Published on May 30, 2019
![]() The sun is essential to optimal health and well-being. Sensible sun exposure could greatly improve health by improving vitamin D status for disease reduction, initiating the release of nitric oxide for heart health, stimulating the production of serotonin and beta-endorphins for mood enhancement and pain relief, and regulating circadian rhythms. Mid-day sunlight is the most important for vitamin D production, but it is important to start gradually and personalize your sun exposure based on skin type and UV Index so that you do not burn. Even though May is coming to an end, we encourage you to get outside and continue celebrating the sun this summer!
The sun is essential to optimal health and well-being. Sensible sun exposure could greatly improve health by improving vitamin D status for disease reduction, initiating the release of nitric oxide for heart health, stimulating the production of serotonin and beta-endorphins for mood enhancement and pain relief, and regulating circadian rhythms. Mid-day sunlight is the most important for vitamin D production, but it is important to start gradually and personalize your sun exposure based on skin type and UV Index so that you do not burn. Even though May is coming to an end, we encourage you to get outside and continue celebrating the sun this summer!
Below is a list of the topics we covered during Sunshine Month (May); be sure to check out any that you missed.
May is Sunshine Month!
How much time do GrassrootsHealth participants spend in the mid-day sun?
Benefits of sun exposure: vitamin D and more!
Lower colorectal cancer risk with increased sun exposure
Disease prevention with the sun: Multiple Sclerosis
Lower type 1 diabetes and cancer rates associated with higher UVB
Better cognitive function with increased sun exposure
The healing power of the sun: a history of phototherapy
Vitamin D and skin cancer
Assessing sun exposure: skin type, UV Index, and duration
All about the UV Index
Can you achieve an optimal vitamin D level with the sun?
Vitamin D levels of indoor tanners
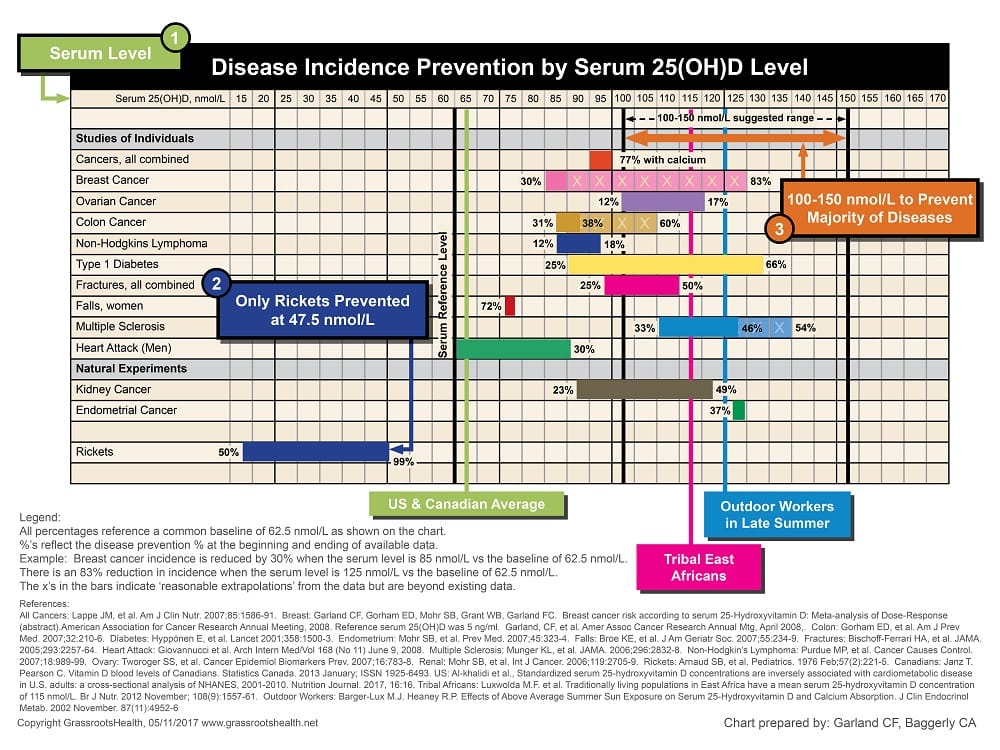
Disease prevention with vitamin D levels at 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L)
The chart below shows that the incidence of many diseases could be significantly reduced with vitamin D levels between 40 ng/ml and 60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L) compared to 25 ng/ml (62 nmol/L). Also shown on the chart is the average vitamin D level of those in the United States and Canada as well as groups of people with consistent sun exposure, the latter being in the optimal range for health.
Click to Download & Print – ng/ml and nmol/L Versions
Outside Magazine’s “Is Sunscreen the New Margarine” – a vitamin D expert’s perspective, by Dr. Cedric Garland
In January, an article was published in Outside magazine entitled “Is Sunscreen the New Margarine.” It points out that years of advice about people needing to apply chemical sunscreens whenever they are outdoors in the sun is based on very limited science with regard to melanoma. Chemical sunscreens are dyes that absorb some bands of UV, including UVB. This band is what allows your body to make vitamin D from cholesterol. It is also the trigger for the human photoprotective response which includes thickening of the outermost layer of the skin known as the stratum corneum, synthesis of melanin that absorbs UV and visible light, and increased synthesis of enzymes that repair DNA that may be reconfigured by sunlight. This normal skin response helps prevent melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer. This protective response of the skin is prevented by wearing sunscreens. So be careful about choice of sunscreens, and do not use them if trying to make vitamin D3 from sunlight conversion of cholesterol in the skin.
 It is inconvenient and can be painful to experience a sunburn, an experience that can often be prevented with the use of sunscreens. Sadly, though, harm to the basal layer of the skin can happen with prolonged exposure to the sun whether or not the person is wearing a chemical sunscreen. This is because UVB, the band of UV that produces the symptom of reddening and painful sunburn, is only 5% of total noon solar UV energy. Until recently, most sunscreens have blocked only that tiny 5%. The result is that most chemical sunscreens create a false sense of security with regard to melanoma, although they help with control of less serious forms of skin diseases such as actinic keratosis and, to some degree, basal and squamous cell skin cancers.
It is inconvenient and can be painful to experience a sunburn, an experience that can often be prevented with the use of sunscreens. Sadly, though, harm to the basal layer of the skin can happen with prolonged exposure to the sun whether or not the person is wearing a chemical sunscreen. This is because UVB, the band of UV that produces the symptom of reddening and painful sunburn, is only 5% of total noon solar UV energy. Until recently, most sunscreens have blocked only that tiny 5%. The result is that most chemical sunscreens create a false sense of security with regard to melanoma, although they help with control of less serious forms of skin diseases such as actinic keratosis and, to some degree, basal and squamous cell skin cancers.
If you choose to wear a sunscreen after a period of sun exposure (lasting 10-15 minutes), it should be a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVB and UVA or, better yet, an inert clay, such as a formulation containing natural titanium dioxide or zinc oxide. Test even these on a small portion of your skin first, to be sure you are not sensitive to even these clay sunscreens.
The Outside article also mentioned that a recent clinical trial of vitamin D, the VITAL trial, found “no impact on cancer.” What the article does not mention is that the study did find a 25% lower risk of fatal cancer in people given vitamin D3, a positive finding, when the vitamin D was given a year to work. This is an example of writers placing undue reliance on headlines from the latest study published, and neglecting the details in the study. Additionally, there was no mention of previous worthy studies that have conclusively confirmed the finding of benefit of vitamin D3 against cancer. These prior studies include a meticulous study by Drs. Joan Lappe, the late Dr. Robert M. Heaney, and their colleagues at Creighton University that found almost 80% reduction in incidence of cancer in women who consumed vitamin D3 and calcium (1,100 IU/day of vitamin D3 and 1500 mg/day of calcium). This study established with considerable finality that vitamin D3 and calcium prevent the majority of cancer in women. A follow-up study found a substantial but weaker reduction. The powerful reduction in incidence of cancer was confirmed in a cohort study by GrassrootsHealth that pooled Creighton University cohort data with data from the GrassrootsHealth cohort and found an approximately 65% reduction in all cancers in people whose serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D was at least 40 ng/ml. Hooray for vitamin D against cancer!
Are you using UV or sun exposure as a source of vitamin D?
Is UV or sun exposure helping to improve your vitamin D level? Make sure you know your vitamin D level, and see if you are in the target range of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L). Find out your levels today! Log on to the shop (click the link below) to get your tests and see for yourself if your levels can be improved. Use coupon code SunMonth to receive 15% off during Sunshine Month only!
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
Click Here to Access the Shop Page
How can I track my UV, sun exposure and my vitamin D levels?
To help you track your UV and sun exposure and vitamin D levels, GrassrootsHealth has created an online tracking system called myData-myAnswers. You can also track your dietary intake and supplement use to see how both sun exposure and vitamin D from food and supplements impact your vitamin D levels and your health. Check it out today!