Published on September 13, 2019
 Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a serious mental health issue that affects an estimated 7% of American adults every year, and it is a leading cause of disability world-wide. Previously, we have discussed the association between depression and magnesium, vitamin D, and omega-3s.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a serious mental health issue that affects an estimated 7% of American adults every year, and it is a leading cause of disability world-wide. Previously, we have discussed the association between depression and magnesium, vitamin D, and omega-3s.
Omega-3 Effect on Depression Backed by Strongest Level of Evidence
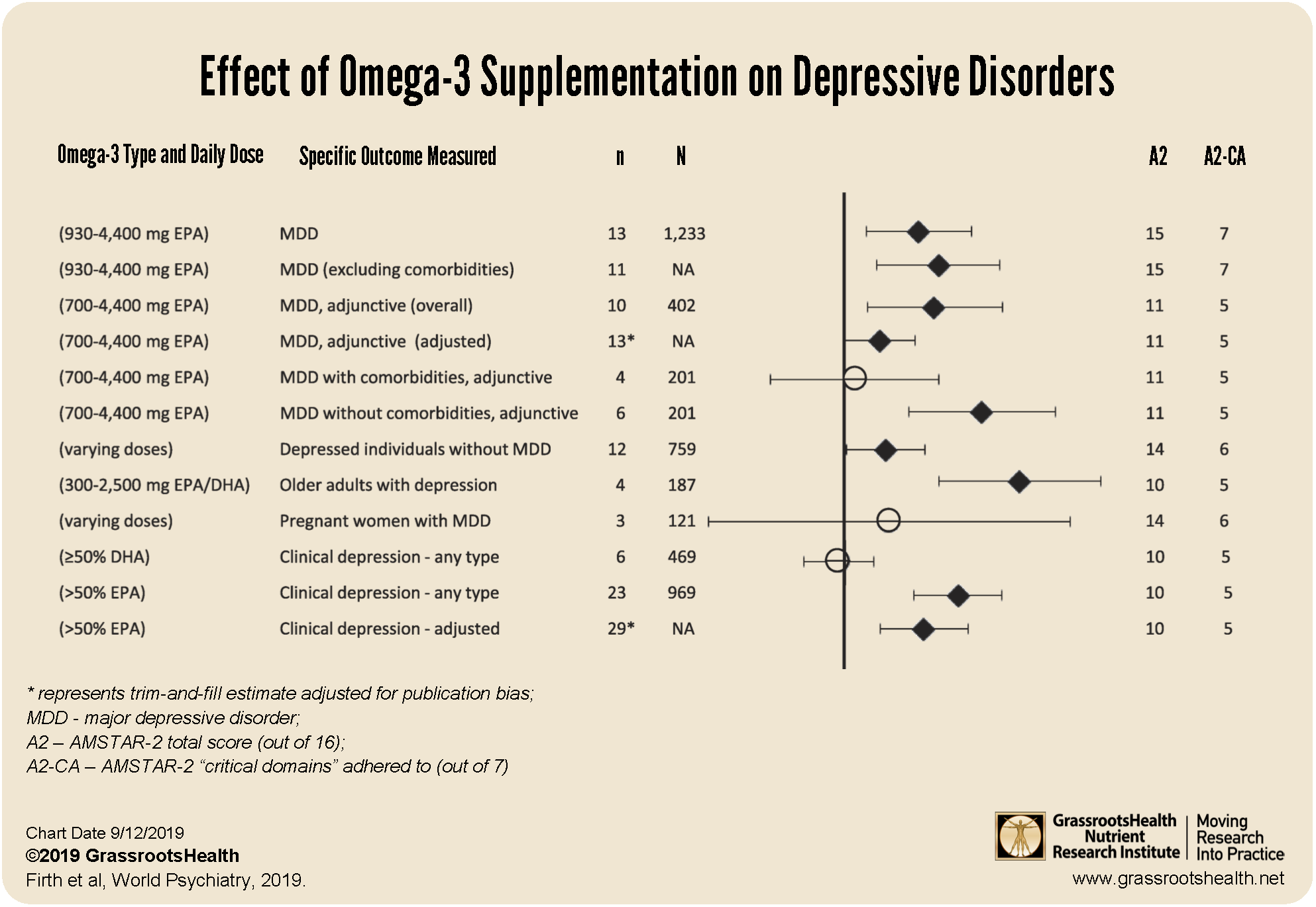
The world’s largest review (called a meta-synthesis) of nutrient supplements and mental disorders published by Firth et al. examined 33 meta analyses of randomized controlled trials on dietary supplements and mental health. The analysis included data from 10,951 individuals with diagnoses such as depression, stress and anxiety, bipolar, personality disorder, schizophrenia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The researchers looked at the potential benefits of specific nutrient supplements, including dosage, target symptoms, safety and tolerability, for each of the mood and mental disorders.
The strongest evidence from this review showed the effect of omega-3s (with an average dose of 1422 mg/day of EPA) on reducing symptoms of MDD, which produced benefits beyond those of taking antidepressants alone. The strongest effect was seen with omega-3 supplements that contained at least 50% EPA.
The chart below is a plot of the effect of omega-3 supplementation on depressive disorders as found in this analysis. The black diamonds represent studies with significant findings (where p<0.05) compared to placebo (9 out of the 12 studies included); circles represent studies with non-significant findings compared to placebo (3 out of 12 studies).
Other findings from this review included the safety of all nutrients reviewed when taken as recommended, the absence of any serious adverse effect or contraindication between each nutrient and the psychiatric medications taken, a positive effect of omega-3 supplements on ADHD, a positive effect of folate on MDD and schizophrenia, and a positive effect of N-acetycysteine on mood and schizophrenia.
Why is it Important to Focus on Your Omega-3 Index vs Intake?
The Omega-3 Index is a blood test that measures the amount of EPA and DHA in red blood cell (RBC) membranes and is expressed as a percent of total RBC fatty acids. It is a long-term and stable marker of omega-3 status, and it reflects tissue levels of EPA+DHA.
An Omega-3 Index of over 8% is associated with the lowest risk of death from heart disease and below 4% with the highest.
While individual levels of omega-3s vary across the globe, most countries and regions have levels that are considered low to very low.
Measure Your Level Today!
Have you measured your Omega-3 Index, which shows you how much DHA and EPA are in your blood and tissues? Scientists recommend a target Omega-3 Index of 8% or higher. Testing is essential, as there is a large amount of variability in the omega-3 status for different people with the same intake amount (similar to vitamin D!). For example, a GrassrootsHealth analysis showed that the range of response with 1000 mg of EPA+DHA per day was 5.7% to 10.2%. Therefore, it is recommended that individuals measure their Omega-3 Index and determine a personalized dose using the Omega-3 calculator to achieve a minimum Omega-3 Index of 8%.
Measure Your Omega-3 Levels with Vitamin D Today!