Published on May 19, 2023
The latest research on why getting sensible sunshine exposure is important for your mental and emotional wellbeing
Key Points
- In addition to producing vitamin D, exposure to sunlight results in the release of other chemicals that promote mood enhancement, relaxation, pain relief, and other mental-emotional benefits; these chemicals include beta-endorphins, nitric oxide, melatonin, serotonin, and dopamine
- When the skin is exposed to UVB, beta-endorphins (the endogenous opioids made in the body) and vitamin D are produced simultaneously, suggesting a “reward” for UV-induced vitamin D synthesis when vitamin D levels are low, during which time a greater amount of beta-endorphins are released upon exposure to UVB
- Participants in a study on cognitive health with the highest sun exposure had higher average mental state scores of cognitive function compared to participants with medium or low exposure; this study concluded that long-term high sun exposure throughout life could reduce the risk of cognitive impairment in the later years of life
Research has shown a definite link between higher vitamin D levels and improved cognitive health and mental-emotional wellbeing. For this reason, it makes sense that higher amounts of UVB from sunshine exposure, which generates vitamin D in the body, would also be related to improved mood and cognition.
However, there are so many ways through which exposure to sunlight can boost our mood and benefit our mind, besides those related to increased vitamin D levels!
 What happens in your body when it is exposed to sunlight?
What happens in your body when it is exposed to sunlight?
Watch this snippet of a video interview with Dr. Michael Holick, as he describes some of the reactions that happen within the body when it is exposed to sunlight.
 Can the benefits of sunshine exposure be replaced by a pill?
Can the benefits of sunshine exposure be replaced by a pill?
Watch this snippet of a video interview with Dr. Michael Holick, as he describes the multiple benefits of sunshine exposure, and why the health benefits of sunshine cannot be replaced.
Sunlight Initiates the Release of “Feel-Good” Chemicals in the Body
In addition to producing vitamin D, sunlight or UVB exposure results in the release of beta-endorphins, which are naturally occurring opioids that promote mood enhancement, relaxation, and pain relief. Nitric oxide, which is produced upon exposure to UVA from sunlight, has been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, resulting in decreased anxiety and depression. The release of melatonin and serotonin is also prompted with sun exposure, both of which are associated with sleep regulation, improved mood, and easing anxiety.
Dopamine is another chemical in the body that is released upon exposure to sunshine. Dopamine, AKA the “feel-good neurotransmitter,” is known to boost mood and motivation, and is also linked to reduced depression and anxiety. A study evaluating the correlation between dopamine and sunshine, by Tsai et al., found that dopamine receptor availability was significantly greater among participants with the highest amount of sunshine exposure compared to the lowest, indicating a sensitivity of the dopamine system to variations in the amount of sun exposure a person gets.
Built-In Reward System in the Body for Sun-Seeking Behavior and UVB-Induced Vitamin D Synthesis
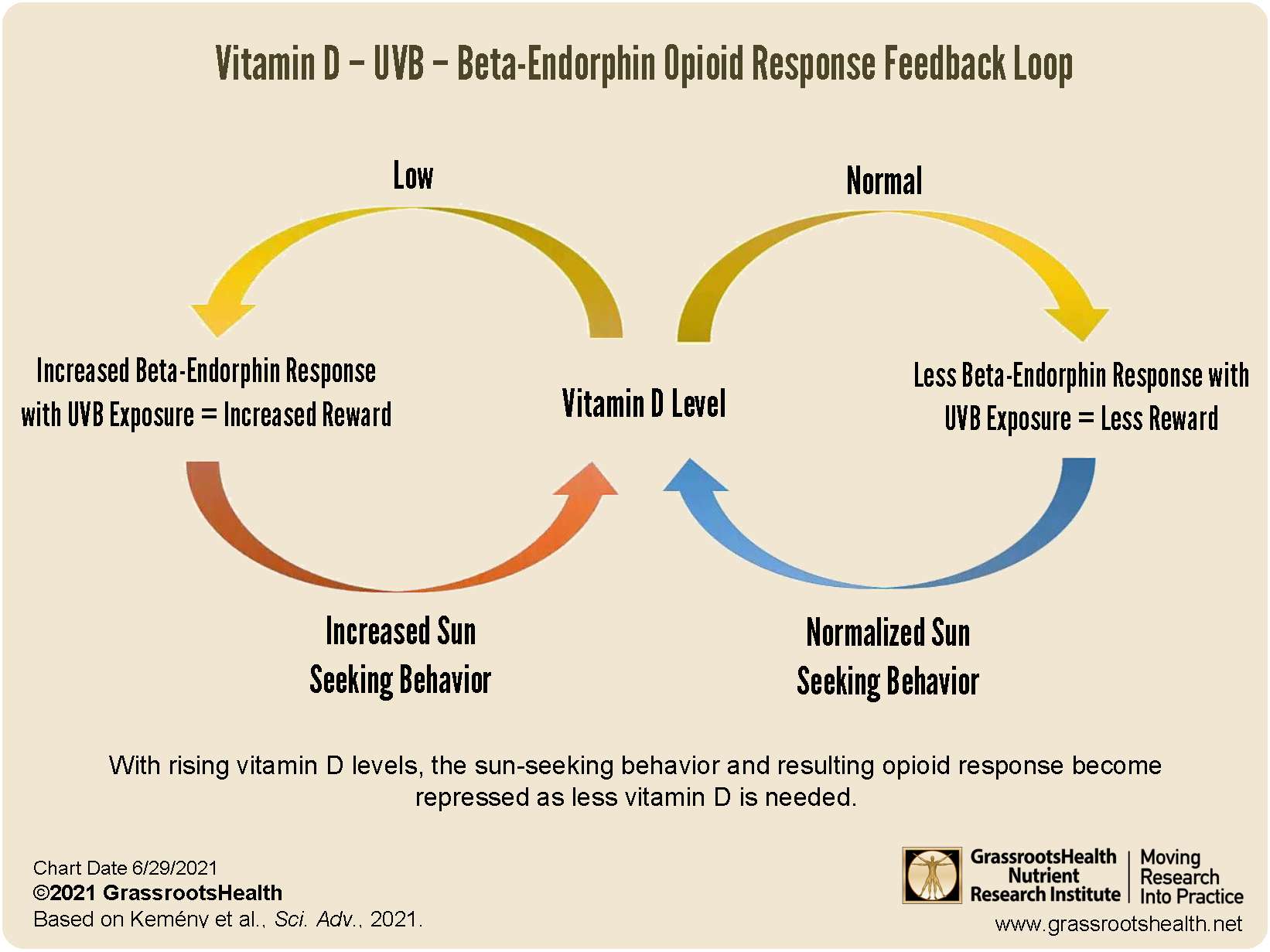
Recent research has identified an “endogenous opioid-mediated addiction-like pathway,” or a built-in feedback loop between vitamin D levels and sun seeking behavior, triggered by the UV-induced release of beta-endorphins. When the skin is exposed to UVB, beta-endorphins (the endogenous opioids made in the body) and vitamin D are produced simultaneously. The suggested benefit is to provide a “reward” for UV-induced vitamin D synthesis when vitamin D levels are low, during which time a greater amount of beta-endorphins are released upon exposure to UVB. As vitamin D levels rise, the sun-seeking behavior and resulting opioid response become repressed as less vitamin D is needed, representing a dose-dependent relationship between sun-seeking behavior, opioid response, and vitamin D levels.
There are even studies showing how vitamin D deficiency can be a contributing factor to opioid addiction, such as a study by Kemeny et al., which reviews how the intake of opioid drugs bypasses vitamin D production and the proposed feedback-control loop that is managed by vitamin D levels – which is hypothesized to contribute to continued opioid seeking behavior and resulting addiction. Using mouse models to help explain their hypothesis, the authors found that
- vitamin D deficiency increased UV radiation-induced endogenous pain relief and reward
- vitamin D deficiency did increase the UV/opioid reward, likely to maximize vitamin D synthesis, which normalized with the correction of vitamin D levels
- and more
Other Ways Sunshine and UVB Exposure Affect Mental Health
Lower Risk of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Limited or minimized sunshine exposure has also been associated with and increased risk of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). A 2022 study by Al Anouti et al. found such an association among female college students who practiced more sun avoidance habits that minimized their exposure to sunshine; in fact, the score used to assess sun exposure habits was a strong predictor of GAD status. The risk of GAD was also increased among women with a low dietary intake of vitamin D, and those with a history of vitamin D deficiency.
“The findings showed clear evidence that sun avoidance behaviors are strongly associated with an elevated risk of generalized anxiety disorder…”
Better Mood and Improved Sense of Wellbeing
Studies have correlated increased levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) with major depressive disorder, and cortisol with immune and mood imbalances. A study by Toledo et al. found an improvement in mood and wellbeing with narrow-band UVB exposure. The study looked at whole-body exposure to narrow-band UVB and its impact on mood, as well as resulting levels of vitamin D, interleukin-6 (IL-6), cortisol, and beta-endorphins (B-END). Mood was scored based on satisfaction, tiredness, wellbeing and irritation, with higher scores representing worse moods. Participants experienced significant improvements in mood over the five days following NB UVB exposure. Both vitamin D and cortisol levels were correlated with the baseline mood state, and from beginning to end of the study, vitamin D levels increased while IL-6 levels decreased.
Improved Infant Motor Development and Postpartum Depression
A study by Zhang et al. found that infants receiving vitamin D (400 IU/day) plus sunlight had better motor development scores and lower cortisol levels over the next two months compared to infants only taking vitamin D supplements (400 or 1000 IU/day) or the control group. Infants in the highest sun exposure group (7-14 hours/week) achieved the best scores and had the lowest cortisol levels.
Further, mothers who received sunlight exposure had improved depression scores and lower cortisol levels compared to mothers who did not receive sunlight exposure. These findings indicate that sunlight and vitamin D supplements combined can improve motor development, lower cortisol levels, and improve depressive symptoms.
Seasonal Affective Disorder
One in ten Americans suffer from a recurring depression called Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) for which their symptoms often start in late fall or early winter when the days are short, and go away in the spring when the days lengthen. In other words, they feel better when there is more UVB available with sunlight. The risk is much higher for people who live further from the equator, where the length of the days varies more greatly throughout the year. Light therapy, exposure to artificial UVB lamps, has been shown to be an effective treatment for people with SAD, improving symptoms by 50-80%.
Reduced Risk of Cognitive Impairment
A study by Gao et al. looked at data from 1192 participants aged 60 years and older and residing in rural China who provided information about their long-term sun exposure behaviors including time of day when outdoors, duration outdoors, and use of sun protection. The research team used the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE; maximum score of 30) to assess participant’s orientation, memory, language, calculation, and attention. They found that participants in the high sun exposure group had higher average mental state scores of cognitive function compared to participants in the medium or low exposure groups. This study concluded that long-term high sun exposure throughout life could reduce the risk of cognitive impairment in the later years of life.
Additional Points Regarding Sunlight and Mental-Emotional Health
A study by Kent et al. makes the following additional points regarding sunlight, depression, and other cognitive deficits
- altered serotonin levels, neurodegeneration, depression, and other cognitive deficits may be seen as a result of a lack of sunlight
- both seasonal and non-seasonal depression have been shown to be affected by sunlight
- sunlight and light therapy has been shown to alter abnormalities and regulation of both the melatonin and serotonin systems among SAD, bipolar and schizophrenic patients, and even among those without psychiatric diagnoses; this may be one of the mechanisms by which sunlight can also affect Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and sleep disorders
What Happens in the Body when it is Exposed to Sunlight?
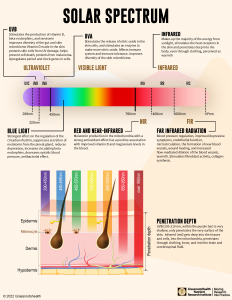
As shown in this illustration, those at the lower wavelengths (such as UVB) only penetrate the very surface of the skin, while those at higher wavelengths (such as visible light) are able to penetrate deeper. Think of how you are able to see the light from a flashlight on the back of your hand when held against the skin on the palm of the hand – you can visually see the energy traveling through the skin, muscles, blood vessels and tissues of the hand. Infrared radiation can even get into the cells and mitochondria, and can get through clothing and bone!
Are You Getting Enough Vitamin D from Sunshine?
 Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Choose which additional nutrients to measure, such as your omega-3s and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. With measurement you can then determine how much is needed and steps to achieve your goals. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Choose which additional nutrients to measure, such as your omega-3s and essential minerals including magnesium and zinc, by creating your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. With measurement you can then determine how much is needed and steps to achieve your goals. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Enroll in D*action and Test Your Levels Today!



 What happens in your body when it is exposed to sunlight?
What happens in your body when it is exposed to sunlight? Can the benefits of sunshine exposure be replaced by a pill?
Can the benefits of sunshine exposure be replaced by a pill?