Published on May 19, 2020
 There is much research on the relationship between vitamin D and cancer incidence – but what about sunshine? Studies covered in a recent post on sunshine exposure and mortality illustrated the relationship between higher rates of sun exposure and a decreased risk of death from several diseases, including cardiovascular disease and cancer. Considering this and the steady rise in incidence of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer in younger populations, there is growing interest around the role of vitamin D and sunshine in reducing the risk of development and progression of different types of cancer.
There is much research on the relationship between vitamin D and cancer incidence – but what about sunshine? Studies covered in a recent post on sunshine exposure and mortality illustrated the relationship between higher rates of sun exposure and a decreased risk of death from several diseases, including cardiovascular disease and cancer. Considering this and the steady rise in incidence of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer in younger populations, there is growing interest around the role of vitamin D and sunshine in reducing the risk of development and progression of different types of cancer.
Low sunlight exposure associated with increased cancer risk
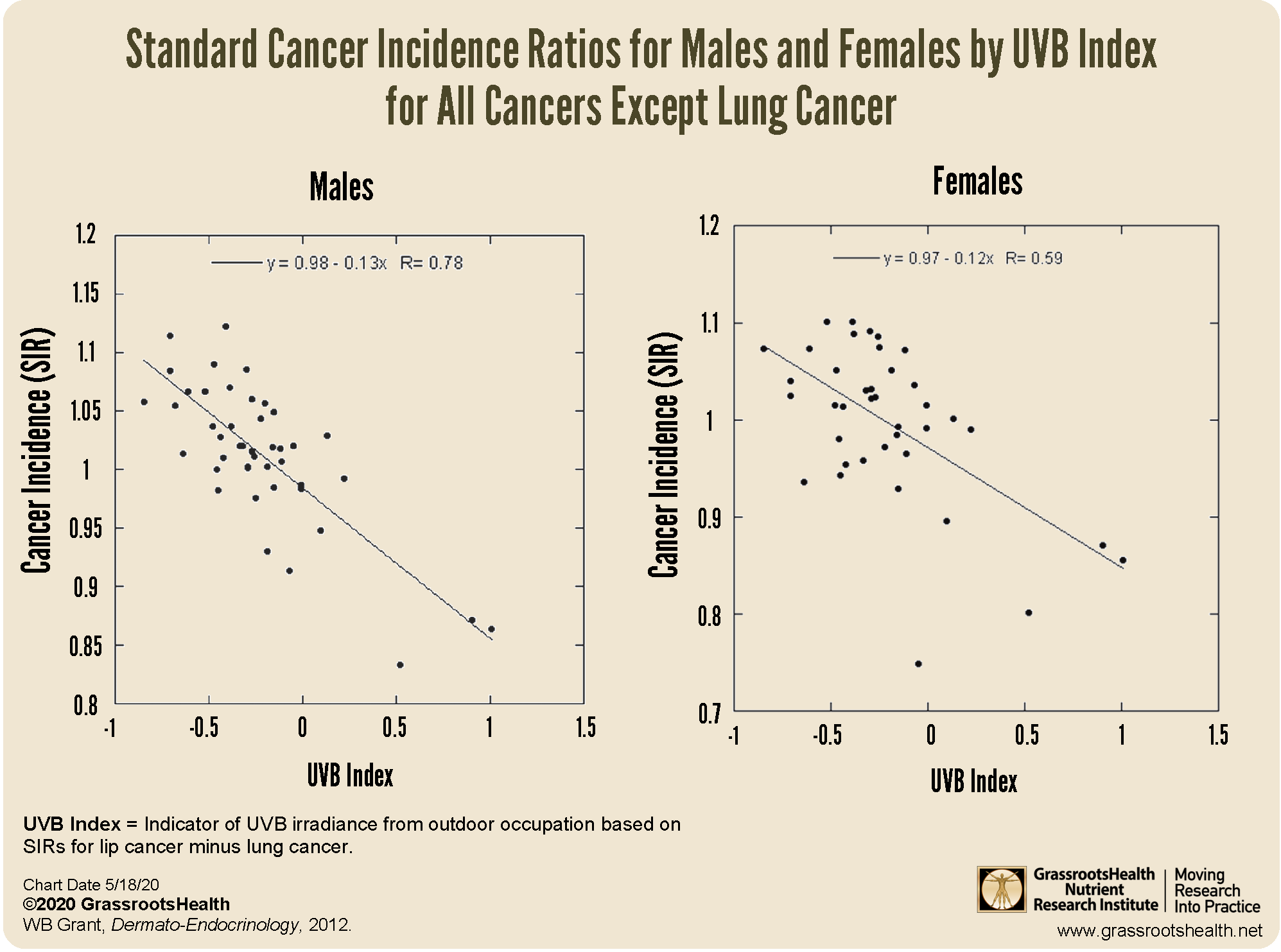
For a study published in 2012, Dr. William B. Grant looked at cancer data from five Nordic countries, between 1961 and 2005, to evaluate the relationship between solar UVB and cancer rates based on 54 different occupation categories. The occupation categories were further divided into those that were primarily outdoor versus those that were primarily indoor.
Findings differed among men and women, with a decreased incidence of several different types of cancer among those with higher UVB exposure. For men, 15 different cancers were significantly inversely correlated to UVB: bladder, breast, colon, gallbladder, kidney, laryngeal, liver, lung, oral, pancreatic, pharyngeal, prostate, rectal, small intestine cancer, and melanoma. For women, UVB was significantly inversely correlated to bladder, breast, colon and rectal cancer.
Sunshine and colorectal cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States in both men and women. Results from a study covered in a previous blog post found that people exposed to 2 or more hours of sunshine per day had a 19% lower risk of developing colorectal cancer compared to those who had less sun (P < 0.01).
Drs. Frank and Cedric Garland, both prominent figures in vitamin D and cancer research, were among the first to acknowledge the relationship between geographic location, sunshine exposure, and incidence of cancer. They, with their team of colleagues, published two now famous studies in The Lancet, a well-respected international medicine journal. Both studies showed markedly reduced incidence of colon cancer in populations with the highest intake of vitamin D and the highest serum concentrations of vitamin D. Additional studies describing the relationship between UVB exposure, sunlight, and vitamin D on the incidence of colon, breast, and ovarian cancer have also been published by the Garland brothers, with a recurring theme of decreased cancer risk with increased UVB and vitamin D.
Testing Vitamin D Levels is Important for Cancer Prevention Too
This sunshine month, as always, it is important to remember that getting regular, proper sun exposure, without burning, is essential to good health – for reasons beyond vitamin D. However, it is still important to know what your vitamin D levels are, especially when it comes to cancer prevention, as having a vitamin D level of at least 60 ng/ml may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer by up to 80%, compared to levels of 20 ng/ml or below.
Test today, and take the necessary steps to get your vitamin D level to your target range for health!
Do You Have Enough Vitamin D to Support a Healthy Immune System?
Do you know what your vitamin D level is? Be sure to test today to find out, and take steps to keep it within a target of 40-60 ng/ml or 100-150 nmol/L! Give your immune system the nutrients it needs to support a healthy you and protect yourself from unnecessary diseases.
Through GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute, you can also test your essential elements magnesium, copper, zinc and selenium, toxins such as lead, mercury and cadmium, as well as your omega-3 levels, inflammation levels and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level. Find out your levels today!
Create your custom home blood spot kit by adding any of the following measurements:
- Vitamin D (Required)
- Omega-3 Index (with or without Ratios)
- HbA1c (as a marker of blood sugar health)
- Magnesium (with or without additional Elements – copper, zinc, selenium, mercury, cadmium, lead)
- hsCRP (as a marker of inflammation)