Published on March 14, 2022
March is Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month – A great time to spread awareness of the significant influence vitamin D has on cancer rates and survival, especially colorectal cancer!
Key Points
- Vitamin D has many cancer-fighting functions within the body, and evidence associating vitamin D and cancer is so strong that vitamin D is now thought to be a causal factor in the risk-reduction of most types of cancer.
- A GrassrootsHealth study found that women with a mean vitamin D level of at least 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L) had a 71% lower risk of all invasive cancers combined, excluding skin cancer, compared to women with levels below 20 ng/ml (<50 nmol/L)
- Several studies have shown a significant relationship between vitamin D and the risk of disease progression and death among colorectal cancer patients

The evidence associating vitamin D and cancer is so strong that vitamin D is now thought to be a causal factor in the risk-reduction of most types of cancer. Causation can be determined using a set of scientific guidelines called Hill’s criteria for causality, which looks at data based on the strength of association, consistency between studies, temporality, biological gradient, plausibility, coherence with known scientific facts, experiment, and analogy. Two separate publications (WB Grant and Mohr et al.) have confirmed vitamin D as a causal risk-modifying factor for most cancers using Hill’s criteria.
How Does Vitamin D Help Fight Cancer?
Vitamin D has many anti-cancer functions, including:
- Inhibits cancer cell growth and proliferation
- Reduces cancer metastasis
- Stimulates maturation of healthy cells (differentiation)
- Induces death of cancer cells (apoptosis or programmed cell death)
- Prevents blood vessel growth in tumors (angiogenesis)
- Prevents inflammation associated with cancer
- Reduces the risk of incidence and/or death due to cancer
More details on how vitamin D fights cancer can be found in this detailed post, Anticancer Effects of Vitamin D. You can also download, print and share our Cancer Prevention with Vitamin D brochure here.
GrassrootsHealth Analysis Shows 71% Lower Cancer Risk
In April 2016, GrassrootsHealth partnered with leading vitamin D and cancer researchers Drs. Garland, Gorham, Heaney, and Lappe to publish Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations ≥40 ng/ml Are Associated with >65% Lower Cancer Risk: Pooled Analysis of Randomized Trial and Prospective Cohort Study, a paper focused on achieved vitamin D serum levels and cancer incidence. Data was combined for women 55 and older from our GrassrootsHealth cohort (N = 1,135, median serum level = 48 ng/ml or 120 nmol/L) and the cohort of a previously published randomized controlled trial (RCT) of vitamin D and calcium supplementation with respect to cancer (Lappe RCT paper; N= 1,169, median serum level = 30 ng/ml or 75 nmol/L).
In the analysis, without adjusting for other risk factors, we found that women with a mean vitamin D serum level greater than or equal to 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L) had a 71% lower risk of cancer than women with serum levels <20 ng/ml (<50 nmol/L; P-value = .02). This was for cancer incidence over a median of 3.9 years for all invasive cancers combined, excluding skin cancer.
What About Vitamin D and Colorectal Cancer?
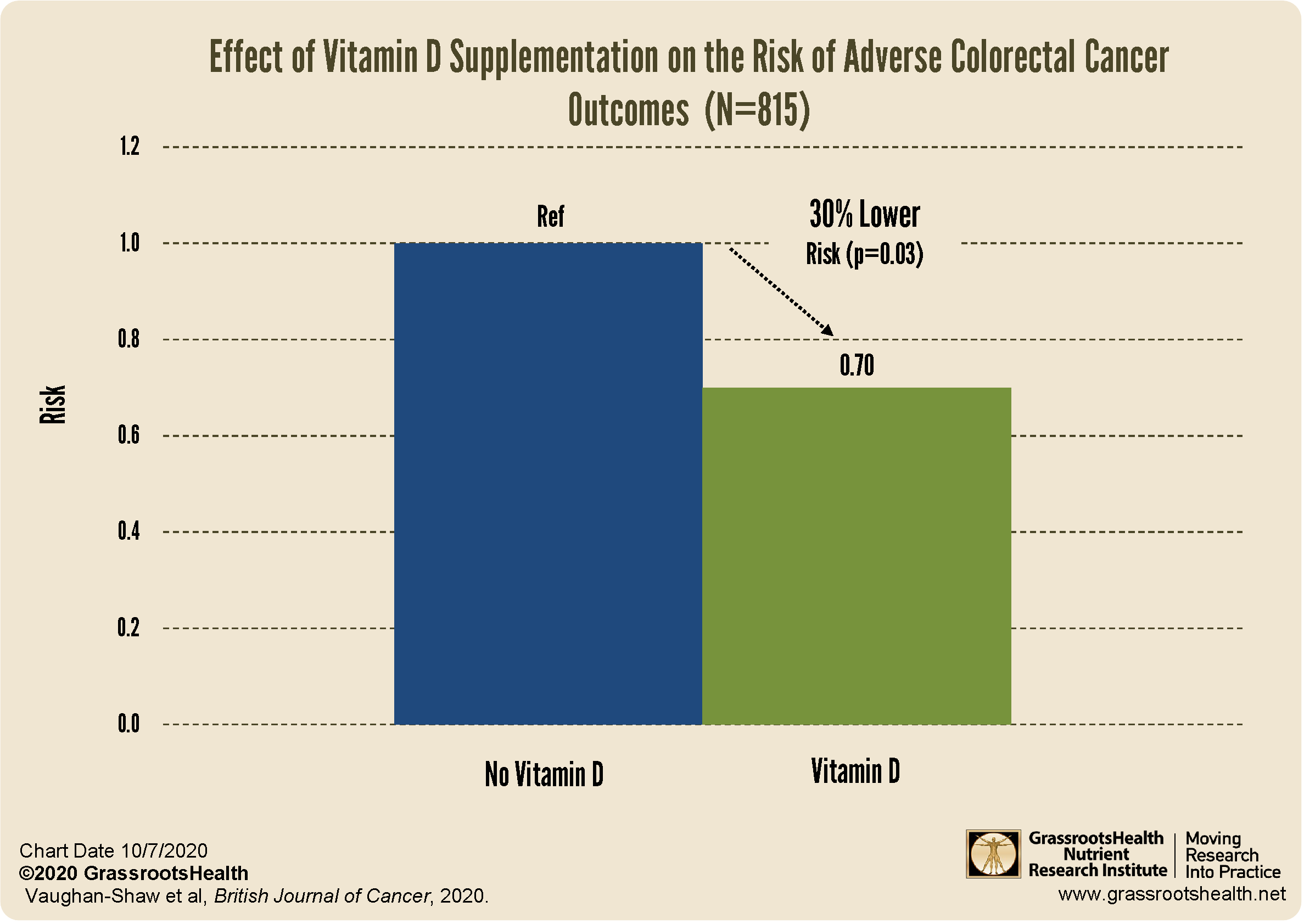
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer world-wide and affects millions of lives each year with approximately 860,000 deaths annually. Research on vitamin D and colorectal cancer specifically has shown a
30% Overall Reduction in Disease Progression or Death from colorectal cancer among those who supplemented with vitamin D
(Vaughan-Shaw et al., 2020 Meta-analysis)
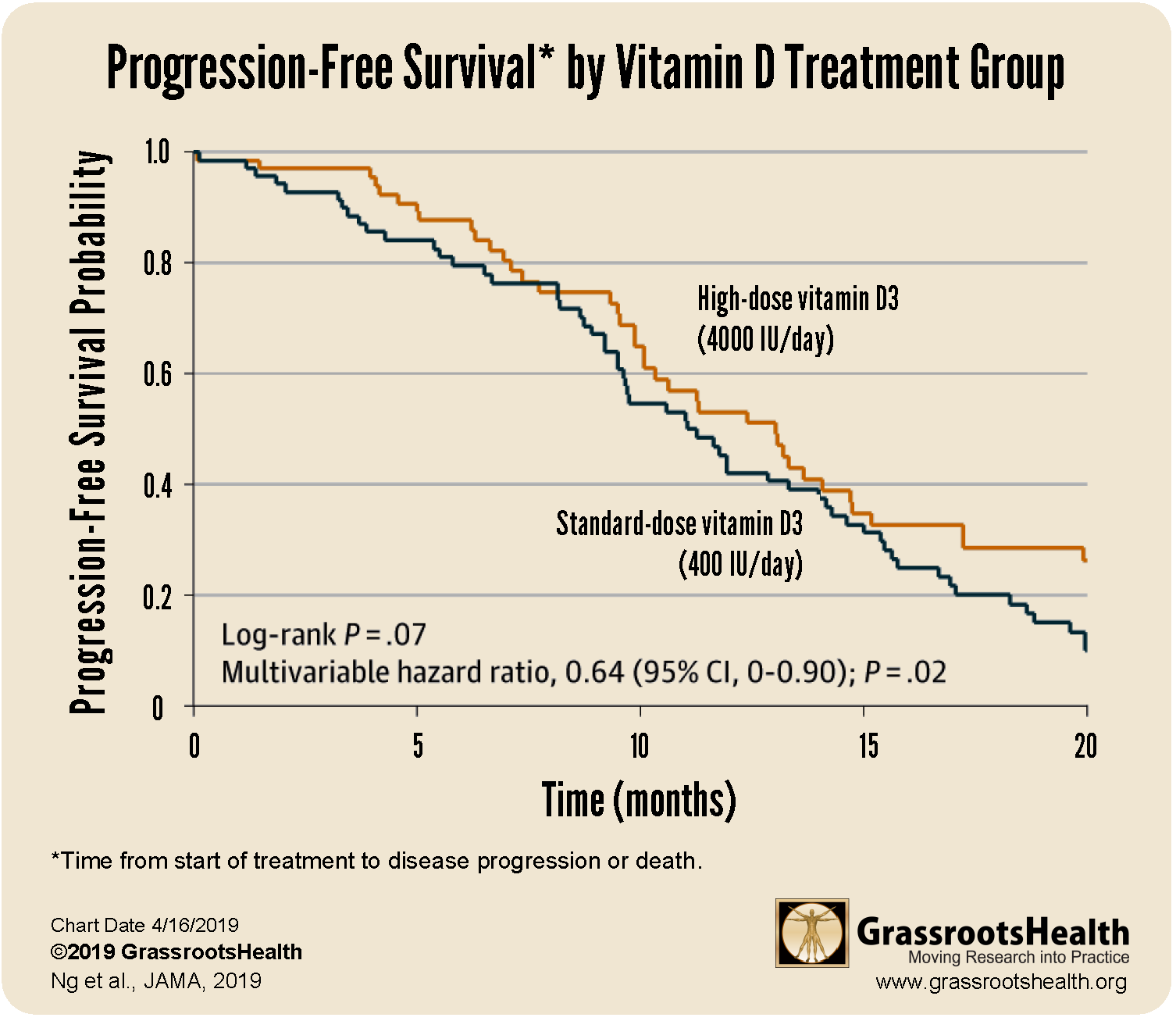
36% Lower Risk of Disease Progression or Death among those taking a higher dose of vitamin D [8,000 IU/day of vitamin D for 14 days then 4,000 IU/day, average vitamin D level of 35 ng/ml (87 nmol/L)] than those in the lower dose group [400 IU/day, average vitamin D level 19 ng/ml (47 nmol/L)]
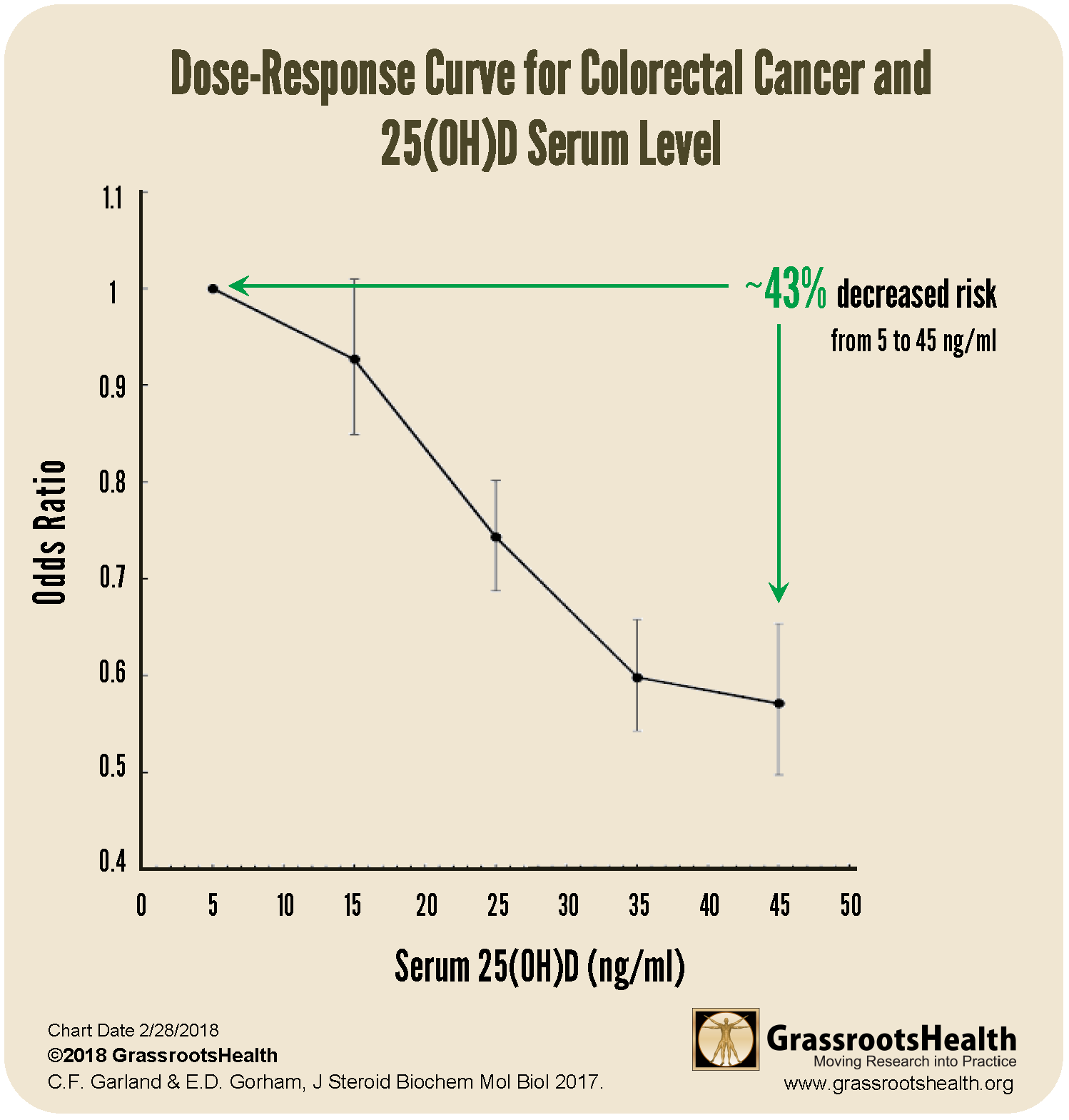
43% Decreased Risk of Colorectal Cancer with a higher vitamin D level [45 ng/ml vs 5 ng/ml (112 nmol/L vs 13 nmol/L)]
(Garland & Gorham, 2017 meta-analysis)
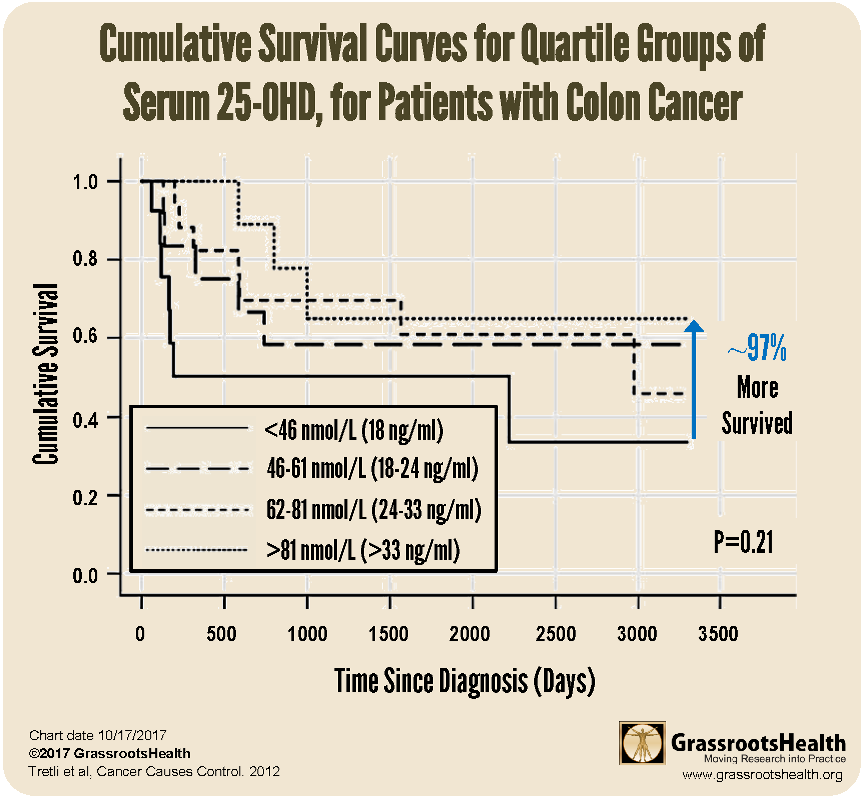
97% More Colorectal Cancer Patients Survived when their vitamin D level was at least 33 ng/ml (81 nmol/L) compared to less than 18 ng/ml (46 nmol/L)
Co-Factors Important for Colorectal Cancer
Magnesium is an important co-nutrient for vitamin D! A study by Gorczyca et al. found a significantly lower risk of colorectal cancer among postmenopausal women whose total daily magnesium intake was greater than 400 mg/day.
Sunshine is good for you too! A study by Valles et al. found a 19% lower risk of colorectal cancer for participants who reported sun exposure of 2 or more hours per day compared to 1-2 hours per day.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need? Find Out with Your Home Test!
 Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Choose which additional nutrients to measure, such as your omega-3s and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. With measurement you can then determine how much is needed and steps to achieve your goals. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Choose which additional nutrients to measure, such as your omega-3s and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. With measurement you can then determine how much is needed and steps to achieve your goals. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Enroll in D*action and Test Your Levels Today!