Published on September 11, 2019
 Most of the vitamin D we have in our bodies is in the form of vitamin D3, which is synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight and other forms of UVB radiation. Additional sources of vitamin D3 are from supplements, with a small amount coming from foods, mainly animal food sources such as meat, eggs and dairy. Other foods with vitamin D are those that are fortified and some plant foods, although these mostly contain vitamin D2.
Most of the vitamin D we have in our bodies is in the form of vitamin D3, which is synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight and other forms of UVB radiation. Additional sources of vitamin D3 are from supplements, with a small amount coming from foods, mainly animal food sources such as meat, eggs and dairy. Other foods with vitamin D are those that are fortified and some plant foods, although these mostly contain vitamin D2.
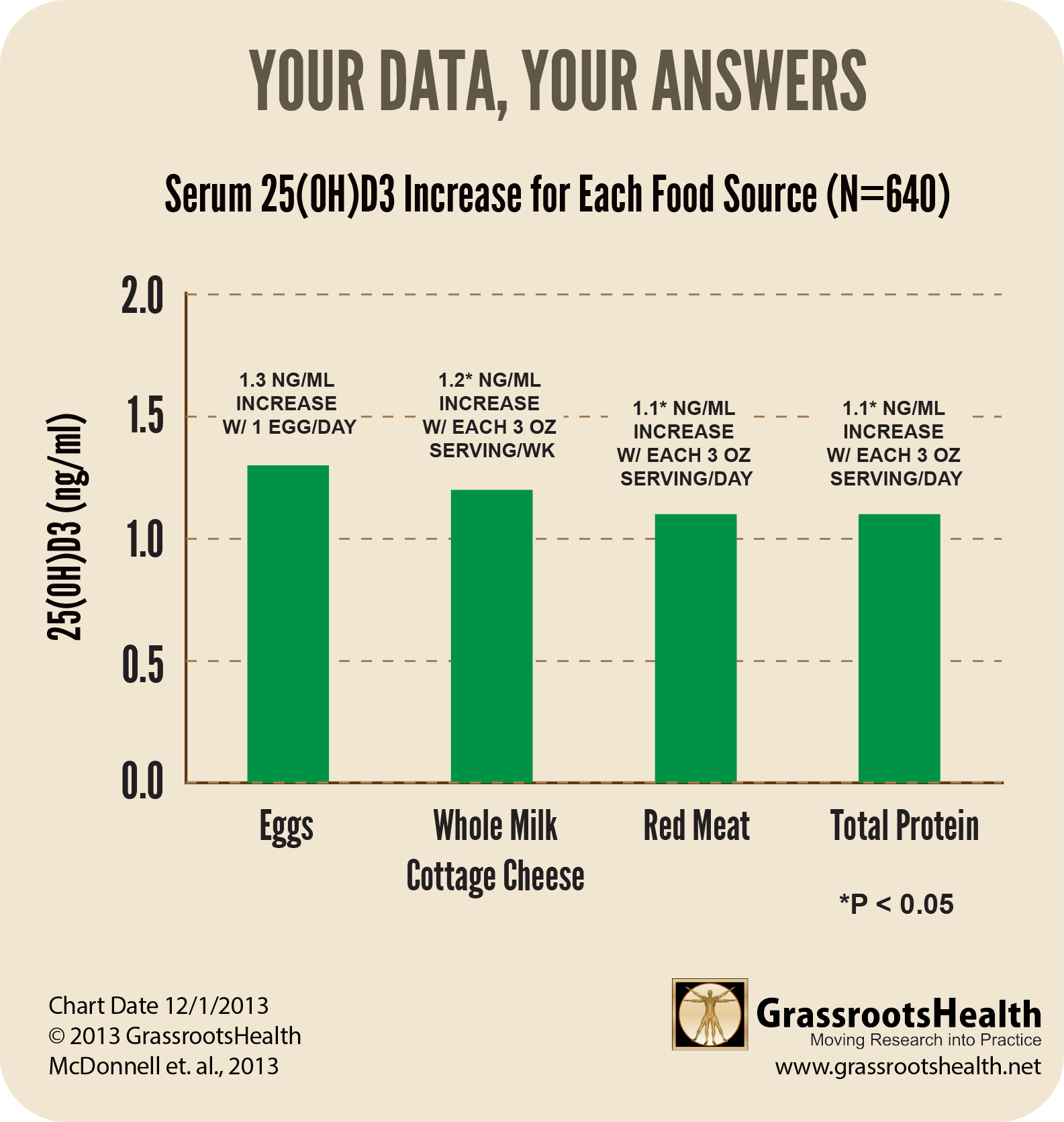
Which foods have the greatest impact on vitamin D levels?
An analysis by GrassrootsHealth looked at which foods had the greatest effect on serum levels of vitamin D (as 25(OH)D3), and found that the foods that had the most impact were whole milk cottage cheese, eggs, meat, and total protein.
Vitamin D in plants
Most of the vitamin D found in plants is in the form of vitamin D2. Fungi and yeasts produce vitamin D2 in response to UVB exposure, with wild mushrooms having the highest content. An interesting observation is that plants with higher levels of sun exposure and plants at a higher level of maturity contain more vitamin D2.
What about vitamin D3 in plants?
For many years it was believed that only vitamin D2 was present in plants, however, scientists have recently discovered vitamin D3 in some plant species. Vitamin D3 has been found in microalgae, both as vitamin D3 and provitamin D3 (the form that is converted to vitamin D3 upon exposure to UVB).
Fruits and vegetables, especially those in the Solanaceae family (which includes potatoes, tomatoes, and peppers), have the potential for containing some vitamin D3, although current research can only support that there is measurable vitamin D3 in the leaves of these plants.
Other foods with vitamin D
Some foods known to contain vitamin D include:
- Salmon (significantly more found in wild salmon vs farmed salmon)
- Herring and Sardines (including pickled)
- Cod Liver Oil
- Canned Tuna (Light tuna may be a better choice since it contains less methylmercury than solid white)
- Oysters (also high in vitamin B12, copper and zinc)
- Shrimp (one serving contains approximately 152 IU of vitamin D)
- Egg Yolks (higher amounts found in eggs from pasture-raised chickens and those fed vitamin D enriched feed)
- Mushrooms (wild or those treated with UV light)
- Foods fortified with vitamin D
Are you using foods as a source of vitamin D and omega-3?
Is food, whether those containing vitamin D3 or vitamin D2, helping to improve your vitamin D level? How about foods with omega-3s? Testing your vitamin D and Omega-3 Index levels and taking daily steps to keep your Omega-3 Index at a target of at least 8%, and your vitamin D at a target level of 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L), is important for all stages of health. Find out your levels today! Log on to the shop (click the link below) to get your tests and see for yourself if your levels can be improved.
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
 Click Here to Access the Shop Page
Click Here to Access the Shop Page
How can I track my food intake and my vitamin D and omega-3 levels?
To help you track your food intake along with vitamin D levels, GrassrootsHealth has created an online tracking system called myData-myAnswers. You can also track your sun exposure and supplement use to see how vitamin D from food, sun and supplements impact your vitamin D levels and your health. Check it out today!