Published on December 7, 2020
The Role of Vitamin D in Seasonal Affective Disorder
 This time of year, the days are short and for those who live further north that means it is dark when you start your day and dark again by the time you drive home at the end of the day. The change in season signals building snowmen, skiing and sledding down the nearest hill for some. For others, it can start to look pretty bleak.
This time of year, the days are short and for those who live further north that means it is dark when you start your day and dark again by the time you drive home at the end of the day. The change in season signals building snowmen, skiing and sledding down the nearest hill for some. For others, it can start to look pretty bleak.
One in ten Americans suffer from a recurring depression called Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) for which their symptoms often start in late fall or early winter when the days are short, and go away in the spring when the days lengthen.
While it is not known what the exact cause of SAD is, the risk is much higher for people who live further from the equator, where the length of the days varies more greatly throughout the year. Women are three times more likely to develop SAD than men, and younger people are also at higher risk.
The Link Between Vitamin D and SAD
Light therapy, exposure to artificial UV lamps, is an effective treatment for people with SAD, improving symptoms by 50-80%. Despite research, we’re unsure how sunlight improves the symptoms of SAD. At first, researchers hypothesized that light therapy helped with melatonin metabolism; however, subsequent investigation failed to support this hypothesis. Now, some researchers have suggested that the increased vitamin D levels resulting from light therapy may be responsible for improved mood in people with SAD.
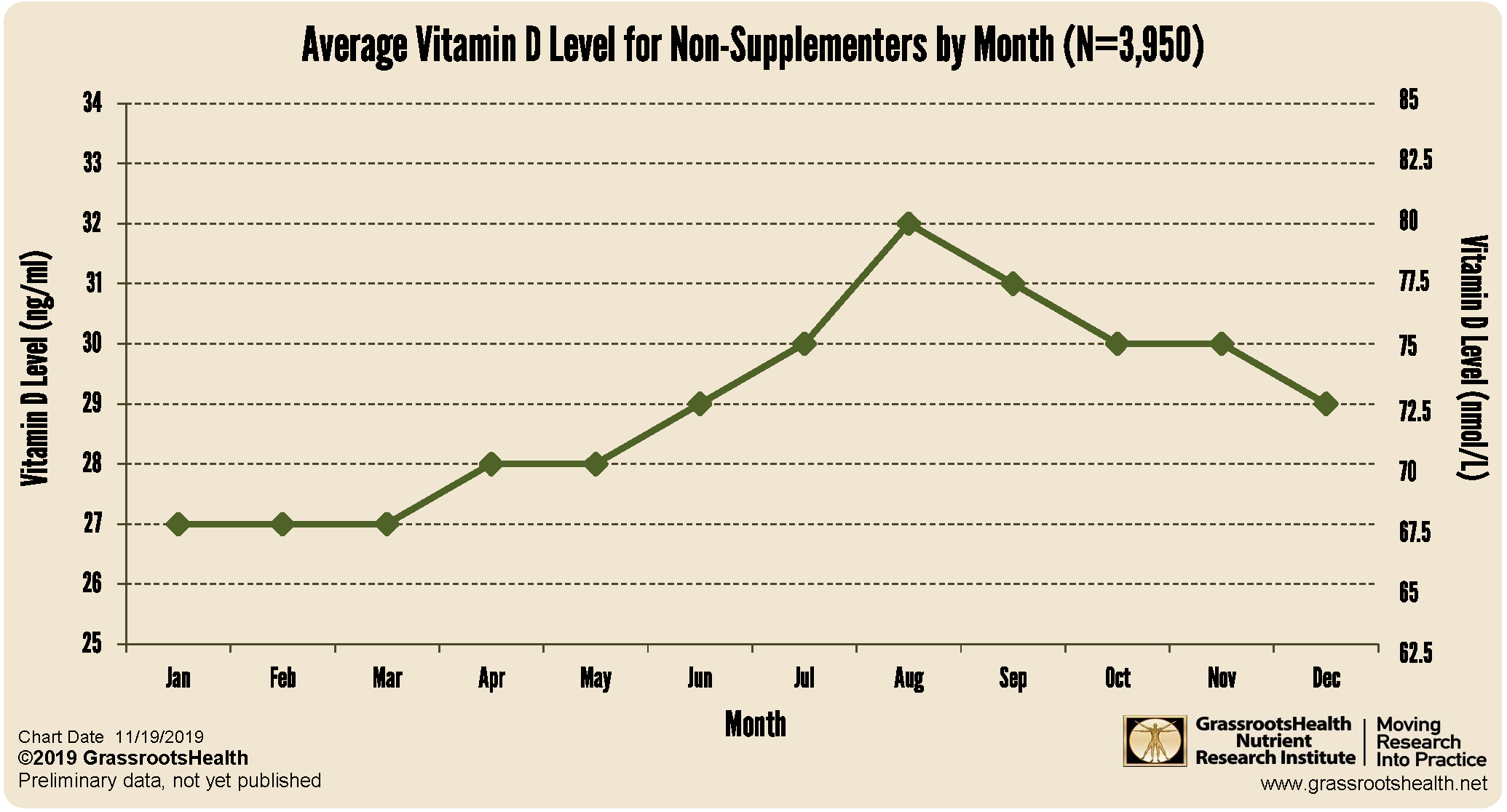
The “sunshine” vitamin is known to vary by season in people who live further away from the equator because they are not able to make vitamin D in the winter months from sunshine. The angle of the earth tilts and reduces the spectrum of sunlight such that the amount of ultraviolet (UV) B rays, which are responsible for vitamin D production in the skin, become scarce or unavailable during the day. We have previously reported on the seasonal variation in vitamin D levels using data from NHANES as well as GrassrootsHealth participants, as illustrated in the chart below.
How might vitamin D work to affect seasonal depression? — Vitamin D and the Brain
Widespread throughout the brain and central nervous system are the enzymes required to make active vitamin D [1,25(OH)2D], and vitamin D receptors (VDR), indicating that these cells can make and use vitamin D. This includes the hippocampus, a region of the brain important for learning and consolidation of memories, and which has also been implicated in the development of depression.
Vitamin D regulates factors called “neurotrophins” which signal brain cells to grow, mature and survive. For example, vitamin D is essential for the release of nerve growth factor (NGF) that is necessary for hippocampal neurons to survive. More directly, vitamin D plays a role in the production of serotonin and dopamine, the “happy chemicals” in the brain that are often low when someone has depression. Vitamin D regulates immune cells in the brain, called glial cells. In addition, animal and laboratory studies suggest vitamin D protects neurons and reduces inflammation.
Feeling Better with Vitamin D
Treatments for SAD include light therapy, supplementation with vitamin D, psychotherapy, and medications (antidepressants).
In a meta-analysis including 15 randomized controlled trials, Spedding assessed the effect of vitamin D supplementation for depression. He found that in studies that demonstrate a change in vitamin levels, vitamin D supplementation reduced depressive symptoms with an effect size that was comparable to that of anti-depressant medication.
Once again we find that maintaining vitamin D blood levels in the target range of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L) is important for health, both physical and mental.
Ensure Vitamin D Levels of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L) for You, Your Children, Loved Ones
Correcting a vitamin D deficiency at any age and any time of life decrease potential disease severity and improve outcomes! Test your vitamin D level today, learn what steps to take to improve your level, and take action to achieve and maintain a vitamin D level of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L).
Using the GrassrootsHealth Custom Kit Builder, you can create a test kit that measures your status of vitamin D and other important nutrients (such as omega-3s, zinc and magnesium), as well as your CRP level to measure inflammation. Click here to build and order your test kit today – measure your status and take the steps necessary to improve them if needed; make an impact on your health today and for your future! When you know what your levels are, you can determine next steps to take and how much supplementation may be needed if you are not at your target levels.