Published on March 22, 2024
A new meta-analysis supports previous findings that vitamin D supplementation prior to COVID-19 infection greatly reduced risk of infection and ICU admission due to COVID-19
Key Points
- A new systematic review and meta-analysis looked at data from 19 different studies (including 7 randomized controlled trials and 12 analytical studies) with a total of 1,262,235 participants to see if vitamin D supplementation prior to the onset of COVID-19 infection was linked to improved outcomes
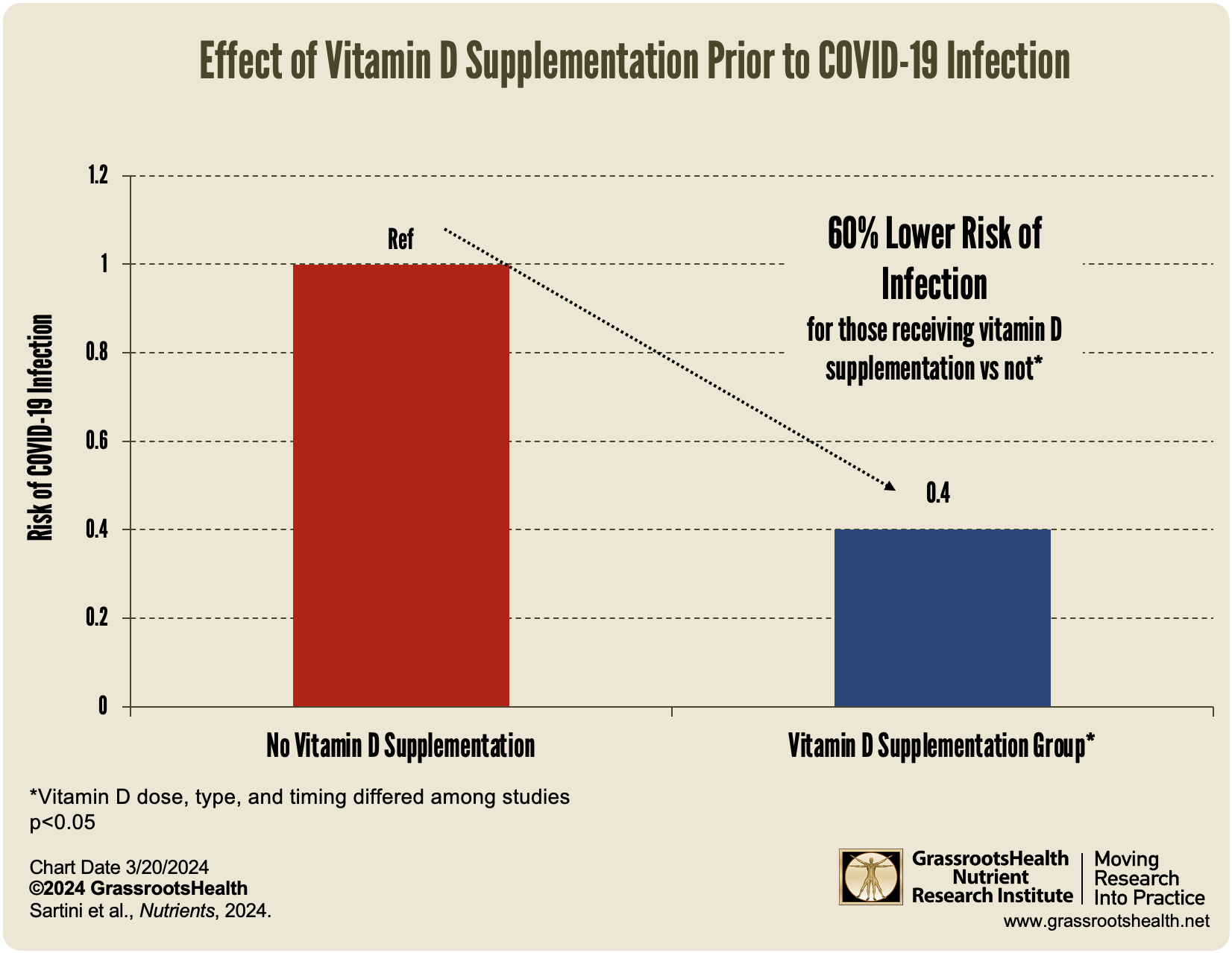
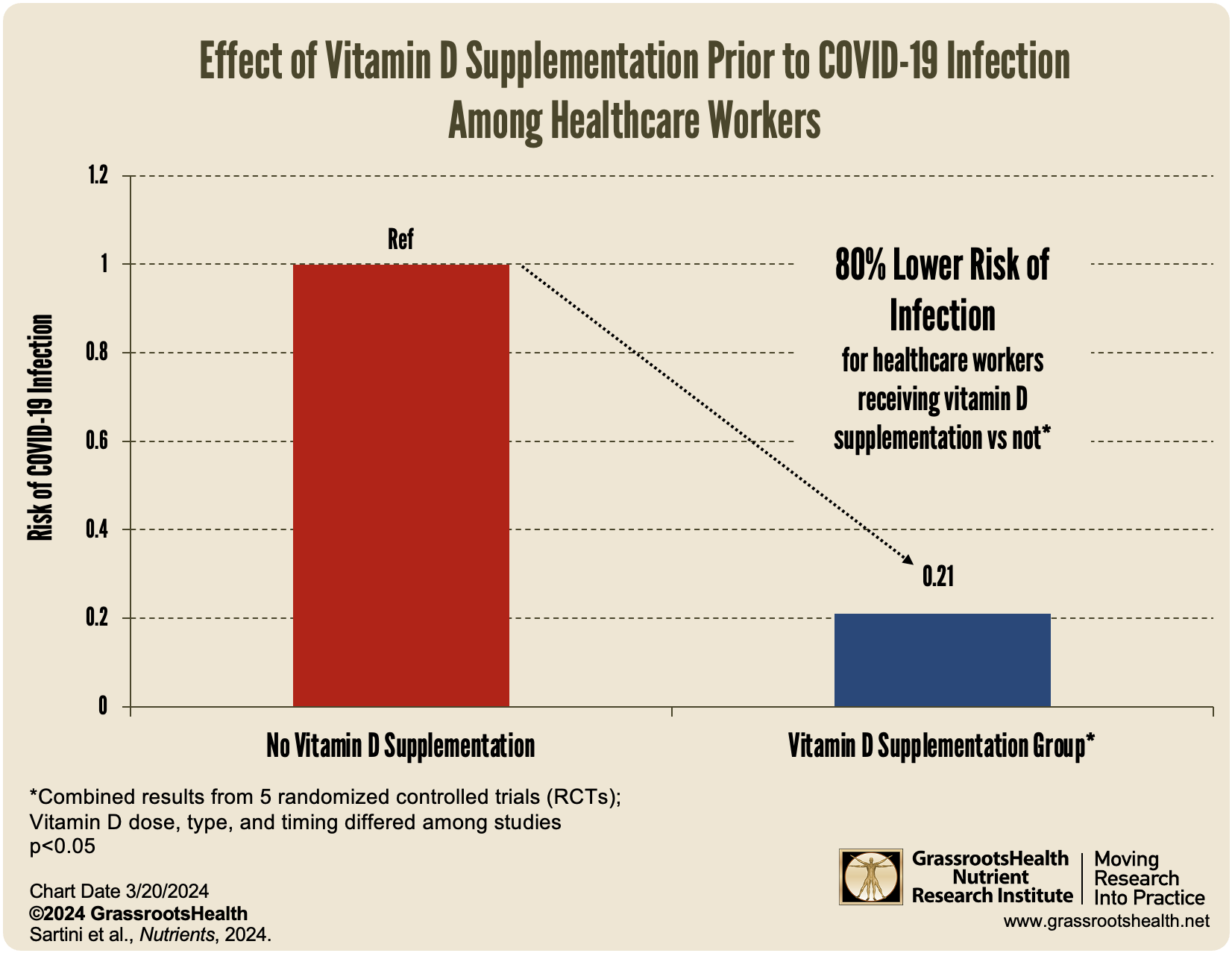
- The analysis of the seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs) combined found that vitamin D supplementation (of up to 5000 IU per day) was associated with a 60% decreased risk of COVID-19 infection; when only considering data from RCTs among healthcare workers (5 studies included), there was an impressive 80% reduced risk of infection.
- When analyzing data from the analytic studies only, there was an overall 40% reduced risk of COVID-19 infection and a 68% decreased risk of ICU admission due to complications of COVID-19 with prior vitamin D supplementation
 Vitamin D is a major and easily modifiable factor that helps reduce the incidence and severity of COVID-19. Many studies to date have demonstrated a reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, severity, and death with increased vitamin D levels, as well as with other important nutrients. Many of these studies are summarized in our Vitamin D & COVID-19: A Summary of Published Research eBook – FREE with any purchase when using the code eBookGift.
Vitamin D is a major and easily modifiable factor that helps reduce the incidence and severity of COVID-19. Many studies to date have demonstrated a reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, severity, and death with increased vitamin D levels, as well as with other important nutrients. Many of these studies are summarized in our Vitamin D & COVID-19: A Summary of Published Research eBook – FREE with any purchase when using the code eBookGift.
A new systematic review and meta-analysis published by Sartini et al. looked at data from 19 different studies (including 7 randomized controlled trials and 12 analytical studies) with a total of 1,262,235 participants to see if vitamin D supplementation prior to the onset of COVID-19 infection was linked to improved outcomes.
What did the study find?
First, it is important to note that the studies included in the analysis used different doses of vitamin D as well as different dosing frequencies, and not all studies measured vitamin D levels. Among the studies that measured vitamin D levels, the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was between 55-67%, while 27-30% of participants were vitamin D insufficient. Only 6-15% of participants in the studies that measured vitamin D levels had a level that was considered “normal.”
The analysis of the seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs) combined found that vitamin D supplementation (of up to 5000 IU per day) was associated with a 60% decreased risk of COVID-19 infection.
When only considering data from RCTs among healthcare workers (5 studies included), there was an impressive 80% reduced risk of infection.
One RCT among non-health care workers found no effect of vitamin D supplementation, however, the dose was only 400 IU per day.
When analyzing data from the analytic studies only, there was an overall 40% reduced risk of COVID-19 infection among those receiving vitamin D supplementation. There was also a 68% decreased risk of ICU admission due to complications of COVID-19 with prior vitamin D supplementation, based on 3 of the studies.
How do these Findings Relate to Previous Findings on Vitamin D and COVID-19?
A previous review by D’Ecclesiis et al. of 38 studies and 207,587 patients found that low vitamin D levels were associated with a significantly doubled increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, severe COVID-19, and COVID-19 death. This review
- Found a 118% increased risk of infection, a 138% increased risk of severe COVID-19 disease, and a 135% increased risk of death due to COVID-19 among those with low vitamin D levels compared to higher vitamin D levels
- Showed that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a 62% lower risk of severe COVID-19 disease and a 65% lower risk of death among those supplementing with vitamin D; an even higher risk reduction was found among patients who were older as well as those living at higher latitudes
Learn more about this study here.
Additional Studies on COVID-19, Vitamin D, and other Nutrients
 A number of studies by now, such as those included in our Vitamin D & COVID-19: A Summary of Published Research eBook, have provided much evidence showing the significant effect that vitamin D status has on COVID-19 disease progression and outcomes, where higher vitamin D levels can reduce the risk of infection and severity and help prevent death. Studies on vitamin D and other nutrients and how they affect COVID-19 and overall immune response can also be reviewed on this COVID-19 research summary page.
A number of studies by now, such as those included in our Vitamin D & COVID-19: A Summary of Published Research eBook, have provided much evidence showing the significant effect that vitamin D status has on COVID-19 disease progression and outcomes, where higher vitamin D levels can reduce the risk of infection and severity and help prevent death. Studies on vitamin D and other nutrients and how they affect COVID-19 and overall immune response can also be reviewed on this COVID-19 research summary page.
Have you taken action on this information yet, for yourself and those around you? Measure your vitamin D level if you haven’t already, and easily share this life-saving information with others. PLUS, get a copy of the Vitamin D & COVID-19 eBook FREE with any purchase when using the code eBookGift.
How Are Your Levels of Important Nutrients?
Do you know what your vitamin D level is? Check yours along with omega-3s, magnesium, and other levels today as part of the vitamin D*action project; add the Ratios for more about how to balance your Omega-3s and 6s!
Measure your:
- Vitamin D
- Magnesium PLUS Elements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- hsCRP (for Inflammation)
- HbA1c (for Blood Sugar)
- and more
Did you know that each of the above can be measured at home using a simple blood spot test? As part of our ongoing research project, you can order your home blood spot test kit to get your levels, followed by education and steps to take to help you reach your optimal target levels. Start by enrolling and ordering your kit to measure each of the above important markers, and make sure you are getting enough of each to support better mood and wellbeing!
Build your custom kit here – be sure to include your Omega-3 Index along with your vitamin D.
Start Here to Measure Your Levels