Published on November 1, 2019
Last month, October, was Breast Cancer Awareness Month, although here at GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute we prefer to focus on breast cancer prevention. To help educate the public on the effects of certain nutrients and breast cancer prevention, we created a series of posts focused on key research, with highlights from several published studies showing the effects of vitamin D and omega-3s on breast cancer risk. Today we are taking a look at magnesium and how it may play a role in reducing breast cancer risk as well.
Please share this informational series with all you know who may have or be concerned with getting breast cancer.
What about magnesium and breast cancer risk?
 Previous research has identified a relationship between magnesium and breast cancer risk. Magnesium has also been shown to play a role in the inflammatory response and in DNA and cell repair. There has been additional evidence showing a potential relationship between chronic inflammation, CRP levels, and the development of multiple types of cancer.
Previous research has identified a relationship between magnesium and breast cancer risk. Magnesium has also been shown to play a role in the inflammatory response and in DNA and cell repair. There has been additional evidence showing a potential relationship between chronic inflammation, CRP levels, and the development of multiple types of cancer.
To investigate the possibility that magnesium intake may directly affect breast cancer risk due to its role in regulating inflammation, Huang et al created a study in which they recruited 1050 breast cancer patients and 1229 controls (women without breast cancer) in China and collected information about dietary magnesium intake. A subgroup of randomly selected participants also had serum measurements of CRP and interleukin-6 (IL-6) taken as markers of inflammation. Potential confounders were adjusted for in the final analysis, including BMI, age of menarche, smoking, educational level, family history of cancer, physical activity, and income.
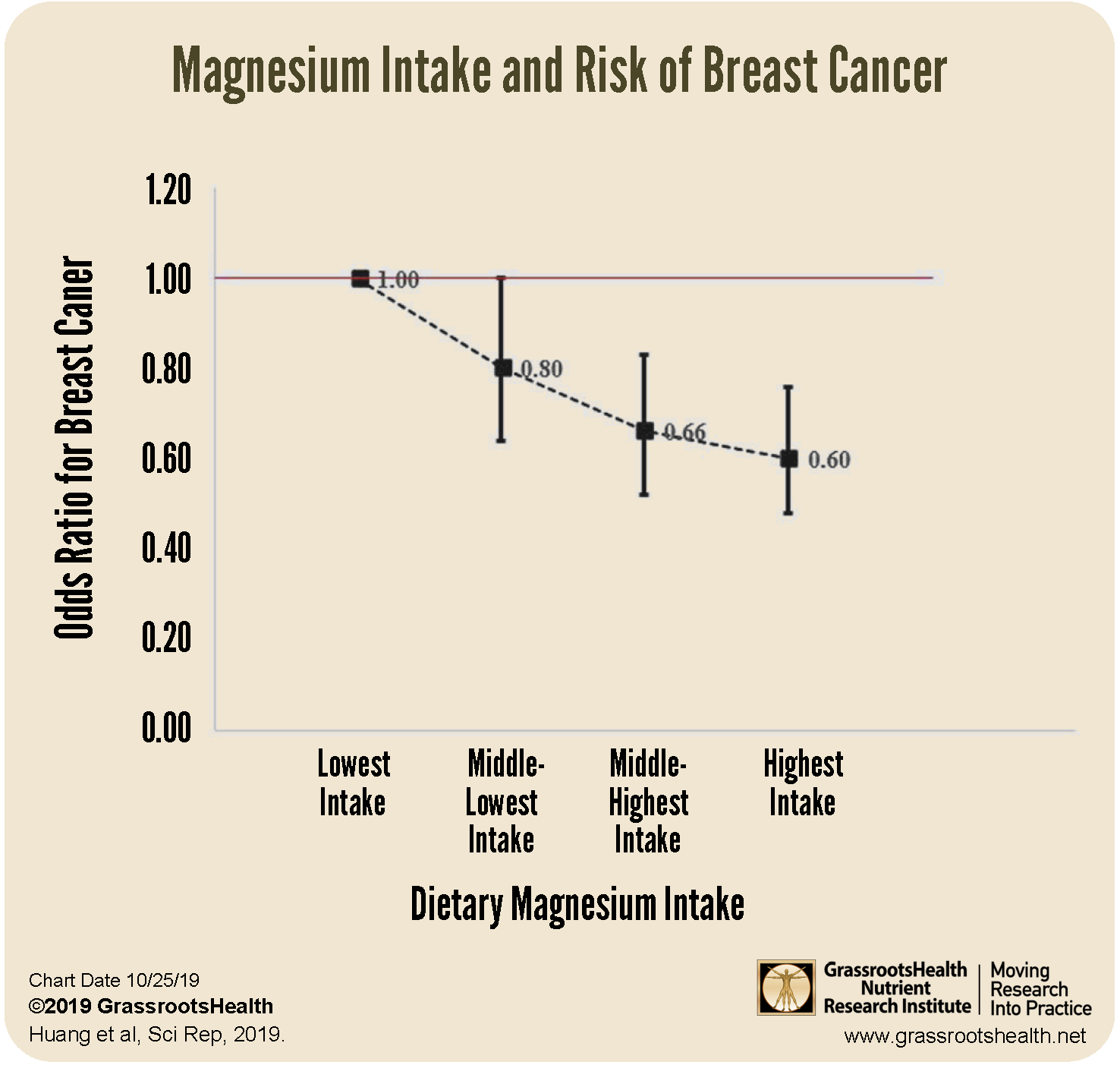
The chart above illustrates the dose response decrease in breast cancer risk with higher magnesium intake. There was a 40% decrease in breast cancer risk for those with the highest dietary magnesium intake vs the lowest (P<0.05). While the specific intake amounts for each group were not provided for this chart, the researchers also compared those ingesting at or above vs below 280 mg per day (the Estimated Average Requirement for Chinese residents) and found a 20% lower risk of breast cancer for those ingesting at least 280 mg per day (P=0.047).
The researchers also found that those with CRP levels less than 3000 ng/mL had an 30% lower risk of breast cancer than those with levels at or above 3000 ng/mL (P=0.037). Additionally, dietary magnesium was found to have both a direct association (via its role in inflammation and DNA and cell repair) and an indirect association (via its influence on CRP levels) with breast cancer risk.
Join the Study to Help Reduce Breast Cancer Incidence
Reduce Breast Cancer NOW! is a field trial of GrassrootsHealth using our methodology for moving nutrient research into practice. This model was developed and tested over 7 years, with over 10,000 participants, through the D*action project. All women can join this project to help demonstrate the effects of vitamin D on breast cancer prevention.
Donate to this project today!
Are you concerned that your nutrient levels may not be optimized for potential cancer risk reduction?
Make sure you know your vitamin D level (with a target of 40-60 ng/ml or 100-150 nmol/L) and Omega-3 Index (with a target of 8% or higher) levels, as well as your levels of essential nutrients, such as magensium. Through GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute, you can also test your inflammation levels, including your level of hsCRP. Find out your levels today! Log on to the shop (click the link below) to get your tests and see for yourself if your level can be improved.
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
Click Here to Access the Shop Page
How can I track my nutrient intake and levels over time?
To help you track your supplement use and nutrient levels, GrassrootsHealth has created an online tracking system called myData-myAnswers. For each specific supplement, you can track what days you take it, how much, and many other details. This will help you know your true supplemental intake and what patterns of use work for you to reach and maintain optimum nutrient levels. Check it out today!