Published on August 25, 2022
Help improve focus for you and your students by measuring your Omega-3 Index
Key Points
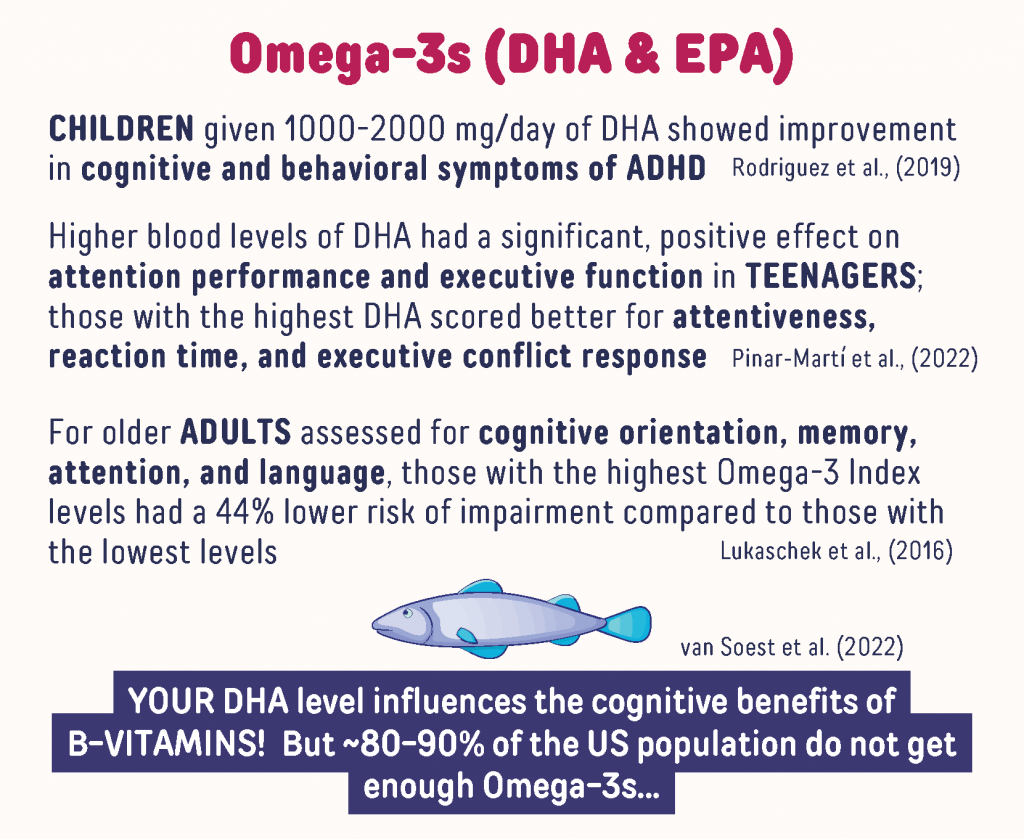
- Reviews of the research on omega-3s specifically have shown improved general cognitive performance, attention, and processing speed with both omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and improved memory function with DHA
- Results from a recent study suggest a role of DHA in selective and sustained attention, as well as executive function in detecting and resolving conflict, especially among healthy teenagers
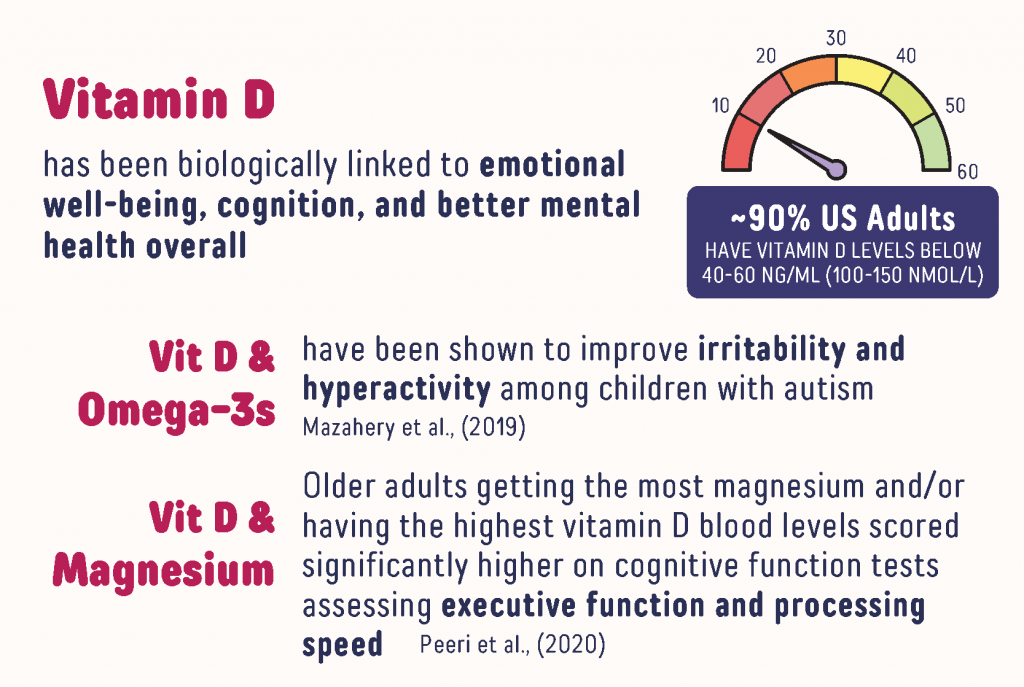
- Vitamin D is also essential to healthy brain function, and has been biologically linked to emotional well-being, mood, cognition, and better mental health overall
 Studies have shown that several nutrients have protective benefits when it comes to the brain and cognition, including vitamin D, magnesium, probiotics, B vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are especially important to neural tissue health, playing an important role in brain development and function. Reviews of the research on omega-3s specifically have shown improved general cognitive performance, attention, and processing speed with both omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and improved memory function with DHA.
Studies have shown that several nutrients have protective benefits when it comes to the brain and cognition, including vitamin D, magnesium, probiotics, B vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are especially important to neural tissue health, playing an important role in brain development and function. Reviews of the research on omega-3s specifically have shown improved general cognitive performance, attention, and processing speed with both omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and improved memory function with DHA.
Levels of DHA and EPA in the blood have been associated with cognition and attention among older adults as well as children. Previous studies have shown benefits of omega-3s for individuals with a wide range of mental disorders, including a study looking at the relationship between omega-3s and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and a study on the effect of both vitamin D and omega-3 on irritability and hyperactivity in autistic children.
Higher DHA Levels in the Blood Associated with Higher Attention Scores Among Teenagers
A recent study by Pinar‑Martí et al. examined the association between blood levels of omega-3 fatty acid DHA and attention in a study involving 372 healthy teenagers, with an average age of 14 years old. Several different aspects of attention were assessed via computer-based neuropsychological tests, including selective and sustained attention, conflict response (for executive attention), and impulsivity.
Data for the study was grouped into tertiles according to blood levels of DHA, and comparisons in attention scores were made between the group with the highest levels of DHA to the group with the lowest levels of DHA. The teenagers with the highest levels of DHA showed significantly better scores for attentiveness, reaction time, and executive conflict response. DHA had a significant, positive effect on overall attention performance. The omega-3 fatty acid ALA (a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid) was also measured and compared to attention, although it was only associated with improvements in impulsivity.
The results of this study suggest a role of DHA in selective and sustained attention, as well as executive function in detecting and resolving conflict, especially among healthy teenagers.
The Brain Needs Vitamin D, Too
Vitamin D is also essential to healthy brain function, and has been biologically linked to emotional well-being, mood, cognition, and better mental health overall. One study on vitamin D and mental health in particular found that self-perceived measurements of mental and emotional wellness were positively associated with higher vitamin D levels.
Vitamin C May Improve Attention and Mental Vitality
Another study found that, when looking at changes in mental vitality among individuals given vitamin C supplementation, compared to baseline, 4 weeks of supplementation resulted in significantly
- decreased levels of fatigue
- increased attention span
- increased level of work engagement and absorption (suggestive of motivation)
- increase in vigor
- increased self-control resources
This study concluded that “vitamin C supplementation significantly increased subjective feelings of concentration and promoted better cognitive performance requiring sustained attention.”
Interestingly, supplemental vitamin C intake has been shown to affect how a person’s vitamin D level responds to vitamin D supplementation (called the dose-response), such that those taking 1000 mg/day of vitamin C or more had a higher vitamin D level for any given vitamin D intake amount than those taking less supplemental vitamin C. Specifically, 94% more supplemental vitamin D was needed for 50% of the population to reach a vitamin D level of 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L).
Help Increase Attention and Focus with Vitamin D, Omega-3s, and Other Nutrients!
Measuring your vitamin D level and calculating a supplementation amount to help reach and maintain a target level, or taking loading doses to correct deficiency faster, could possibly make all the difference in overall health, wellbeing, and how a current disease situation progresses. Test your level now!
Create your custom home blood spot kit by adding any of the following measurements, along with your vitamin D:
- Omega-3 Index (with or without Ratios)
- Magnesium (with or without additional Elements – copper, zinc, selenium, mercury, cadmium, lead)
- hsCRP as a marker of inflammation and HbA1c as a marker of blood sugar health, two other important factors influencing cognitive health
Having and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and other nutrient levels can help improve your health, now and for the future. Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of vitamin D (see below) and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.