Published on July 16, 2023
A new study describes the relationship between omega-3s, chronic inflammation, metabolism and mood disorders
Key Points
- A new publication by Wu et al. discusses the promising alternative of omega-3 fatty acids in addressing these conditions, especially since pharmacotherapy fails to adequately treat major depressive disorder in at least 30-40% of cases
- Omega-3s have been shown to reduce levels of inflammation and help regulate metabolic dysfunction, leading to improved body composition and weight
- The authors stress the importance of personalized omega-3 dosing for individuals to achieve a potential therapeutic action in addressing depression, obesity, and metabolic dysregulation; this includes measuring the omega-3 status to determine an optimal dose and monitoring levels of inflammation, which can be done through a combination of testing the Omega-3 Index, the AA:EPA Ratio, and levels of CRP

Metabolic dysfunction is characterized by inflammation, insulin resistance, leptin resistance, and hypertension. Individuals with metabolic dysfunction are at much higher risk for both obesity and depression. It is a condition that can even lead to structural and functional changes within the brain.
Research indicates that chronic low-grade inflammation, which results in increased levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, may be a driving factor for metabolic disfunction and depression. A new publication by Wu et al. discusses the promising alternative of omega-3 fatty acids in addressing these conditions, especially since pharmacotherapy fails to adequately treat major depressive disorder in at least 30-40% of cases.
Omega-3s Show Very Promising Effects
The world’s largest review (called a meta-synthesis) of nutrient supplements and mental disorders published by Firth et al. in 2019 examined 33 meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials on dietary supplements and mental health. The strongest evidence from this review showed the effect of omega-3s (with an average dose of 1422 mg/day of EPA) on reducing symptoms of major depressive disorder, which produced benefits beyond those of taking antidepressants alone. Low levels of omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA (as measured by the Omega-3 Index) are commonly found in individuals with depression, especially those who are not responsive to antidepressants.
According to Wu et al., there exists a “bidirectional relationship between depression and metabolic dysfunction, with each condition increasing the progressive risk of the other by 50–60%.” Chronic inflammation related to obesity has been linked to mood disorders as well as other cognitive diseases, heart disease, increased risk of cancers, decreased immune function, and more.
How Do Omega-3s Affect Weight, Metabolism, and Mood?
Omega-3s have been shown to reduce levels of inflammation and help regulate metabolic dysfunction. Studies have also shown that omega-3s may help to improve body composition and weight, with increased omega-3s linked to reduced body weight, fat mass, and waist circumference.
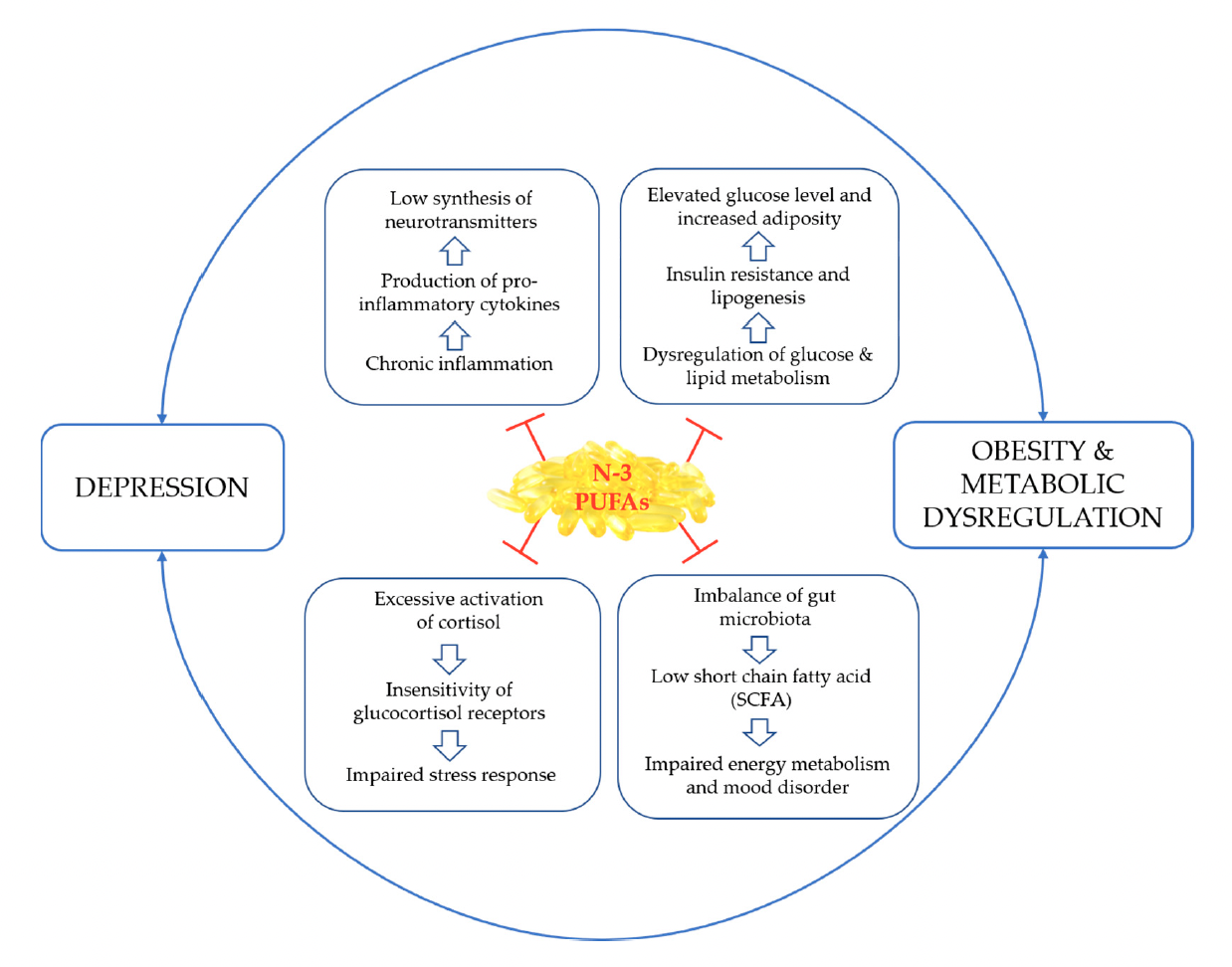
The figure below illustrates the relationship between omega-3s (N-3 PUFAs) and inflammation, metabolism, mood disorders and stress.
Wu et al., 2023
When the body does not have enough omega-3 fatty acids, it can result in several different cascading effects that can then lead to obesity, metabolic dysregulation, and depression.
The authors stress the importance of personalized omega-3 dosing for individuals in order to achieve a potential therapeutic action in addressing depression, obesity, and metabolic dysregulation. Part of that personalized approach includes measuring the omega-3 status to determine an optimal dose, as well as monitoring levels of inflammation. This can be done through a combination of testing the Omega-3 Index, the AA:EPA Ratio, and levels of CRP.
Vitamin D and magnesium are also important for cognitive and metabolic health – be sure you are getting enough of each of these nutrients on a regular basis!
Getting Enough of the Right Nutrients to Support Metabolism and Mood
See if your nutrient status could improve to support better metabolism and mood. Create your custom home blood spot kit with the following measurements to help determine if you are getting enough of the following nutrients shown to benefit sleep:
- Vitamin D
- Omega-3 Index plus AA:EPA Ratio
- Magnesium
- hsCRP
Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of omega-3s, vitamin D and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.
Are You Getting Enough of These Nutrients? Check Now!
Why is it Important to Focus on Your Omega-3 Index vs Intake?
The Omega-3 Index is a blood test that measures the amount of EPA and DHA in red blood cell (RBC) membranes and is expressed as a percent of total RBC fatty acids. It is a long-term and stable marker of omega-3 status, and it reflects tissue levels of EPA+DHA.
An Omega-3 Index of over 8% is associated with the lowest risk of death from heart disease and below 4% with the highest.
While individual levels of omega-3s vary across the globe, most countries and regions have levels that are considered low to very low. Testing is essential, as there is a large amount of variability in the omega-3 status for different people with the same intake amount (similar to vitamin D!). For example, a GrassrootsHealth analysis showed that the range of response with 1000 mg of EPA+DHA per day was 5.7% to 10.2%. Therefore, it is recommended that individuals measure their Omega-3 Index and determine a personalized dose using the Omega-3 calculator to achieve a minimum Omega-3 Index of 8%.