supplementing with less or no vitamin D
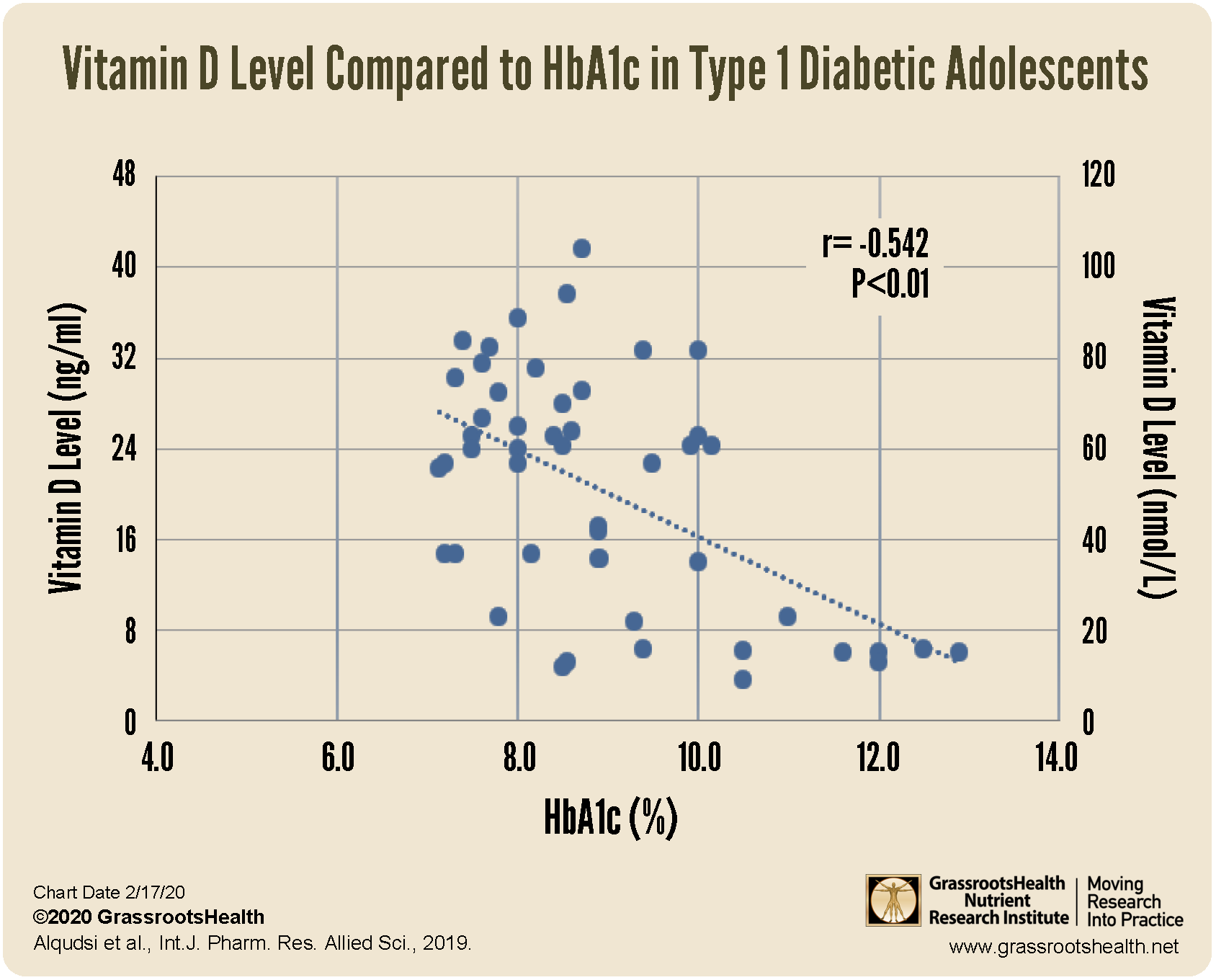
- A 2019 study among adolescents diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) found an inverse, linear correlation between the HbA1c values and vitamin D levels (as vitamin D levels increased, HbA1c levels decreased) for those with T1D
 Hemoglobin A1c, or HbA1c, is the compound formed in the blood when a hemoglobin molecule in a red blood cell binds with a glucose molecule. The more glucose that enters the bloodstream, the higher the amount of HbA1c. Measuring the percentage of HbA1c in the blood provides information about the average blood glucose levels over the prior few months. This test can be used by a health care professional, along with other tests and a physical exam, to help diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes and for diabetes management.
Hemoglobin A1c, or HbA1c, is the compound formed in the blood when a hemoglobin molecule in a red blood cell binds with a glucose molecule. The more glucose that enters the bloodstream, the higher the amount of HbA1c. Measuring the percentage of HbA1c in the blood provides information about the average blood glucose levels over the prior few months. This test can be used by a health care professional, along with other tests and a physical exam, to help diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes and for diabetes management.
Add HbA1c to Your Home Test Kit Here
Is There a Relationship between Vitamin D Status and HbA1c Level?
Previous studies have associated lower vitamin D levels with
- insulin resistance
- severity of diabetic ketoacidosis
- higher insulin requirements
- worse glycemic control
A brand-new study published in 2024 by Ahola et al. found that vitamin D supplementation of at least 1200 IU per day was associated with better glycemic control among type 1 diabetics compared to those supplementing with less or no vitamin D.
The study looked at data from 1181 adult individuals who were participants of the Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy Study to assess supplement intake. 62% reported some kind of dietary supplement use during the past 30 days. They found that vitamin D was the most frequently reported vitamin supplement used among the cohort (45%). Magnesium was the most commonly reported mineral supplement (31%). The most commonly reported non-vitamin non-mineral supplement was fish oils (22%).
This study found that, overall, those taking vitamin D supplements had a lower HbA1c than those not taking vitamin D supplements. However, the dose of vitamin D made a difference. When comparing HbA1c levels between individuals taking doses of 1200 IU or more of vitamin D, the comparison showed that those in the higher intake groups had better glycemic control compared to those in the lower intake groups. This finding remained statistically significant after adjusting for several confounders, including age, BMI, season, and a number of self-management variables.
In summary, the authors found that,
“…in the comparisons between those supplementing with ≥30 and <30 μg, ≥40 and <40 μg, ≥50 and <50 μg, ≥60 and <60 μg and ≥70 and <70 μg, the glycaemic control was in all cases better in those with higher dosing. Furthermore, with increasing vitamin D dose, also the B-value was observed to decrease which could be suggestive of a dose–response.”
Previous Study finds Similar Relationship Between Vitamin D and HbA1c among Adolescents with T1D
A 2019 study among adolescents diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) found an inverse, linear correlation between the HbA1c values and vitamin D levels (as vitamin D levels increased, HbA1c levels decreased) for those with T1D. While this finding was statistically significant within the T1D group, there was no correlation in the healthy, non-T1D control group.
Learn more about the study here.
Check Out the Following Related Posts and Studies
Higher HbA1c Linked to Decline in Cognitive Function for Teenagers and Adults
 Could this be evidence of Type 3 Diabetes? 40-year-old adults with glucose levels at the higher end of the normal range have an increased risk of Alzheimer’s by 15% …
Could this be evidence of Type 3 Diabetes? 40-year-old adults with glucose levels at the higher end of the normal range have an increased risk of Alzheimer’s by 15% …
Read More
Analysis by Vitamin D Level: A 76% Decreased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Among those with Prediabetes
 Many individuals are unaware that they have prediabetes or are already diabetic. Watch this short video on a recent meta-analysis showing how vitamin D reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, and take steps to measure your status and reduce your risk!
Many individuals are unaware that they have prediabetes or are already diabetic. Watch this short video on a recent meta-analysis showing how vitamin D reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, and take steps to measure your status and reduce your risk!
Read More
New Meta-analysis Shows Significant Effect of Vitamin D on Regulating Insulin Resistance
 Studies have shown that the risk of developing insulin resistance and/or diabetes over time increases with lower vitamin D levels. Because of this observation, Lei et al. recently completed a meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 20 observational studies to more clearly define the relationship between vitamin D, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Read More
Studies have shown that the risk of developing insulin resistance and/or diabetes over time increases with lower vitamin D levels. Because of this observation, Lei et al. recently completed a meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 20 observational studies to more clearly define the relationship between vitamin D, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Read More
How Are Your Levels of HbA1c, Vitamin D and Others?
The Omega-3 Index measures the amount of EPA and DHA in your blood and tissues. Do you know what your Omega-3 Index is? Check yours along with your vitamin D and magnesium levels today as part of the vitamin D*action project, and add the Ratios for more about how to balance your Omega-3s and 6s!
Measure your:
- Vitamin D
- Magnesium PLUS Elements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- hsCRP (for Inflammation)
- HbA1c (for Blood Sugar)
- and more
Did you know that each of the above can be measured at home using a simple blood spot test? As part of our ongoing research project, you can order your home blood spot test kit to get your levels, followed by education and steps to take to help you reach your optimal target levels. Start by enrolling and ordering your kit to measure each of the above important markers, and make sure you are getting enough of each to support better mood and wellbeing!
Build your custom kit here – be sure to include your Omega-3 Index along with your vitamin D.
Start Here to Measure Your Levels