Published on March 8, 2024
Vitamin D supplementation resulted in a 64% reduced risk of suicide and self-harm among those presenting with vitamin D deficiency at baseline, and a 45-48% decreased risk overall
Key Points
- Research has found that 30-50% of veterans and service members have vitamin D levels below 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L)
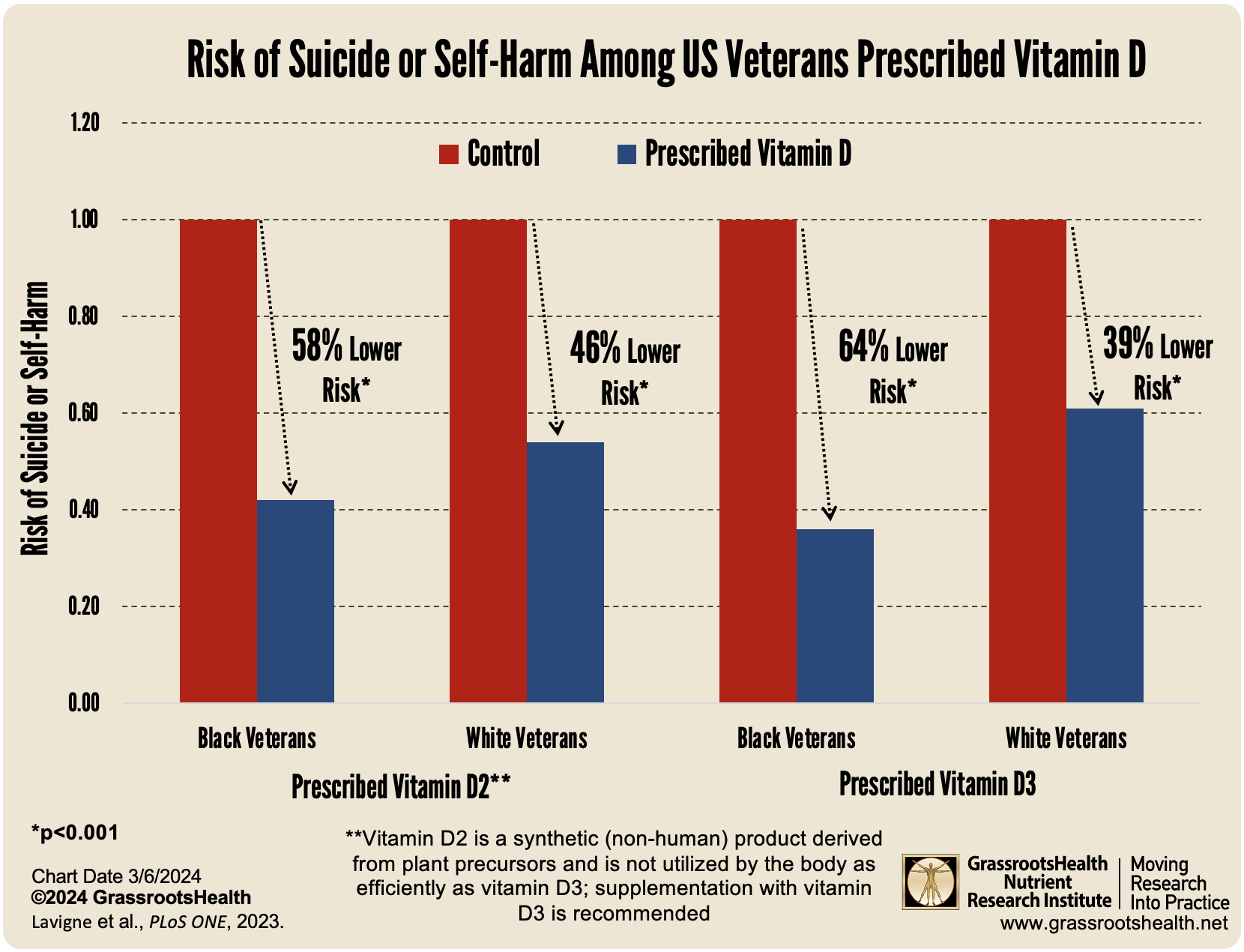
- A 2023 study among US Veterans found that vitamin D3 supplementation was associated with a 45% lower risk of suicide attempt and self-harm, while vitamin D2 supplementation was associated with a 48% lower risk; the higher the dose of vitamin D, the greater the risk reduction, with a greater risk reduction found among Black veterans compared to White veterans
- Analysis by baseline vitamin D level found a 64.1% reduced risk among those with a starting vitamin D level between 0-19 ng/ml who were then prescribed vitamin D3 compared to those who were not prescribed vitamin D3; each additional percentage point increase in average daily dose of vitamin D3 among this group was associated with a 13.8% reduction in risk, showing a dose-dependent relationship
- Other nutrients, including magnesium, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, have also shown to be beneficial in reducing the risk of depression and other mental disorders that have been associated with an increased risk of suicide
How are Your Levels of Vitamin D and Other Nutrients? Check Now!
 Suicide is a complex issue, and addressing the problem can require multiple interventional and therapeutic options, as well as a personal approach. While the factors and causes that contribute to the risk of suicide are many, certain nutrients and lifestyle interventions can help reduce the risk of suicide and self-harm, including vitamin D.
Suicide is a complex issue, and addressing the problem can require multiple interventional and therapeutic options, as well as a personal approach. While the factors and causes that contribute to the risk of suicide are many, certain nutrients and lifestyle interventions can help reduce the risk of suicide and self-harm, including vitamin D.
Addressing vitamin D deficiency to help combat suicide among veterans is of extreme importance, especially with some studies showing 30-50% of veterans and service members as having vitamin D levels below 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L).
Suicide Risk Cut by 45-48% with Vitamin D
A 2023 study by Lavigne et al. examined the risk of suicide attempts and intentional self-harm among US Veterans who had either received vitamin D treatment or who had not received vitamin D treatment in the previous years. Included in the analysis were 169,241 veterans who had been treated with vitamin D2 and 490,885 veterans who had been treated with vitamin D3, each matched to an equal number of controls. Comparisons were also made by race, gender, baseline vitamin D blood level, and average daily dose of vitamin D3 or D2.
Suicide attempts and self-harm rates among each group were
- .52% among D2 controls
- .27% among D2 treated
- .36% among D3 controls
- .20% among D3 treated
Vitamin D3 supplementation was associated with a 45% lower risk of suicide attempt and self-harm, while vitamin D2 supplementation was associated with a 48% lower risk. The higher the dose of vitamin D, the greater the risk reduction.
When analyzed by race, the study found notable differences between Black and White veterans, specifically a
- 57.9% reduced risk among Black veterans taking D2
- 46.3% reduced risk among White veterans taking D2
- 63.8% reduced risk among Black veterans taking D3
- 38.7% reduced risk among White veterans taking D3
Greatest Risk Reduction Found Among Those with Vitamin D Deficiency
Analysis by baseline vitamin D level found a 64.1% reduced risk among those with a starting vitamin D level between 0-19 ng/ml who were then prescribed vitamin D3 compared to those who were not prescribed vitamin D3. Among those who were treated with vitamin D in this group, “each additional percentage point increase in average daily dosage was associated with a 13.8% reduction in risk,” showing a dose-dependent relationship. Among those with a starting level between 20-30 ng/ml, those taking vitamin D3 had a 9.6% reduced risk for each percentage point increase in average daily dose. No significant associations were found for those whose vitamin D level at baseline was at or above 40 ng/ml.
As the authors of this study concluded,
“Vitamin D supplementation was associated with a reduced risk of suicide attempt and self-harm in Veterans, especially in veterans with low blood serum levels and Black veterans.”
A Note About Vitamin D2
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is a synthetic (non-human) product that is derived from plant precursors that is not utilized by the body as efficiently as vitamin D3. With a much shorter half-life, it remains in the blood for only a few hours. Supplementation with vitamin D3 is recommended.
How Can Vitamin D Affect Suicide Risk?
One reason could be because of its effects within the brain. Brain tissue contains high levels of vitamin D in the form of 25(OH)D3. A unique study on dementia found that higher vitamin D levels in the brain tissue of recently deceased individuals was associated with better global cognitive function scores, a slower rate of cognitive decline, and better semantic and working memory before death – a finding that indicates improved brain function overall with higher vitamin D. Vitamin D receptors are found in many areas of the brain including the hippocampus and hypothalamus, both of which are involved in the development of depression, a major contributor to suicide.
Additional Nutrients are Also Important
Other nutrients, including magnesium, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, have also shown to be beneficial in reducing the risk of depression and other mental disorders that have been associated with an increased risk of suicide. In fact, the world’s largest review (called a meta-synthesis) of nutrient supplements and mental disorders showed that omega-3s (with an average dose of 1422 mg/day of EPA) reduced symptoms of major depressive disorder with benefits beyond those of taking antidepressants alone; the strongest effect was seen with omega-3 supplements that contained at least 50% EPA.
Magnesium and zinc have also demonstrated significant benefits for those with depression, anxiety, emotional instability, and other mental illnesses. Learn more about additional benefits of these important nutrients for mental health here.
How Are Your Levels of Important Nutrients?
Do you know what your vitamin D level is? Check yours along with omega-3s, magnesium, zinc, and other levels today as part of the vitamin D*action project; add the Ratios for more about how to balance your Omega-3s and 6s!
Measure your:
- Vitamin D
- Magnesium PLUS Elements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- hsCRP (for Inflammation)
- HbA1c (for Blood Sugar)
- and more
Did you know that each of the above can be measured at home using a simple blood spot test? As part of our ongoing research project, you can order your home blood spot test kit to get your levels, followed by education and steps to take to help you reach your optimal target levels. Start by enrolling and ordering your kit to measure each of the above important markers, and make sure you are getting enough of each to support better mood and wellbeing!
Build your custom kit here – be sure to include your Omega-3 Index along with your vitamin D.
Start Here to Measure Your Levels